Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) affects approximately 5–10% of all individuals and is more predominant in women (Breslau, 2001). Advances in treatment and prevention will require identifying biomarkers to aid early diagnosis and understanding the mechanisms underlying maladaptive responses to trauma.
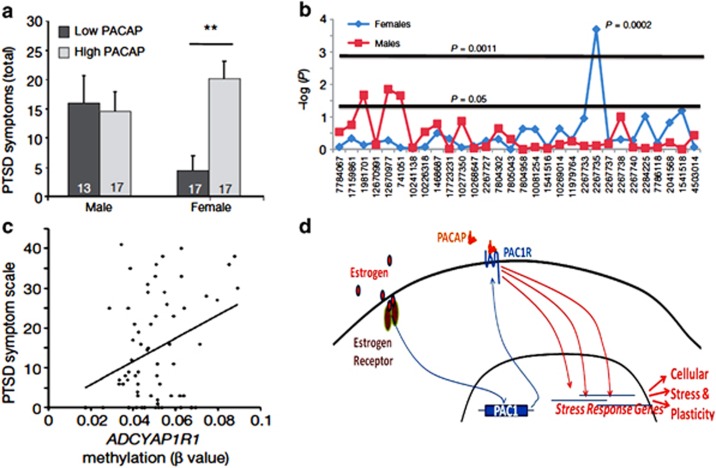
In a highly traumatized, urban civilian population, we have recently reported that women (but not men) that had been diagnosed with PTSD had higher blood PACAP (pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide) levels (Ressler et al, 2011) (Figure 1a). The high PACAP levels were correlated with physiological measures of the acoustic startle reflex, which have previously also been associated with PTSD risk. In addition, to further understand the responsiveness of the PACAP system to emotionally relevant cues and ovarian hormones, we showed that mRNA levels of the receptor for PACAP–PAC1R, are increased in the extended amygdala of adult rodents following classical fear conditioning and as a function of estrogen exposure. These findings suggested that PACAP might be involved in the symptoms characteristic of women diagnosed with PTSD.
Figure 1.
Relationship between the pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP)–PAC1 receptor (PAC1R) system and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). (a) Females, but not males with high plasma PACAP38 levels show more PTSD symptoms. (b) rs2267735 is the only SNP spanning the PAC1R gene that is significantly associated with PTSD symptoms in females, not males. (c) Epigenetic modifications are observed at the PAC1R gene with PTSD symptoms being positively correlated with methylation at the PAC1R locus. (d) Working hypothesis to suggest that the responsiveness of the PACAP and PAC1R system to estrogen might be important in the sex-bias in PTSD prevalence. (a, b, and c reproduced from Ressler et al, Nature (2011)).
To further genetically probe this association, we analyzed the PACAP (Adcyap1) gene and its receptor-PAC1 (Adcyap1r1). Only the Adcyap1r1 SNP (rs2267735) was found to be associated with PTSD diagnosis in women (again not in males) (Figure 1b). Although note that this SNP association was not replicated in a less traumatized cohort (Chang et al., 2012). At the epigenetic level, we also found that differential methylation of the Adcyap1r1 gene was associated with PTSD symptoms (Figure 1c). Given the approximately 2 : 1 sex-bias in PTSD prevalence, we find it exciting that the Adcyap1r1 SNP is within a predicted estrogen response element (ERE). Furthermore, in a postmortem sample, we found that females had differential cortical expression of Adcyap1r1 mRNA levels as a function of their genotype. Notably, a recent follow-up study finds that the same genetic risk is associated with higher acoustic startle in traumatized boys and girls before puberty, suggesting that the estrogen effect may be age-dependent (Jovanovic et al, 2012).
Looking to the future, the association between PTSD and the PACAP–PAC1 receptor system in traumatized populations warrants further investigation on several important levels. For example, longitudinal prospective studies are needed to ascertain whether peripheral PACAP levels would serve as a robust predictive biomarker of eventual PTSD diagnosis. The PACAP–PAC1 receptor system has been studied for its role in stress responsiveness (Vaudry et al, 2009; Stroth et al, 2011), and as such presents a convergence between the stress and learning components of PTSD that should be investigated further. The genetic observation of a predicted ERE supports other findings that hormonal mechanisms may underlie the sex-bias in PTSD prevalence (Ferree et al, 2011; Lebron-Milad and Milad, 2012), but replications of this finding are necessary. Finally, learning is accompanied by epigenetic modifications at key genetic loci (Zovkic and Sweatt, 2012), and probing the epigenetic signatures at the Adcyap1and Adcyap1r1 genes as a result of previous traumatic experience or hormonal condition presents fertile ground for empirical analysis (Figure 1).
In summary, the relationship between PTSD and the PACAP–PAC1 receptor system affords us the opportunity to address PTSD from the perspectives of stress physiology, endocrinology, epigenetics, and predictive biomarkers using human samples and animal models—a truly multi-pronged attack that may be required for understanding complex neuropsychiatric disorders.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Breslau N. The epidemiology of posttraumatic stress disorder: what is the extent of the problem. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62 (Suppl 17:16–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang SC, Xie P, Anton RF, De Vivo I, Farrer LA, Kranzler HR, et al. No association between ADCYAP1R1 and post-traumatic stress disorder in two independent samples. Mol Psychiatry. 2012;17:239–241. doi: 10.1038/mp.2011.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferree NK, Kamat R, Cahill L. Influences of menstrual cycle position and sex hormone levels on spontaneous intrusive recollections following emotional stimuli. Conscious Cogn. 2011;20:1154–1162. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2011.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovanovic T, Norrholm SD, Davis J, Mercer KB, Almli L, Nelson A, et al. 2012PAC1 receptor (ADCYAP1R1) genotype is associated with dark-enhanced startle in children Mol Psychiatrydoi: 10.1038/mp.2012.98(Epub ahead of print). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lebron-Milad K, Milad MR. Sex differences, gonadal hormones and the fear extinction network: implications for anxiety disorders. Biol Mood Anxiety Disord. 2012;2:3. doi: 10.1186/2045-5380-2-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ressler KJ, Mercer KB, Bradley B, Jovanovic T, Mahan A, Kerley K, et al. Post-traumatic stress disorder is associated with PACAP and the PAC1 receptor. Nature. 2011;470:492–497. doi: 10.1038/nature09856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroth N, Holighaus Y, Ait-Ali D, Eiden LE. PACAP: a master regulator of neuroendocrine stress circuits and the cellular stress response. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2011;1220:49–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.05904.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudry D, Falluel-Morel A, Bourgault S, Basille M, Burel D, Wurtz O, et al. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide and its receptors: 20 years after the discovery. Pharmacol Rev. 2009;61:283–357. doi: 10.1124/pr.109.001370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zovkic IB, Sweatt JD.2012Epigenetic mechanisms in learned fear: implications for PTSD Neuropsychopharmacologydoi: 10.1038/npp.2012.79(E-pub ahead of print). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]