Abstract
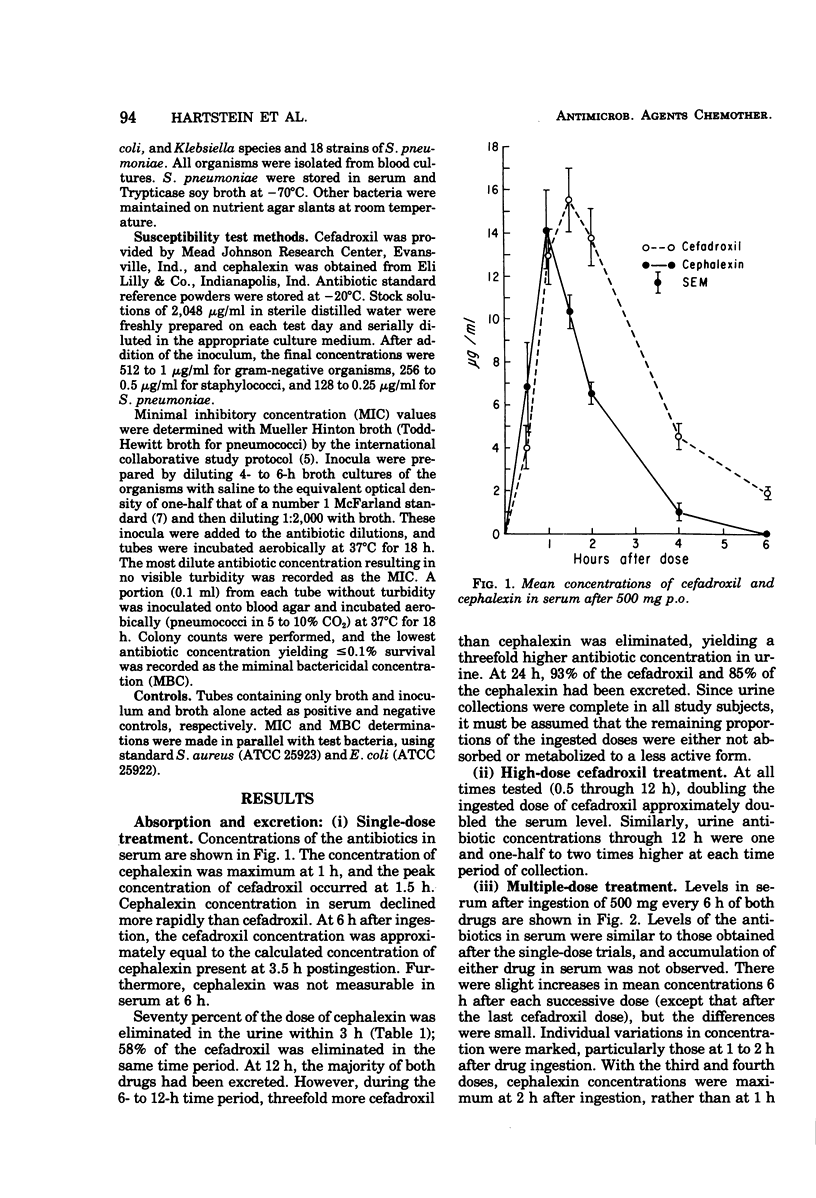
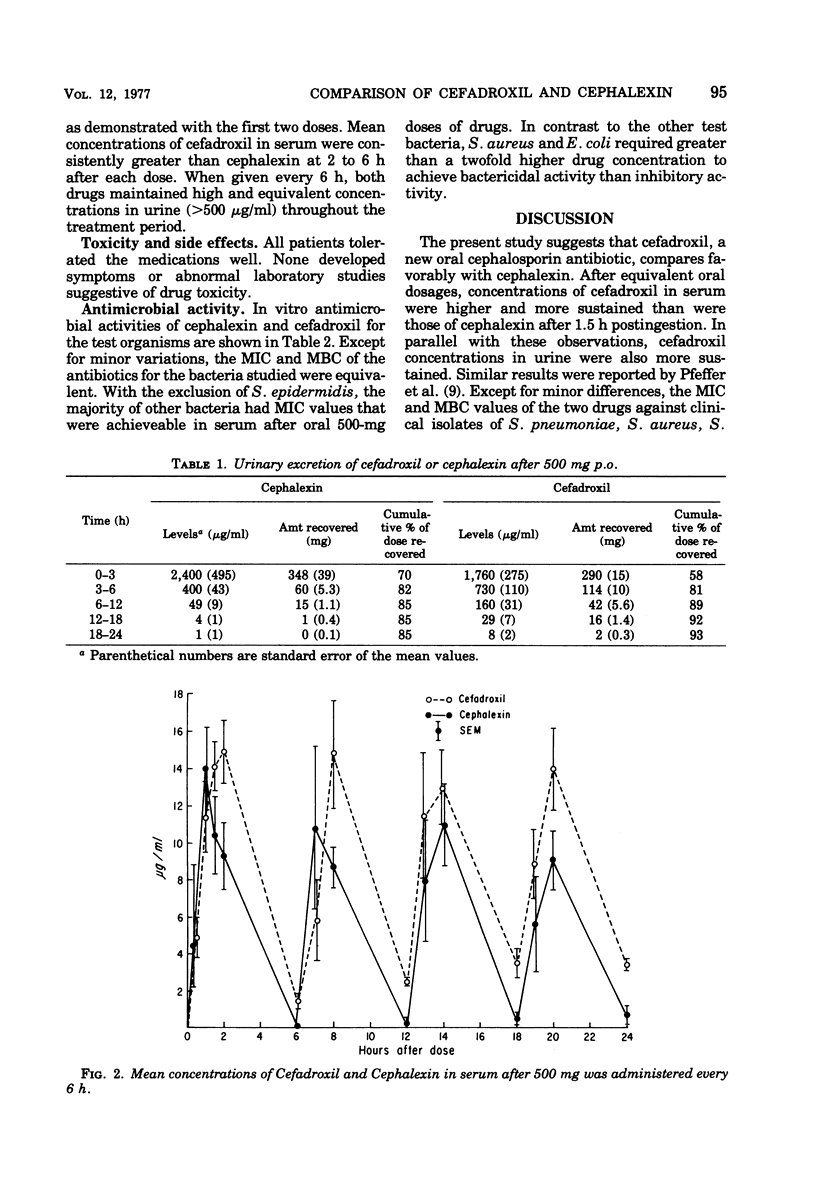
Pharmacological and antimicrobial properties of cefadroxil, a new cephalosporin antibiotic, were compared with cephalexin. Absorption and excretion were studied in 20 healthy men. Peak concentrations of the drugs in serum were similar after ingestion of single 500-mg tablets. The concentration of cefadroxil in serum was more sustained than that of cephalexin. Levels of cefadroxil in serum after a dose of 1,000 mg were approximately twice those after a 500-mg dose through 6 h. Each drug administered in a dose of 500 mg every 6 h for 24 h resulted in concentrations in serum that were similar to a single dose without accumulation. Ninety-three percent of the cefadroxil and 85% of the cephalexin were excreted in urine after ingestions of single 500-mg tablets. The urine concentration of cefadroxil was more sustained than cephalexin. Minimal inhibitory and minimal bactericidal concentrations for clinical isolates were comparable with each drug. Cefadroxil compares favorably with cephalexin in this study. Sustained levels of cefadroxil in serum and urine suggest that this drug may be given at less frequent intervals than cephalexin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell S. M. The significance of sensitivity tests of Staphylococcus aureus to cephaloridine. Med J Aust. 1974 Dec 21;2(25):902–904. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1974.tb93756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck R. E., Price K. E. Cefadroxil, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):324–330. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney E., Bynum R., Eldredge D., Frank D., MacWhinney J. B., McNabb N., Scheiner A., Sumpter E. A., Iker H. How well do patients take oral penicillin? A collaborative study in private practice. Pediatrics. 1967 Aug;40(2):188–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson H. M., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;217(Suppl):1+–1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landes R. R. Single daily doses of tobramycin in therapy of urinary tract infections. J Infect Dis. 1976 Aug;134 (Suppl):S142–S145. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.supplement_1.s142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer M., Jackson A., Ximenes J., de Menezes J. P. Comparative human oral clinical pharmacology of cefadroxil, cephalexin, and cephradine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):331–338. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regamey C., Libke R. D., Engelking E. R., Clarke J. T., Kirby M. M. Inactivation of cefazolin, cephaloridine, and cephalothin by methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Mar;131(3):291–294. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.3.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronald A. R., Boutros P., Mourtada H. Bacteriuria localization and response to single-dose therapy in women. JAMA. 1976 Apr 26;235(17):1854–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamey T. A., Fair W. R., Timothy M. M., Millar M. A., Mihara G., Lowery Y. C. Serum versus urinary antimicrobial concentrations in cure of urinary-tract infections. N Engl J Med. 1974 Nov 28;291(22):1159–1163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197411282912204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURCK M., ANDERSON K. N., SMITH R. H., WALLACE J. F., PETERSDORF R. G. LABORATORY AND CLINICAL EVALUATION OF A NEW ANTIBIOTIC--CEPHALOTHIN. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Aug;63:199–211. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-63-2-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L., Schlesinger J. Treatment of infective endocarditis--1973. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1973 Nov-Dec;16(3):275–302. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(73)80002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westlake W. J. The use of balanced incomplete block designs in comparative bioavailability trails. Biometrics. 1974 Jun;30(2):319–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



