Abstract
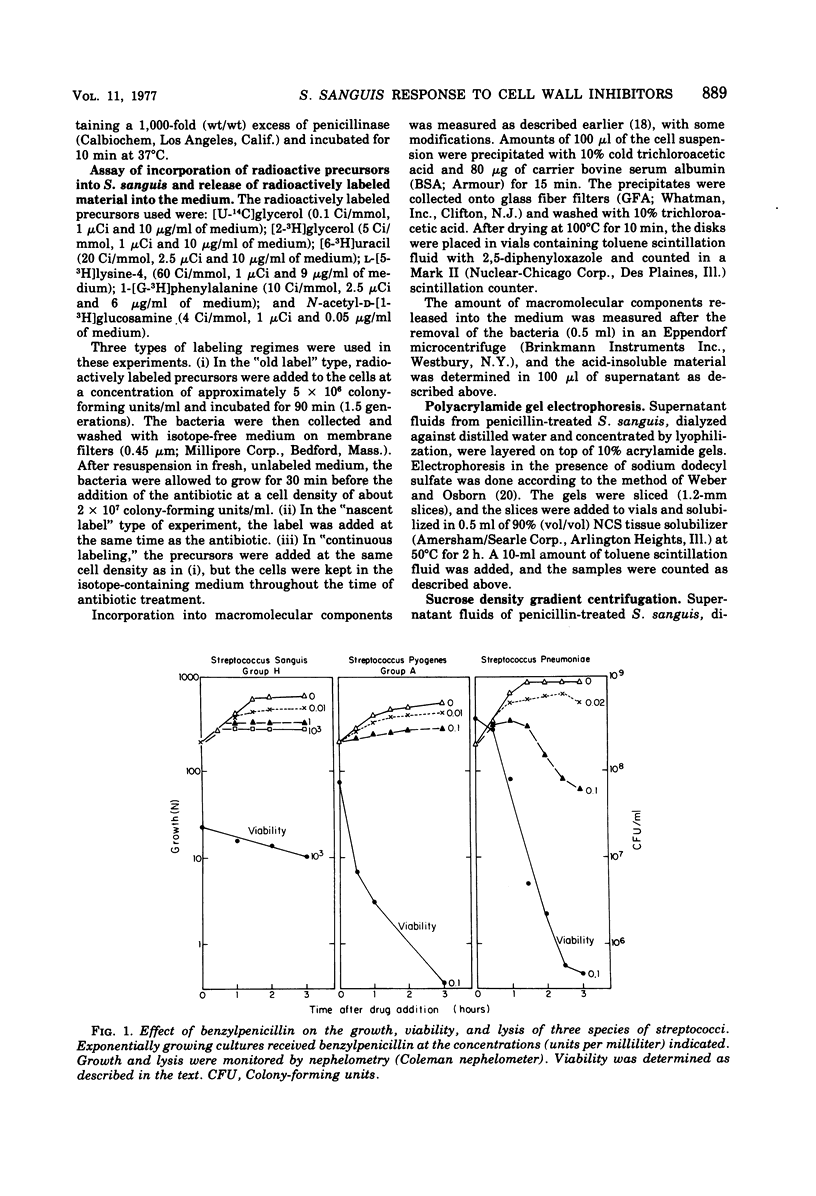
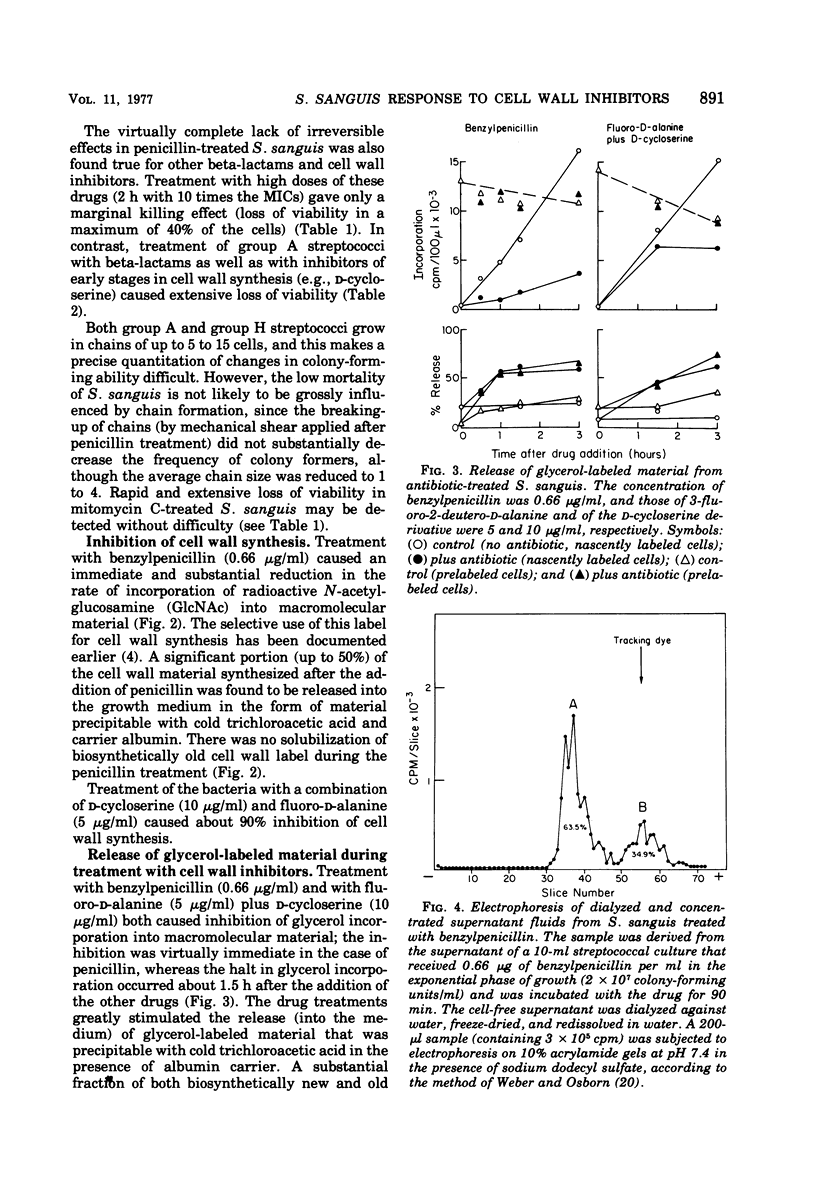
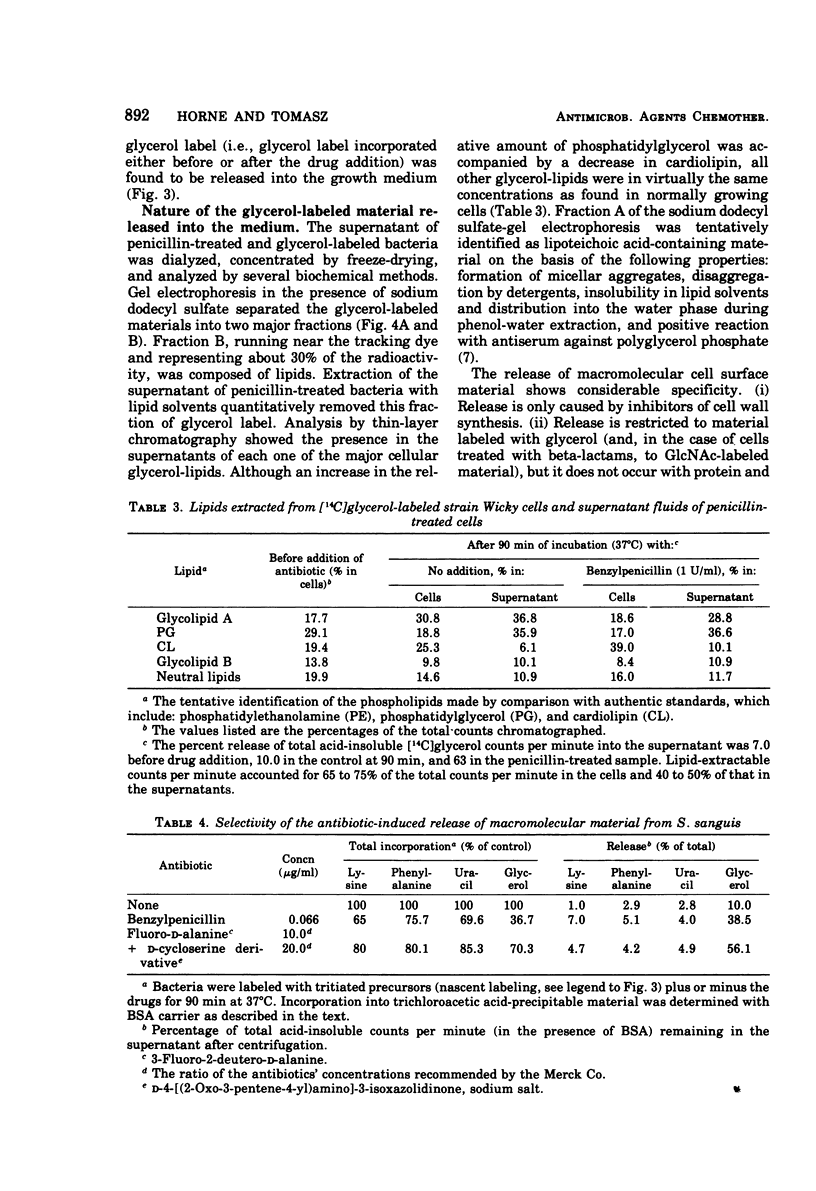
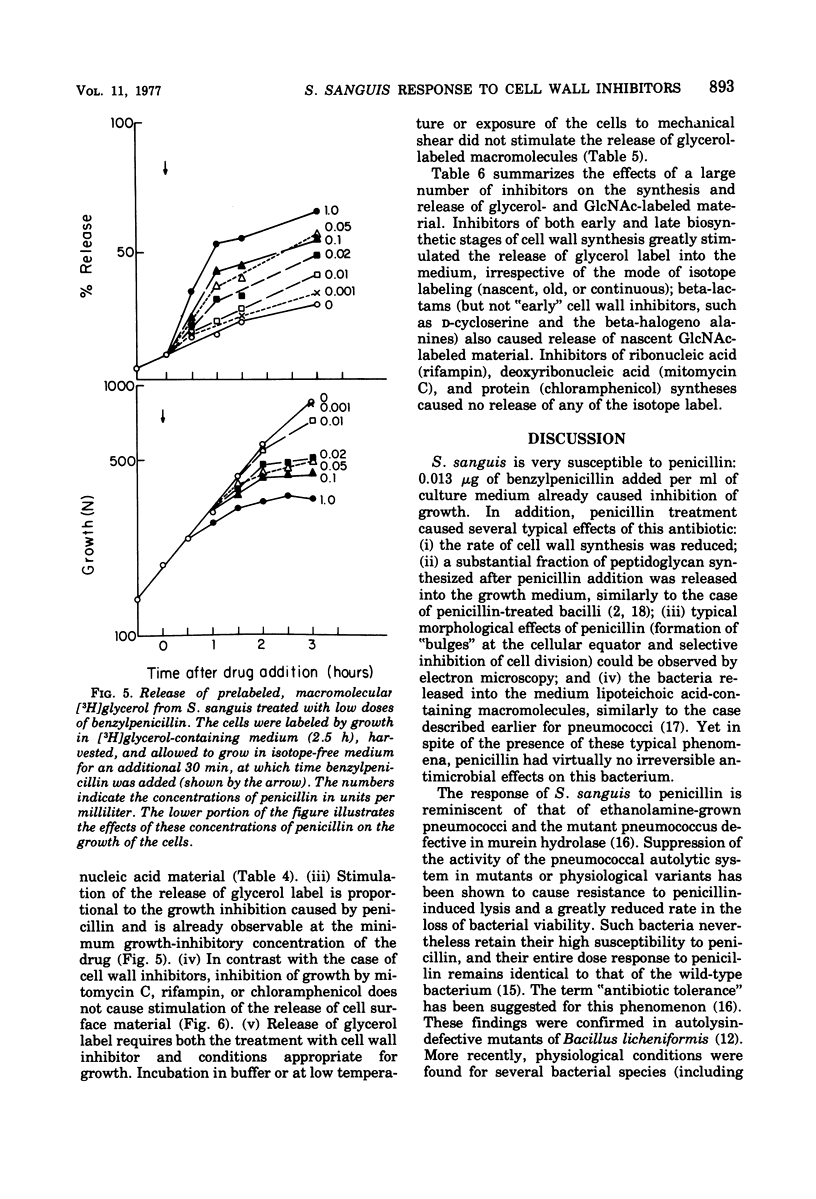
In contrast to group A streptococci or Streptococcus pneumoniae, cells of Streptococcus sanguis (group H) do not exhibit the irreversible effects of penicillin treatment, such as loss of viability or lysis. On the other hand, the same bacteria show typical effects of penicillin, such as morphological alterations, reduction in the rate of cell wall synthesis, and secretion of murein and lipoteichoic acid polymers into the medium. A novel effect of cell wall inhibitors was also noted: treatment with beta-lactams or with fosfomycin, d-cycloserine, or beta-halogeno-d-alanine caused the release of substantial amounts of glycerol lipids into the growth medium. The antibiotic “tolerance” of S. sanguis is interpreted in terms of the hypothesis that the activity of bacterial murein hydrolases is essential for the irreversible effects of cell wall inhibitors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbogast L. Y., Henderson T. O. Effect of inhibition of protein synthesis on lipid metabolism in Lactobacillus plantarum. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):962–971. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.962-971.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. S., Ward J. B., Rogers H. J. Formation of cell wall polymers by reverting protoplasts of Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):623–632. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.623-632.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Lopez R., Tomasz A. Suppression of lytic effect of beta lactams on Escherichia coli and other bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3293–3297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D. S., Perry D. Effect of competence induction on macromolecular synthesis in a group H streptococcus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):830–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.830-836.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D. S., Perry D. Relationship of macromolecular synthesis to competence induction in a group H streptococcus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1014–1021. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1014-1021.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Shockman G. D. Synthesis and excretion of glycerol teichoic acid during growth of two streptococcal species. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):333–338. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.333-338.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Immunological properties of teichoic acids. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):215–257. doi: 10.1128/br.37.2.215-257.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACKS S., HOTCHKISS R. D. A study of the genetic material determining an enzyme in Pneumococcus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Apr 22;39:508–518. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90205-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez R., Ronda-Lain C., Tapia A., Waks S. B., Tomasz A. Suppression of the lytic and bactericidal effects of cell wallinhibitory antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):697–706. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham J. L., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J., Hewett M. J. Formation of extracellular lipoteichoic acid by oral streptococci and lactobacilli. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):378–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.378-386.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranhand J. M., Leonard C. G., Cole R. M. Autolytic activity associated with competent group H streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):257–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.257-268.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J., Forsberg C. W. Role of autolysins in the killing of bacteria by some bactericidal antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1235–1243. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1235-1243.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Albino A., Zanati E. Multiple antibiotic resistance in a bacterium with suppressed autolytic system. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):138–140. doi: 10.1038/227138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Cellular metabolism in genetic transformation of pneumococci: requirement for protein synthesis during induction of competence. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):860–871. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.860-871.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. The role of autolysins in cell death. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):439–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Waks S. Mechanism of action of penicillin: triggering of the pneumococcal autolytic enzyme by inhibitors of cell wall synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4162–4166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tynecka Z., Ward J. B. Peptidoglycan synthesis in Bacillus licheniformis. The inhibition of cross-linking by benzylpenicillin and cephaloridine in vivo accompanied by the formation of soluble peptidoglycan. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):253–267. doi: 10.1042/bj1460253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. B. The synthesis of peptidoglycan in an autolysin-deficient mutant of Bacillus licheniformis N.C.T.C. 6346 and the effect of beta-lactam antibiotics, bacitracin and vancomycin. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;141(1):227–241. doi: 10.1042/bj1410227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


