Abstract
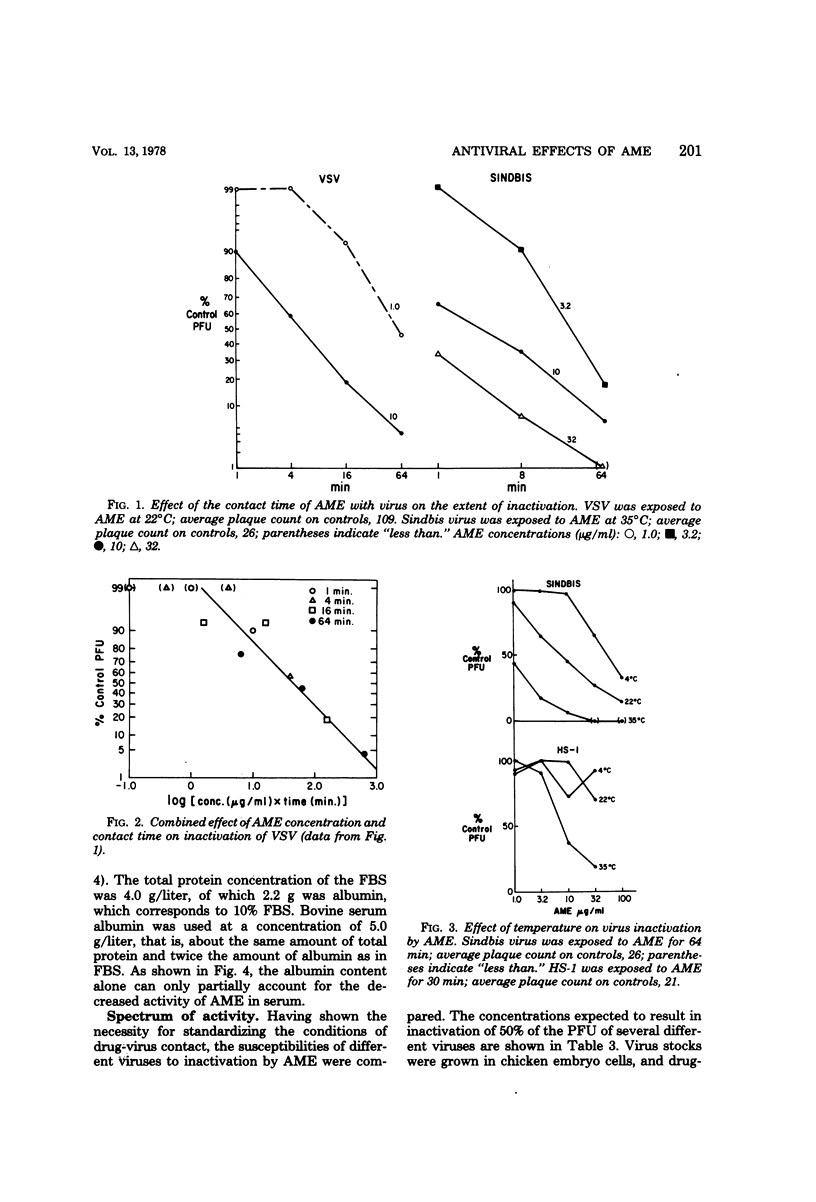
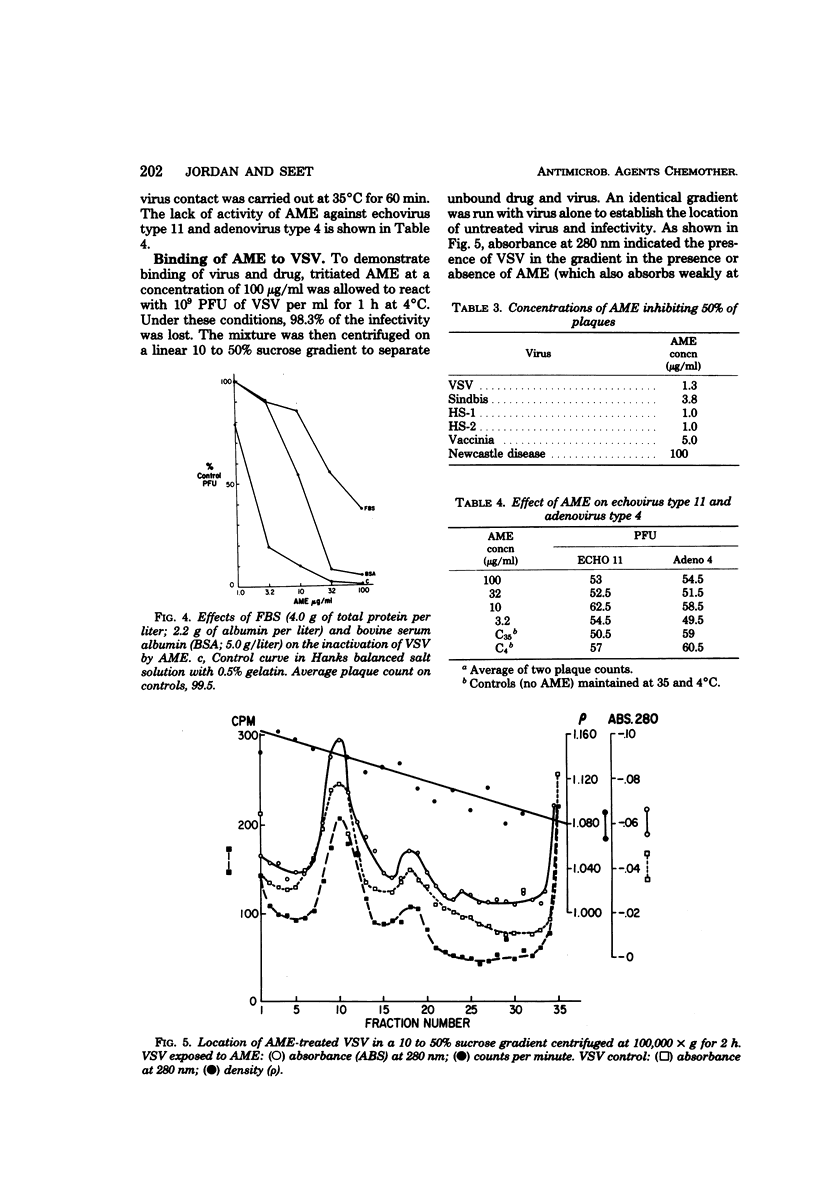
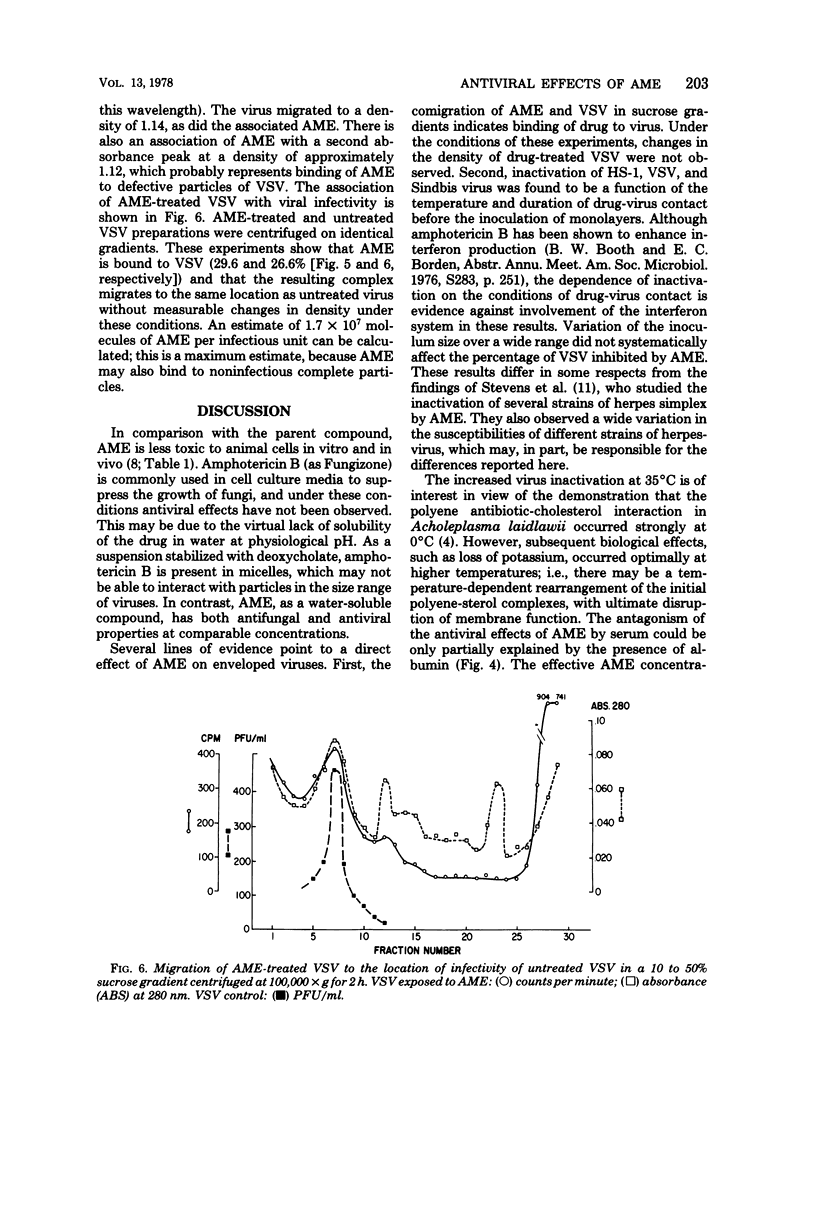
The methyl ester of amphotericin B (AME) is water soluble, retains antifungal activity, and is significantly less toxic in mammals than amphotericin B. In contrast to amphotericin B, which is not water soluble, AME exhibits antiviral effects against vesicular stomatitis virus, herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, Sindbis virus, and vaccinia virus in a plaque reduction assay. No antiviral effects could be demonstrated against the unenveloped adenovirus type 4 or echovirus type 11. The extent of virus inactivation was found to be dependent upon the AME concentration, contact time, and temperature. No consistent effect of the virus concentration on the probability of plaque-forming unit inactivation could be determined. The antiviral effects of AME were partially antagonized by the presence of serum. Binding of AME to vesicular stomatitis virus was demonstrated by the comigration of drug and virus in linear sucrose gradients. AME represents a new class of antiviral agents with activity at concentrations relevant to therapeutics. Sterol components of the host cell membrane that become incorporated into the viral envelope are postulated as the site of reaction with AME.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer D. B., Gale E. F. Antagonism by sterols of the action of amphotericin and filipin on the release of potassium ions from Candida albicans and Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. capri. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Sep;90(1):187–190. doi: 10.1099/00221287-90-1-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M. Chemistry and biology of the polyene macrolide antibiotics. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):166–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keim G. R., Jr, Poutsiaka J. W., Kirpan J., Keysser C. H. Amphotericin B methyl ester hydrochloride and amphotericin B: comparative acute toxicity. Science. 1973 Feb 9;179(4073):584–585. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4073.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. M., Hoeprich P. D. Comparison of amphotericin B and amphotericin B methyl ester: efficacy in murine coccidioidomycosis and toxicity. J Infect Dis. 1976 Feb;133(2):168–174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Compans R. W. The membrane structure of lipid-containing viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 8;344(1):51–94. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(74)90008-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens N. M., Engle C. G., Fisher P. B., Mechlinski W., Schaffner C. P. In vitro antiherpetic activity of water-soluble amphotericin B methyl ester. Arch Virol. 1975;48(4):391–394. doi: 10.1007/BF01317438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B., Gerritsen W. J., Oerlemans A., van Dijck P. W., Demel R. A., van Deenen L. L. Polyene antibiotic-sterol interactions in membranes of Acholesplasma laidlawii cells and lecithin liposomes. II. Temperature dependence of the polyene antibiotic-sterol complex formation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 26;339(1):44–56. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90331-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



