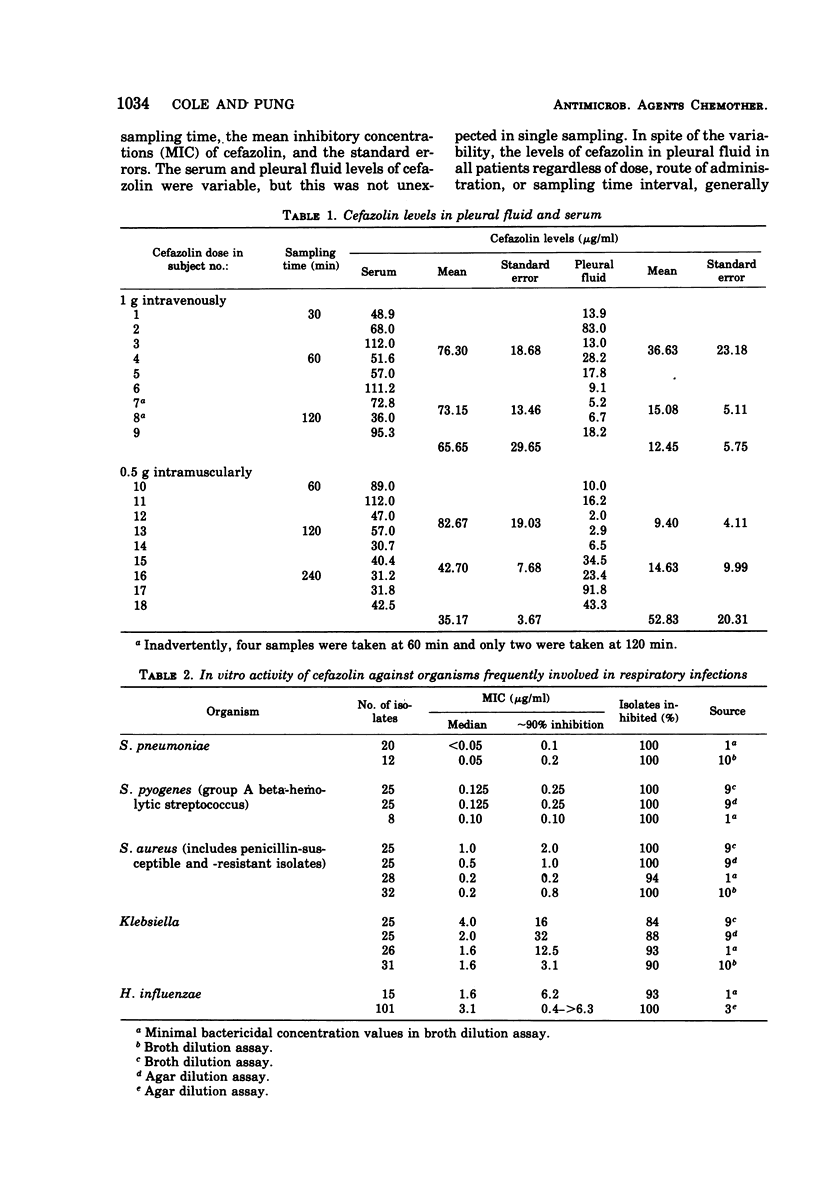
Abstract
Single doses of cefazolin, 500 mg intramuscularly and 1 g intravenously, were administered to 16 patients having lung pathology who were scheduled for thoracic fluid aspiration. Pleural fluid and serum samples were taken at intervals of 30 to 240 min for determination of cefazolin levels. The levels obtained were variable; however, the levels of cefazolin in pleural fluid generally exceeded the reported minimal inhibitory concentration values for Staphylococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus, and group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. In addition, the pleural fluid levels exceeded the minimal inhibitory concentration for cefazolin against most of the Klebsiella and Haemophilus influenzae strains. These data show that cefazolin, despite its comparative high protein binding, produces levels in the pleural fluid capable of inhibiting the organisms commonly found in respiratory tract infections.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergeron M. G., Brusch J. L., Barza M., Weinstein L. Bactericidal activity and pharmacology of cefazolin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):396–401. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. B., Smith A. L., Harding A. L., Smith D. H. Hemophilus influenzae type B susceptibility to 17 antibiotics. J Pediatr. 1975 Apr;86(4):617–620. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gump D. W., Lipson R. L. The penetration of cephalothin into synovial and other body fluids. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1968 Nov;10(11):583–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN J. O., EICKHOFF T. C., TILLES J. G., FINLAND M. CEPHALOTHIN: ACTIVITY IN VITRO, ABSORPTION AND EXCRETION IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND CLINICAL OBSERVATIONS IN 40 PATIENTS. Am J Med Sci. 1964 Dec;248:640–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby W. M., Regamey C. Pharmacokinetics of cefazolin compared with four other cephalosporins. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(Suppl):S341–S346. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_2.s341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhavan T., Quinn E. L., Freimer E., Fisher E. J., Cox F., Burch K., Pohlod D. Clinical studies of cefazolin and comparison with other cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Nov;4(5):525–531. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.5.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motley M., Shadomy S. In vitro studies with cefazolin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):856–861. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ries K., Levison M. E., Kaye D. Clinical and in vitro evaluation of cefazolin, a new cephalosporin antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):168–174. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turck M., Clark R. A., Beaty H. N., Holmes K. K., Karney W. W., Reller L. B. Cefazolin in the treatment of bacterial pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(Suppl):S382–S385. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_2.s382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



