Abstract
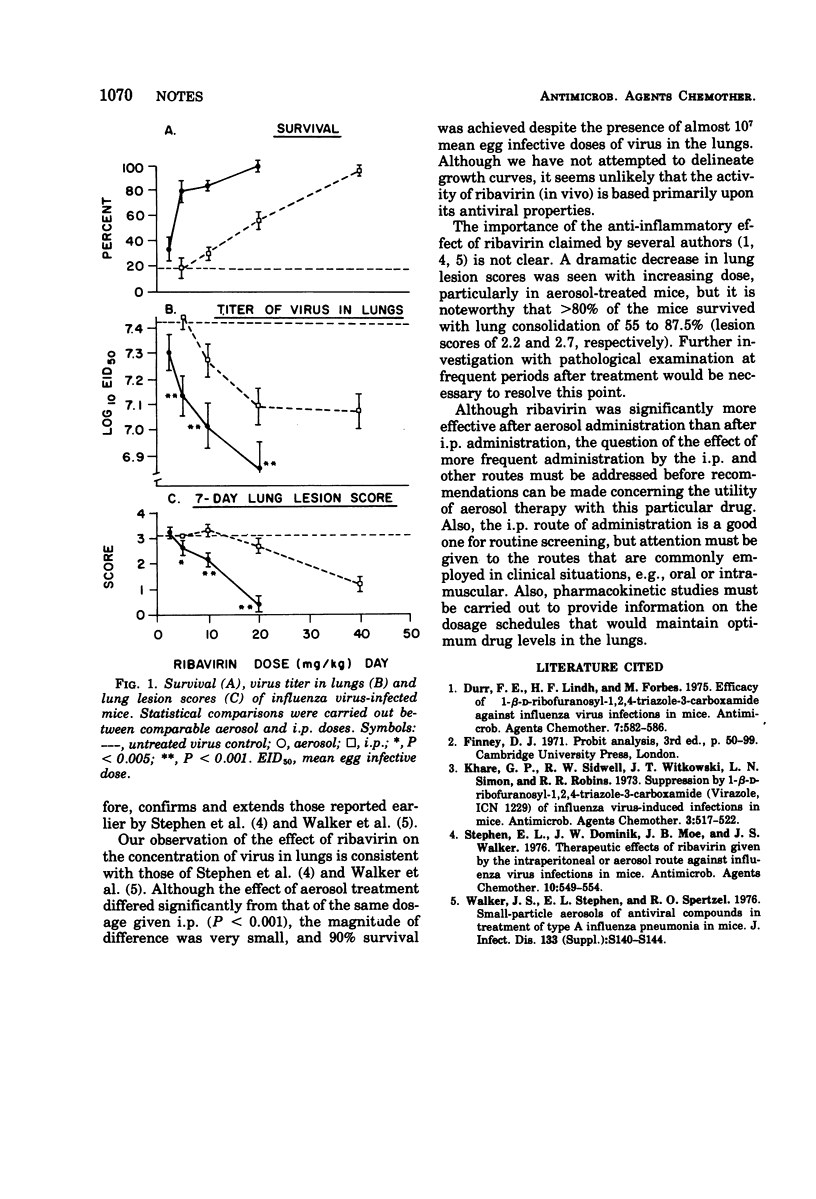
The effects of graded doses of ribavirin administered either by aerosol or intraperitoneally were compared in influenza virus-infected mice. The median effective dose values (based upon percent survival) were 3.3 and 15.8 mg/kg per day for the aerosol and intraperitoneal routes, respectively. Lung lesion scores and titer of virus were lower after aerosol than intraperitoneal therapy.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Durr F. E., Lindh H. F., Forbes M. Efficacy of 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide against influenza virus infections in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):582–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khare G. P., Sidwell R. W., Witkowski J. T., Simon L. N., Robins R. K. Suppression by 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (virazole, ICN 1229) of influenza virus-induced infections in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Apr;3(4):517–522. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.4.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen E. L., Dominik J. W., Moe J. B., Walker J. S. Therapeutic effects of ribavirin given by the intraperitoneal or aerosol route against influenza virus infections in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Sep;10(3):549–554. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



