Abstract
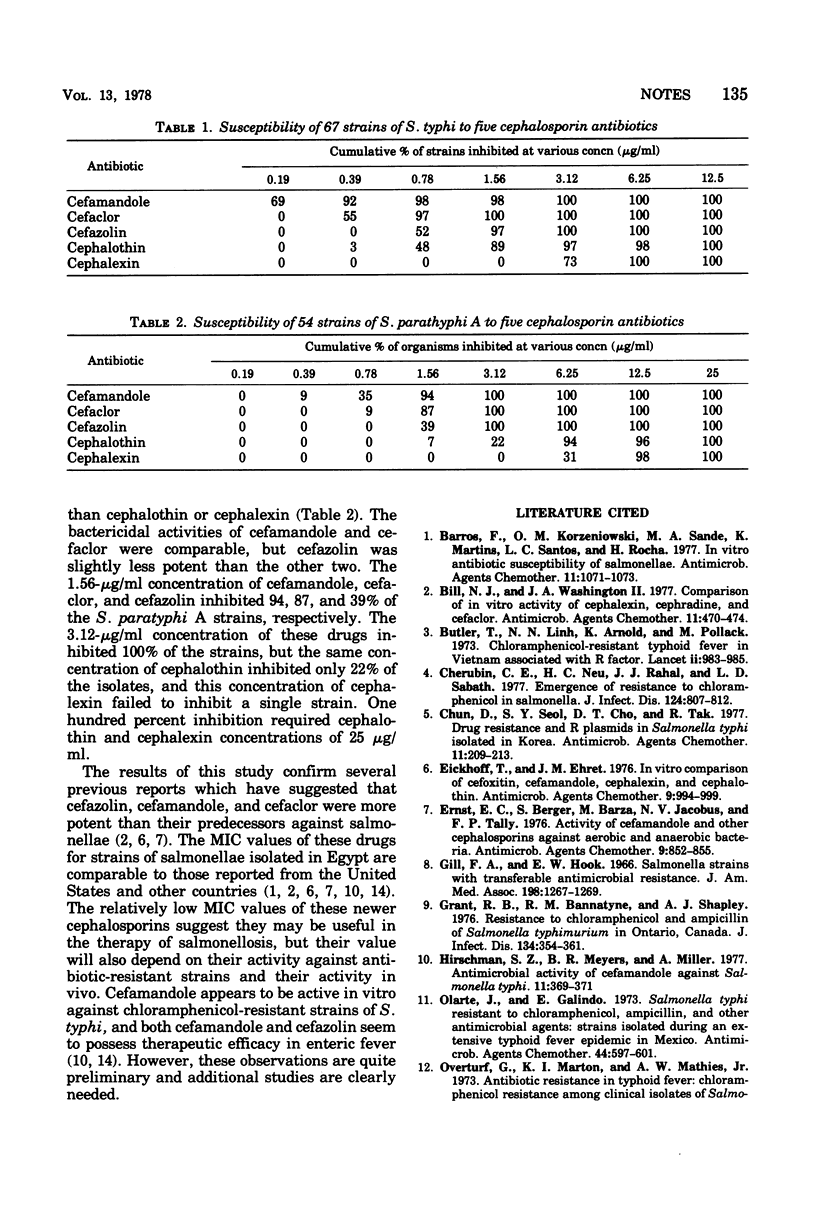
The in vitro activities of five cephalosporin antibiotics against 121 strains of salmonellae were compared. Cefamandole and cefaclor were more potent than cefazolin, and these three drugs were more active than cephalothin and cephalexin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barros F., Korzeniowski O. M., Sande M. A., Martins K., Santos L. C., Rocha H. In vitro antibiotic susceptibility of salmonellae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):1071–1073. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bill N. J., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of in vitro activity of cephalexin, cephradine, and cefaclor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):470–474. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Linh N. N., Arnold K., Pollack M. Chloramphenicol-resistant typhoid fever in Vietnam associated with R factor. Lancet. 1973 Nov 3;302(7836):983–985. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun D., Seol S. Y., Cho D. T., Tak R. Drug resistance and R plasmids in Salmonella typhi isolated in Korea. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):209–213. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickhoff T. C., Ehret J. M. In vitro comparison of cefoxitin, cefamandole, cephalexin, and cephalothin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):994–999. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst E. C., Berger S., Barza M., Jacobus N. V., Tally F. P. Activity of cefamandole and other cephalosporins against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):852–855. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill F. A., Hook E. W. Salmonella strains with transferable antimicrobial resistance. JAMA. 1966 Dec 19;198(12):1267–1269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant R. B., Bannatyne R. M., Shapiey A. J. Resistance to chloramphenicol and ampicillin of Salmonella typhimurium in Ontario, Canada. J Infect Dis. 1976 Oct;134(4):354–361. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.4.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman S. Z., Meyers B. R., Miller A. Antimicrobial activity of cefamandole against Salmonella typhi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):369–371. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olarte J., Galindo E. Salmonella typhi resistant to chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and other antimicrobial agents: strains isolated during an extensive typhoid fever epidemic in Mexico. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Dec;4(6):597–601. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.6.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uwaydah M. Cefazolin in the treatment of acute enteric fever. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):52–56. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



