Abstract
The interaction of penicillin G with human serum proteins was evaluated by three different techniques: rate of dialysis, cross-linked dextran exclusion, and ultracentrifugation. The rate-of-dialysis technique demonstrated that penicillin G binding to serum was immediate but incompletely reversible. Cross-linked dextran adsorbed or trapped significant amounts of penicillin G, necessitating correction factors of more than 10%. Ultracentrifugation was found to be the most reliable method for quantitative protein-binding determinations of penicillins.
Full text
PDF

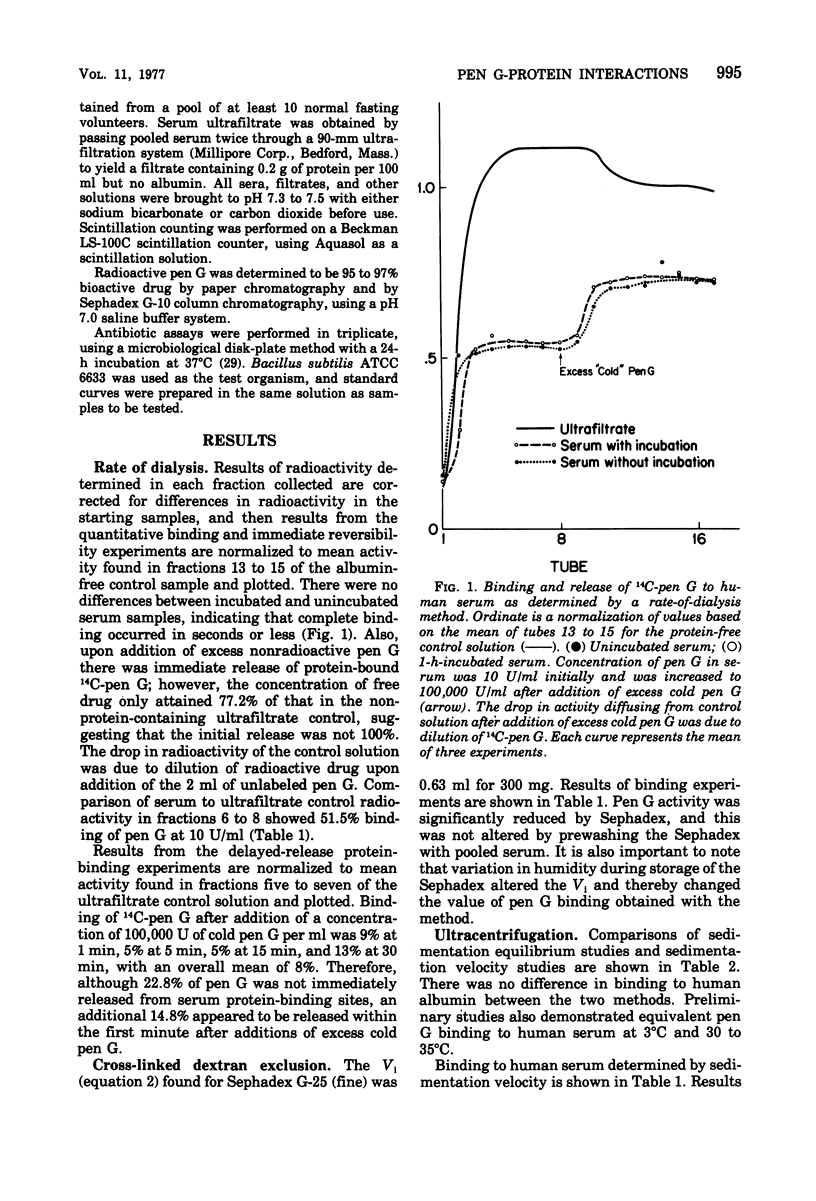


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACRED P., BROWN D. M., HARDY T. L., MANSFORD K. R. A NEW APPROACH TO STUDYING THE PROTEIN-BINDING PROPERTIES OF PENICILLINS. Nature. 1963 Aug 24;199:758–759. doi: 10.1038/199758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUETTNER H., PORTWICH F. [Determination of the binding of sulfonamides to serum proteins with the ultracentrifuge]. Arzneimittelforschung. 1961 Dec;11:1133–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Weinstein L. Pharmacokinetics of the penicillins in man. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1976;1(4):297–308. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197601040-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. V., Kirby W. M. A rapid, modified ultrafiltration method for determining serum protein binding and its application to new penicillins. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Nov;66(5):721–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt W. F., Robinson S. M., Bixler H. J. Membrane ultrafiltration: the diafiltration technique and its application to microsolute exchange and binding phenomena. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 10;26(1):151–173. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow B. F., McKee C. M. INTERACTION BETWEEN CRYSTALLINE PENICILLIN AND HUMAN PLASMA PROTEINS. Science. 1945 Jan 19;101(2612):67–68. doi: 10.1126/science.101.2612.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colowick S. P., Womack F. C. Binding of diffusible molecules by macromolecules: rapid measurement by rate of dialysis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):774–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig W. A., Kunin C. M. Significance of serum protein and tissue binding of antimicrobial agents. Annu Rev Med. 1976;27:287–300. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.27.020176.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith R. S., Black H. R., Brier G. L., Wolny J. D. Cefamandole: in vitro and clinical pharmacokinetics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):814–823. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL J. P., DREYER W. J. Measurement of protein-binding phenomena by gel filtration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;63:530–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch-Kolb H., Kolb H. J., Greenberg D. M. Determination of binding properties of low molecular weight substances to proteins using ultracentrifugation. Anal Biochem. 1970 Apr;34(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M. INHIBITORS OF PENICILLIN BINDING TO SERUM PROTEINS. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Mar;65:416–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keresztes-Nagy S., Mais R. F., Oester Y. T., Zaroslinski J. F. Protein binding methodology: comparison of equilibrium dialysis and frontal analysis chromatography in the study of salicylate binding. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jul;48(1):80–89. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch-Weser J., Sellers E. M. Binding of drugs to serum albumin (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 5;294(6):311–316. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602052940605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornguth M. L., Kunin C. M. Binding of antibiotics to the human intracellular erythrocyte proteins hemoglobin and carbonic anhydase. J Infect Dis. 1976 Feb;133(2):185–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornguth M. L., Monson R. A., Kunin C. M. Binding of antibiotics to a soluble protein from rat liver. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(5):552–558. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.5.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornguth M. L., Monson R. A., Kunin C. M. The binding of penicillin antibiotics to a human liver protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 May;174(1):339–343. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90353-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M. Clinical pharmacology of the new penicillins. 1. The importance of serum protein binding in determining antimicrobial activity and concentration in serum. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1966 Mar-Apr;7(2):166–179. doi: 10.1002/cpt196672166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M. Clinical significance of protein binding of the penicillins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Sep 27;145(2):282–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb50225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattie H., Goslings W. R., Noach E. L. Cloxacillin and nafcillin: serum binding and its relationship to antibacterial effect in mice. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):170–177. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M. C., Guttman D. E. The binding of drugs by plasma proteins. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Jun;57(6):895–918. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600570601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakawa T., Wakai Y., Nishida M. Studies on the relationship of protein binding and gel-affinity of antibiotics including penicillins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Oct;23(10):481–487. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman W. H., Crépy O. Steroid-protein interaction with particular reference to testosterone binding by human serum. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):182–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolinson G. N., Sutherland R. The binding of antibiotics to serum proteins. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Dec;25(3):638–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb01788.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOLTAN W. BESTIMMUNGSMETHODEN UND GESETZMAESSIGKEITEN DER EIWEISSBINDUNG VON SULFONAMIDEN UND PENICILLINEN. Antibiot Chemother. 1964;12:103–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtan W. Die Bindung der Sulfonamide an Eiweisskörper. 6. Bestimmung der Eiweissbindung von Sulfonamiden mittels der Ultrazentrifuge und mittels Gelfiltration. Arzneimittelforschung. 1965 Dec;15(12):1433–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompsett R., Shultz S., McDermott W. The Relation of Protein Binding to the Pharmacology and Antibacterial Activity of Penicillins X, G, Dihydro F, and K. J Bacteriol. 1947 May;53(5):581–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.53.5.581-595.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. H. The prognostic significance of penicillin serum levels and protein binding in clinical medicine. A review of current studies. Chemotherapy. 1965;10(6):339–358. doi: 10.1159/000220427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womack F. C., Colowick S. P. Rapid measurement of binding of ligands by rate of dialysis. Methods Enzymol. 1973;27:464–471. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(73)27020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



