Abstract
Hybrid speciation represents a relatively rapid form of diversification. Early models of homoploid hybrid speciation suggested that reproductive isolation between the hybrid species and progenitors primarily resulted from karyotypic differences between the species. However, genic incompatibilities and ecological divergence may also be responsible for isolation. Iris nelsonii is an example of a homoploid hybrid species that is likely isolated from its progenitors primarily by strong prezygotic isolation, including habitat divergence, floral isolation and post-pollination prezygotic barriers. Here, we used linkage mapping and quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping approaches to investigate genomic collinearity and the genetic architecture of floral differences between I. nelsonii and one of its progenitor species I. hexagona. The linkage map produced from this cross is highly collinear with another linkage map produced between I. fulva and I. brevicaulis (the two other species shown to have contributed to the genomic makeup of I. nelsonii), suggesting that karyotypic differences do not contribute substantially to isolation in this homoploid hybrid species. Similar to other studies of the genetic architecture of floral characteristics, at least one QTL was found that explained >20% variance in each color trait, while minor QTLs were detected for each morphological trait. These QTLs will serve as hypotheses for regions under selection by pollinators.
Keywords: homoploid hybrid speciation, QTL mapping, floral isolation
Introduction
The evolution of new, reproductively isolated species usually involves the gradual accumulation of multiple prezygotic and postzygotic reproductive isolating barriers over time (Coyne and Orr, 1989, 1997; Moyle et al., 2004; Malone and Fontenot, 2008; Scopece et al., 2008). An exception to this is hybrid speciation, where reproductive isolation can evolve quite quickly (James and Abbott, 2005; Mallett, 2007; Buerkle and Rieseberg, 2008). Most commonly, reproductive isolation between a hybrid species and its progenitors results from postzygotic isolation caused primarily by a change in ploidy (polyploid speciation), although a growing number of hybrid species are being detected that are reproductively isolated from their progenitor species without an increase in ploidy (homoploid hybrid species; reviewed by Rieseberg and Willis, 2007).
Reproductive isolation between new homoploid hybrid species and their progenitors may result from the rapid fixation of chromosomal rearrangements and/or genic incompatibilities in addition to ecological divergence between the hybrid taxa and their parental species (Grant, 1971; Buerkle et al., 2000, Buerkle and Rieseberg, 2008). A majority of homoploid hybrid species described to date have a mosaic genome (mosaic genome hybrid speciation; Jiggins et al., 2008), where genomic differences are sorted in the hybrid genome through both fertility and ecological selection (Karrenberg et al., 2007). In the most well studied of these systems, chromosomal rearrangements have a substantial role in strong postzygotic isolation between several independently derived homoploid hybrid sunflower species and their progenitors (Rieseberg et al., 1995; Rieseberg, 2000; Lai et al., 2005), as was predicted in earlier verbal models of homoploid hybrid speciation (Grant, 1971).
Strong reproductive isolation between the homoploid hybrid species and the progenitors may also result primarily from genic differences and ecological divergence (Jiggins et al., 2008). In a few identified homoploid hybrid species (for example, Heliconius butterflies), the introgression of relatively few traits that confer an ecological advantage may be sufficient to cause reproductive (mainly ecological) isolation (hybrid trait speciation; Jiggins et al., 2008; Salazar et al., 2010). Such systems present an opportunity to investigate alternative models of hybrid speciation, especially ones in which genic incompatibilities and ecological isolation are of primary importance in reproductive isolation.
One of the ‘classic examples' (Coyne and Orr, 2004) of homoploid hybrid speciation is that of the Louisiana Iris species I. nelsonii. Randolph (1966) first described this new species and hypothesized a homoploid hybrid origin based on cytological (Randolph et al., 1961) and morphological data (Randolph, 1966). Randolph (1966) suggested that I. nelsonii was derived from hybridization between two widespread species of Louisiana Iris (I. fulva and I. hexagona) and possibly a third widespread species (I. brevicaulis). These three species are all found in southern Louisiana but occupy slightly different habitats and display divergent floral phenotypes. I. fulva flowers are relatively small in size, have a copper red color and have reflexed sepals. The larger I. brevicaulis and I. hexagona flowers are blue, with prominent nectar guides and stiff sepals. I. nelsonii flowers are dark red in color and morphologically intermediate between I. fulva and I. hexagona for some traits, while extreme to the means of the purported progenitors for others (Randolph, 1966). The hybrid origin of I. nelsonii was later confirmed with allozyme (Arnold et al., 1990) and nuclear (Arnold, 1993) data that suggested that a majority of the I. nelsonii genome was derived from I. fulva with contributions of loci from I. hexagona and I. brevicaulis.
When Randolph (1966) initially described I. nelsonii, he proposed ecological isolation as a major barrier to gene flow between I. nelsonii and the progenitors. Indeed, I. nelsonii is endemic to interconnected swamp systems in southern Louisiana and responds differently than its progenitors to abiotic habitat conditions (Taylor et al., 2011). In portions of its limited range, I. nelsonii is sympatric with one of its progenitors, I. hexagona. These two species occupy similar swamp habitats and respond to abiotic habitat characteristics differently than the other species of Louisiana Iris (Taylor et al., 2011). However, I. nelsonii is often found in understory habitats, while I. hexagona is found in more open habitats and seems to be limited by shade (Bennett and Grace, 1990). Additionally, as reflected by their suites of floral characters, these species are pollinated by different suites of pollinators. The large blue flowers of I. hexagona are primarily visited by bumblebees (Emms and Arnold, 2000), while the large red flowers of I. nelsonii are primarily visited by ruby-throated hummingbirds (Taylor et al., 2012). Pollinator isolation, thus, has the potential to be an extremely important ecological barrier to hybridization between I. nelsonii and one of its progenitors, I. hexagona.
This classic example of homoploid hybrid speciation represents an opportunity to investigate hybrid speciation where postzygotic isolation is potentially minimal between the hybrid species and progenitors and, instead, prezygotic isolation—especially ecological isolation—is responsible for inhibiting gene flow in the system. Here, we utilize a comparative mapping approach to investigate genomic collinearity between I. nelsonii and its progenitors, noting that increased collinearity should be consistent with the high first-generation hybrid fertility observed between these species. Additionally, we investigate the genetic architecture of floral differences between I. nelsonii and I. hexagona to identify loci potentially under selection by pollinators and responsible for ecological isolation between these taxa.
Materials and methods
Mapping Population
In order to produce the mapping population used herein, pollen of a wild-collected I. nelsonii individual (In10—collected from Vermillion Parish, LA, USA) was dusted onto the stigmatic surface of a wild-collected I. hexagona individual (IhA32—collected from St Martin Parish, LA, USA) to produce F1 hybrid offspring. Flowers from a single F1 hybrid were self-pollinated to produce the F2 hybrid mapping population, and ultimately several hundred F2 hybrid seeds were produced. The F2 seeds were planted at the University of Georgia greenhouse and monitored for germination success. Successfully germinated seeds were transplanted into six-inch Azalea pots, and repotted into 8-inch Azalea pots. All F2, F1, and pure-species plants were transported to the Texas State University greenhouse in 2007 where they have been maintained and transplanted annually into new 10-inch Azalea pots until the present. In all, 281F2 plants were used in the genetic map construction described herein.
Map construction
DNA was extracted from IhA32, In10, the F1 and the 281 F2 plants using a modified cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide DNA extraction protocol. A total of 282 microsatellite primers (developed by Tang et al. (2009) for I. fulva and I. brevicaulis map production) were screened for utility in the I. nelsonii × I. hexagona F2 mapping population. Of those, 137 markers were both polymorphic and reliably scored in the mapping population. The marker names reported here are the same as those reported for linkage maps previously constructed using I. brevicaulis × I. fulva reciprocal backcross populations (Tang et al., 2010). PCR reactions (modified from Tang et al., 2009) were performed in 10 μl reaction volumes that included 1x PCR buffer, 2.5 mℳ MgCl2, 0.3 mℳ of each deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate, 4 pmol fluorescently labeled forward primer (either 6-FAM/HEX/TAMRA dye), 4 pmol reverse primer, 0.5 units GoTaq Flexi DNA Polymerase (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA), and ∼10 ng of genomic DNA. Loci were amplified using touchdown PCR (Don et al., 1991) to minimize nonspecific amplification. Thermocycling conditions were as follows: initial denaturation was at 94 °C for 1 minute followed by six cycles of: 94 °C for 30 s, 64 °C (decreasing in 1 °C increments each cycle to 58 °C) for 30 s, 72 °C for 30 s, then 33 cycles of: 94 °C for 20 s, 58 oC for 20 s, 72 °C for 30 s with a final extension period of 72 °C for 15 min (Tang et al., 2009). Fragments were multiplexed when possible (when fluorescent labels and/or allele sizes allowed for multiplexing) and run on an ABI 3700xl capillary sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) at the Georgia Genomics Facility and scored by eye in Peakscanner v.1.0 (Applied Biosystems) and GeneMarker v.1.8 (Softgenetics LLC, State College, PA, USA).
Linkage groups were generated in both TMAP (Cartwright et al., 2007) and MAPMAKER 3.0 (Lander et al., 1987; Lincoln et al., 1992) with LOD⩾8 and a maximum distance of 40 cM. Marker order was determined in TMAP (Cartwright et al., 2007). Initially unlinked markers were added to the existing linkage groups at a maximum distance of 45 cM and LOD⩾3 using the ‘near' command in MAPMAKER 3.0. Total map length was calculated by summing the lengths of the linkage groups. Average marker spacing and map coverage was estimated as in Fishman et al. (2001). Genome length was calculated using two methods. First, the genome length was estimated by adding the length of an average marker interval to each end of each linkage group and summing the lengths of the linkage groups. Second, the genome length was estimated as in method 4 of Chakravarti et al. (1991). Map coverage was calculated separately for each of these genome length estimates.
Transmission ratio distortion
Regions of transmission ratio distortion (TRD) are potentially important for preventing (or favoring) locus-specific gene flow between I. nelsonii and I. hexagona when interspecific pollination occurs between the two species. Deviations from expected Mendelian segregation ratios (1AA:2Aa:1aa) in the F2 generation were analyzed for each microsatellite marker by χ2 analyses (2 df). For those loci that significantly deviated from 1:2:1 expectations, we further explored for transmission bias (that is, whether I. nelsonii or I. hexagona homozygotes were overrepresented at each locus), using χ2 analyses (1 df).
Flower color and morphology
Morphological characters potentially responsible for differential pollinator attraction were measured in the Texas State University greenhouses during the spring of 2009. The total length of the sepal, the length of the sepal blade and sepal stalk, width of the sepal and flower stalk height were measured on the first flower of each plant on the second day when the flower was fully opened.
I. nelsonii and I. hexagona flowers differ in multiple aspects of color, with I. nelsonii flowers being dark red and I. hexagona flowers being blue. The concentration of anthocyanin pigments in a single petal of each flower was estimated based on absorbance (Wilken, 1982). Petals were used instead of sepals as they do not have nectar guides, and color is relatively uniform throughout the entirety of the petal. Anthocyanins were extracted from one pre-weighed petal using acidified methanol (1% w/v HCl in methanol). A subset of individual samples (including red, blue and hybrid flowers) was screened between 400 and 800 nm on a Biomate 3 UV–vis spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA). All samples in this subset revealed a maximum absorbance at 537 nm, so absorbance of the full set of samples was measured only at 537 nm. Absorbance values were divided by the weight of the petal to calculate the concentration of anthocyanin pigment (Wilken, 1982). These species also differ with respect to nectar guide area. I. nelsonii flowers are generally devoid of a nectar guide, while I. hexagona flowers display a prominent nectar guide on each sepal. The length and width of the nectar guide of the pure species and F2 plants were both measured in ImageJ (Rasband, 1997). As Iris nectar guides are roughly triangular, the area of the nectar guide was calculated as the area of a triangle.
Phenotypic correlations between traits may potentially result from genetic correlation owing to pleiotropy or tight linkage between genes. Phenotypic correlations in the F2 mapping population were estimated for all pairwise trait combinations. The significance of each phenotypic correlation was assessed after sequentially rejective Bonferroni tests (Holm, 1979).
Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analyses
Genomic regions associated with variation in floral characteristics were detected by composite interval mapping (Zeng, 1994) in Windows QTL Cartographer version 2.5.10 (Wang et al., 2011) using forward and backward regression with the programs default settings (2 cM intervals, 10 cM window size, 5 control markers). A genome-wide significance threshold was set for each trait after 1000 permutations of the data (Churchill and Doerge, 1994; Doerge and Churchill, 1996). A drop below the permutation threshold or a change in the direction of the additive effect was used to distinguish among QTLs on the same linkage group.
Results
Linkage map
All except four markers coalesced into the 22 linkage groups (Figure 1). The remaining markers were unlinked at the minimum criteria set for linking unlinked markers (LOD⩾3, maximum distance 45 cM). For convenience, the linkage groups detected in this mapping population are named to correspond with the linkage groups in Tang et al. (2010). These groups corresponded with 20 of the 21 linkage groups detected in reciprocal backcross linkage maps developed for the closely related I. fulva and I. brevicaulis species (Tang et al., 2010; Supplemental Figure). The linkage map produced by Tang et al. (2010) is denser than the current map (average 4.6 cM intervals between markers in Tang et al., 2010 versus the 12.4 cM intervals in this map). The reduced density of the current map is attributed to the fact that the microsatellite markers used in this and the Tang et al. (2010) study were developed from I. brevicaulis and I. fulva individuals and some of these loci did not amplify in the I. nelsonii × I. hexagona population or were not variable between the mapping parents (IhA32 and In10). As this map contains fewer loci than the map produced by Tang et al. (2010), including markers necessary to link distal ends of the linkage groups, some of the larger linkage groups detected by Tang et al. (2010) were split into the smaller ‘unlinked' linkage groups by the mapping programs with this population. Markers from the ends of the linkage groups 1, 2 and 7, respectively, grouped together (Figure 1), yet because of the large recombination distance between the ends of these linkage groups, they did not link together in the current map. As such, the portions of the current linkage groups are labeled with ‘a' and ‘b' in Figure 1. As the markers from the ‘a' and ‘b' segments are not linked, the orientation of the segments in relation to each other cannot be determined. The placement of the segments in Figure 1 is one interpretation of the possible placement of these segments. No markers from the relatively small linkage group 20 from Tang et al. (2010) were amplified in this F2 population. The sum length of this I. nelsonii × I. hexagona linkage map was 1379.9 cM, with an average marker spacing of 12.4 cM. The estimated genome length was calculated two ways, which yielded similar results. If calculated by adding twice the marker interval spacing to each linkage group, the genome length was estimated as 1926.9 cM. If calculated as method 4 from Chakravarti et al. (1991), the genome length was estimated as 1948.8 cM. Each estimate of genome length was used in calculations of genome coverage. Based on these calculations, ∼74% of the genome is within 10 cM of a marker.
Figure 1.
Linkage map created from an F2 cross between I. nelsonii and I. hexagona. The names of both the markers and linkage groups reflect those used by Tang et al. (2010). Markers revealing significant transmission ratio distortion are denoted with an asterisk after the marker name. Markers with a large number of uncertain genotypes that substantially influenced conclusions about distortion are designated with a caret (^). Boxes indicate the 1-LOD confidence interval and lines indicate the 2-LOD confidence interval for Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) associated with variation in phenotypic traits. Filled boxes indicate QTLs at which the I. hexagona allele increased the trait value. Open boxes indicate QTLs at which the I. hexagona allele decreased the trait value.
Transmission ratio distortion
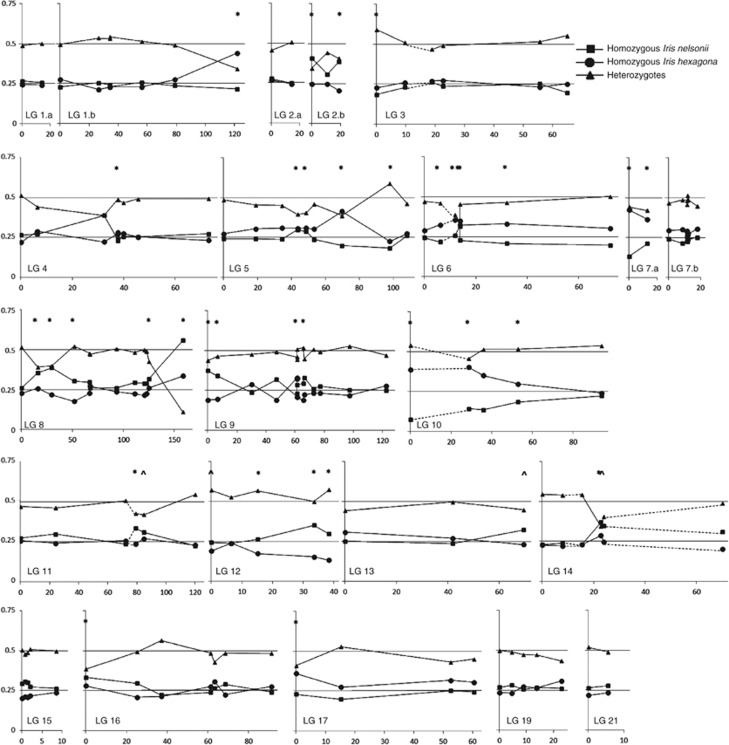
TRD was observed for approximately one-third of the marker loci (Figure 2). Some markers were difficult to genotype with certainty. These markers were re-coded to reflect that uncertainty, which results in a potential loss of genetic information, (for example, for some individuals, it was difficult to distinguish with certainty among homozygotes and heterozygotes for the I. nelsonii allele (to use an example)—yet it was clear that the individual was not homozygous for the I. hexagona allele. These individuals were all coded as a separate category (essentially as ‘not homozygous for I. hexagona') recognized by the mapping programs). Segregation at these loci was investigated under the simplifying assumption that approximately half of the re-coded loci were homozygotes and half were heterozygotes. If this investigation resulted in a substantial change in the TRD (and P-value), the marker was designated with a caret (^) on the linkage map and TRD figures (Figures 1 and 2). No directional bias in TRD was observed. Of the markers that revealed significant TRD and uncertain genotypes did not affect the interpretation of the results, homozygotes for the I. nelsonii allele were overrepresented for 13 markers, while homozygotes for the I. hexagona allele were overrepresented in 14 markers. For the remaining markers, heterozygotes were largely underrepresented (10/13 markers had a heterozygote deficiency, Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Observed genotype frequencies of homozygous I. nelsonii (squares), homozygous I. hexagona (circles) and heterozygotes (triangles). The X-axis denotes the distances (cM) along each linkage group. Lines at 0.25 and 0.5 represent Mendelian expected frequencies for homozygotes and heterozygotes, respectively. Markers that deviated from these expectations (P<0.05) are designated with an asterisk (*). Genotype frequencies of markers designated with a caret (^) are not represented because these markers had a large number of undistinguishable genotypes.
Flower color and morphology
A majority of the F2 plants (N=184) flowered during the 2009 flowering season. However, only six pure-species I. hexagona and five I. nelsonii individuals flowered in the experimental setup during the 2009 flowering season. Owing to this reduced sample size of pure-species individuals and lack of information from the mapping parents, QTL effect sizes are only reported as a proportion of the variance explained in the F2 population. The morphological measurements made in the greenhouse (Tables 1 and 2) reflected measurements made in natural populations by Randolph (1966), suggesting that the few pure-species plants that did flower in the greenhouse represent typical samples of the species. The flower stalks of the I. nelsonii individuals (μ=51.4±12.14 cm) were slightly shorter than those of I. hexagona (μ=64.5±11.77 cm; t=1.6, df=7, P=0.15). One QTL was detected that explained a small percentage of the variance in the F2 population (proportion of the variance explained=0.09; Figure 1, Table 2). At this QTL, the I. hexagona allele resulted in a decrease in flower stalk height.
Table 1. Spearman's correlation coefficients for tests of pairwise phenotypic correlations.
| Stalk height | 170 | ||||||
| Sepal stalk | 0.05 | 176 | |||||
| Sepal blade | 0.08 | 0.34 | 174 | ||||
| Sepal total | 0.06 | 0.66 | 0.92 | 176 | |||
| Sepal width | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.49 | 0.43 | 175 | ||
| Nectar guide | 0.06 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 168 | |
| Anthocyanin | −0.17 | −0.18 | −0.23 | −0.27 | −0.35 | −0.02 | 115 |
| Stalk height | Sepal stalk | Sepal blade | Sepal total | Sepal width | Nectar guide | Anthocyanin |
Coefficients in bold are significant after a sequentially rejective Bonferroni test. Italicized coefficients were significant before, but not after, correction with the sequentially rejective Bonferroni test. Sample size for each trait is given in the diagonal.
Table 2. F2 means, sample sizes, and QTL associated with variation in floral characteristics in Iris nelsonii × I. hexagona F2 hybrids.
| Trait | N | F2 mean (s.d.) | Linkage group | Location (cM) | Proportion of the variance explained | Additive effect | Dominance effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stalk height (cm) | 170 | 87.63 (13.96) | LG14 | 21.4 (6.0–56.4) | 0.09 | −3.228 | 7.414 |
| Sepal stalk (cm) | 176 | 3.14 (34) | LG4 | 21.4 (8.4–37.7) | 0.16 | 0.183 | 0.013 |
| Sepal stalk (cm) | 176 | 3.14 (34) | LG9 | 56.3 (47.3–76.6) | 0.10 | 0.130 | 0.114 |
| Sepal stalk (cm) | 176 | 3.14 (34) | LG19 | 13.8 (7.6–22.8) | 0.09 | 0.136 | 0.052 |
| Sepal blade (cm) | 174 | 5.81 (59) | no QTL detected | ||||
| Sepal total (cm) | 176 | 8.95 (77) | LG4 | 28.4 (14.4–42.8) | 0.12 | 0.367 | 0.042 |
| Sepal total (cm) | 176 | 8.95 (77) | LG4 | 72.6 (54.6–72.6) | 0.09 | −0.338 | −0.033 |
| Sepal total (cm) | 176 | 8.95 (77) | LG9 | 83.1 (73.6–97.1) | 0.10 | 0.303 | 0.178 |
| Sepal total (cm) | 176 | 8.95 (77) | LG14 | 0.0991 (0.03–18) | 0.14 | 0.389 | −0.279 |
| Sepal width (cm) | 175 | 4.32 (39) | LG4 | 72.6 (59.6–72.6) | 0.12 | −0.189 | −0.075 |
| Nectar guide area (cm2) | 168 | 0.61 (47) | LG6 | 0 (0–9.1) | 0.14 | 0.245 | −0.049 |
| Nectar guide area (cm2) | 168 | 0.61 (47) | LG11 | 104.9 (84.9–118.9) | 0.21 | 0.307 | 0.046 |
| Anthocyanin (OD per mg) | 115 | 0.011 (0026) | LG2B | 17.8 (1–17.8) | 0.13 | −0.001 | −0.001 |
| Anthocyanin (OD per mg) | 115 | 0.011 (0026) | LG11 | 82.3 (72.4–103.9) | 0.24 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
The location of the highest likelihood ratio is given with 2-logarithm of odds confidence intervals in parentheses. The magnitude of QTL effect is reported as the proportion of the variance explained in the mapping population. Additive and dominance effects are in units of the trait.
In Iris flowers, the sepal subtends the anther and stigma and is thus likely important in pollinator attraction. The sepal shape of I. nelsonii and I. hexagona differ in that the sepals of I. nelsonii are reflexed and I. hexagona sepals are upright. As the I. nelsonii sepal is reflexed, the sepal stalk of the I. nelsonii flowers (μ=1.84±0.36 cm) is significantly shorter than that of the I. hexagona flowers (μ=3.67±0.45 cm; t=6.6, df=7, P=0.0003). Three QTLs were detected for sepal stalk length. The I. hexagona allele results in an increase in the sepal stalk length at all QTLs detected. The sepal blade of I. nelsonii individuals (μ=4.85±0.60 cm) in the greenhouse was also significantly shorter than the sepal blade of I. hexagona individuals (μ=6.25±0.51 cm; t=3.8, df=7, P=0.007). No QTLs were detected for sepal blade length. The total length of sepals was significantly lower in I. nelsonii (μ=6.69±0.29 cm) than in I. hexagona (μ=9.92±0.82 cm; t=7.5, df=7, P=0.0001). Three of the four QTLs detected for sepal total length were in the expected direction, where the I. hexagona allele results in an increase in sepal total length. The I. hexagona allele decreases the trait value for the other QTL. The sepal width of I. nelsonii flowers (μ=3.27±0.34 cm) was also smaller than I. hexagona flowers (μ=4.13±0.47 cm; t=2.9, df=5, P=0.04). One QTL was detected for sepal width (Figure 1; Table 2). At this QTL, the I. hexagona allele decreases the trait mean, which is opposite expectations given the species means.
Many of the sepal measurements were correlated (Table 1). In two cases, this correlation was coupled with overlapping QTLs. The total sepal length and the sepal stalk length are strongly correlated and have overlapping QTLs on LG4 with effects in the same direction (Figure 1; Table 2). Sepal width and total sepal length are also correlated and QTLs detected on LG4 were overlapping and had effects in the same direction (Figure 1; Table 2).
The species also differ in color, where I. nelsonii flowers are red, as is typical for many hummingbird pollinated flowers, and I. hexagona flowers are blue—typical of many bee-pollinated flowers. I. nelsonii flowers contained a higher concentration of anthocyanin pigments (μ=0.013±0.001 OD per mg) than did I. hexagona flowers (μ=0.005±0.0007 OD per mg; t=10.4, df=8, P<0.0001). Two QTLs were detected that had mixed effects on anthocyanin concentration (Figure 1; Table 2). Also, I. nelsonii typically has no, or a very small, nectar guide (μ=0.06±0.06 cm) while the nectar guide on I. hexagona (μ=0.64±0.15 cm) is prominent (t=7.0, df=9, P<0.0001). Two QTLs were detected that were associated with variation in nectar guide. As predicted by the species mean difference, the I. hexagona allele increased the trait mean at both QTLs.
Discussion
Genomic collinearity
In order for new homoploid hybrid species to arise and persist, they must evolve reproductive isolation from their progenitor species at a relatively early stage. Early verbal models of homoploid hybrid speciation invoked chromosomal rearrangements and the resulting infertility of F1 hybrids as the most likely mechanism by which new homoploid species arise (Grant, 1971). Computer simulations have revealed that, although chromosomal rearrangements have an important role in the establishment of homoploid hybrid species, ecological isolation can greatly increase the degree to which these newly derived species are maintained over time (Buerkle et al., 2000). Indeed, studies in Helianthus support chromosomal differences coupled with ecological isolation as a primary mechanism by which repeated homoploid hybrid species have arisen (Rieseberg et al., 1995, 2003; Lai et al., 2005). However, hybrid speciation may also be achieved without chromosomal rearrangements if genic incompatibilities and/or ecological divergence isolate the hybrid species from its progenitors (Templeton, 1981; Jiggins et al., 2008). The relative importance of karyotypic differences versus genic incompatibilities is not known because there are relatively few studies specifically examining the genomic collinearity of homoploid hybrid species and their progenitors (but see Rieseberg et al., 1995; Lai et al., 2005). While studies in Helianthus support chromosomal differences as a largely important barrier to gene flow (Rieseberg et al., 1995; Lai et al., 2005), a recent study in Cottus (Stemshorn et al., 2011) and the current study reveal high degrees of genomic collinearity between the homoploid hybrid lineage and the progenitors, suggesting that other mechanisms are potentially responsible for reproductive isolation between the hybrid lineage and progenitors.
The genomes of all four hybridizing Louisiana Iris species show a high degree of genetic collinearity. Although I. hexagona has a different chromosome number than the other three species, interspecific linkage maps between the species reveal little evidence of major chromosomal rearrangements between it and the other three Louisiana Iris species (Tang et al., 2010; E. Ballerini et al., unpublished data). The markers in the current study grouped as in maps produced by Tang et al. (2010), and updated by E. Ballerini et al., unpublished data), from crosses between I. brevicaulis and I. fulva, with few exceptions. Marker IM192 is the terminal marker of LG 6 in the I. brevicaulis × I. fulva map, but is 13.8 cM from the top in the current map. Also, on LG9, marker spacing in the current map is greater than marker spacing in Tang et al. (2010) and marker IM364 is the terminal marker of LG 9 in Tang et al. (2010) but in the middle (72.6 cM) of LG 9 in the current map (Figure 1; Supplementary Figure). Future mapping studies in a cross between I. nelsonii and I. fulva and between I. hexagona and I. fulva will allow us to identify the specific order of markers within each of the species. However, the high degree of genetic collinearity observed between these interspecific maps, combined with the fact that F1 hybrids do not reveal substantial reductions in pollen fertility (I. fulva × I. nelsonii, I. nelsonii × I. fulva, and I. nelsonii × I. hexagona preliminary data shows F1 fertility is ∼85% that of pure species fertility) imply that major chromosomal rearrangements are not effecting a high degree of postzygotic isolation, lending support to Randolph's (1966) hypothesis of ecological isolation being primarily responsible for the origin and maintenance of I. nelsonii in its unique cypress swamp habitat.
Transmission ratio distortion
Non-Mendelian transmission of alleles is routinely reported across a wide variety of interspecific and intraspecific crosses and across a wide variety of taxa (Fishman et al., 2001; Bouck et al., 2005; Hall and Willis, 2005; Tang et al., 2010; Casellas et al., 2012; Koevoets et al., 2012). TRD may result from any number of post-pollination prezygotic (for example Fishman et al., 2008), or postzygotic (prior to genotyping) biological processes. Our crossing design could have resulted in some amount of inbreeding depression, as the original parents were wild-collected and they could have been harboring some deleterious alleles in heterozygous form. This could result in an underrepresentation of parental genotypes linked to those deleterious alleles or an overrepresentation of heterozygotes. As such, the TRD observed for loci in which either I. nelsonii or I. hexagona homozygotes are underrepresented could be caused by post-pollination barriers and/or postzygotic processes (including inbreeding depression).
However, for the 13 markers in which TRD was found and the parental genotypes were roughly equal, ten markers revealed heterozygote deficiencies. This pattern cannot be explained by inbreeding depression, and suggests selection against heterozygote individuals at those loci. In reciprocal backcross linkage mapping populations produced between I. fulva and I. brevicaulis and germinated, and grown as seedlings in the same greenhouse as the I. nelsonii × I. hexagona mapping population roughly one-third of the markers revealed significant TRD (Bouck et al., 2005; Tang et al., 2010). In those same maps, TRD was largely asymmetric, in that I. fulva alleles were overrepresented in each genetic background (Tang et al., 2010). Indeed, introgression in natural hybrid populations between these species often shows a pattern of asymmetric introgression of I. fulva alleles across species boundaries (Arnold and Martin, 2010). However, markers in the current F2 mapping population showed no such asymmetries.
Genetic architecture of floral characteristics
Ecological divergence is important in reducing gene flow between the homoploid hybrid lineage and its progenitors (Buerkle et al., 2000; Gross and Rieseberg, 2005). I. nelsonii is likely isolated from at least two of its progenitors (I. hexagona and I. brevicaulis) by pollinator isolation and differs from all of its progenitors in its unique suite of floral characteristics (Randolph, 1966). As a result of these highly divergent floral morphologies, I. nelsonii and I. hexagona are primarily visited by different pollinator groups. I. hexagona is primarily pollinated by bumblebees (Emms and Arnold, 2000) while I. nelsonii is primarily pollinated by hummingbirds (Taylor et al., 2012).
The unique floral morphology of I. nelsonii is likely due to inheritance of a mixture of loci from the progenitor species. As such, I. nelsonii shares some floral characteristics with I. fulva and others with I. hexagona, but it also has characteristics that are outside of the means of the other species (Randolph, 1966). Here, we used QTL mapping to identify loci that differentiate I. nelsonii from one of its progenitor species, I. hexagona. These loci serve as hypotheses for loci under selection during the formation of I. nelsonii. These loci are also likely responsible for maintaining species barriers via pollinator isolation where these species occur in sympatry. Divergent floral morphologies may directly cause reduced interspecific visitation between these two taxa as has been observed between I. fulva and I. brevicaulis (Martin et al., 2008) and between I. fulva and I. hexagona (Emms and Arnold, 2000).
QTL mapping studies have often found genomic regions that influence variation in multiple floral traits (for example, Juenger et al., 2000; Fishman et al., 2002; Goodwillie et al., 2006; Bouck et al., 2007). Pleitropy or tight linkage of QTLs that influence floral traits may constrain floral evolution in a hybrid zone. We detected some colocalization of QTLs for traits in this mapping population. QTLs for sepal traits colocalized on LG4 and LG9. These overlapping QTLs influenced traits for which we detected positive phenotypic correlations (Table 1). Although the remainder of the significant phenotypic correlations is not explained by colocalized QTLs in this map, we caution that many QTLs, especially those of small effect, may remain undetected due to small sample size, as at least half of the phenotypic variance in the F2 population remains unexplained for all traits.
The genetic architecture of floral characteristics in this system is similar to studies examining the genetic architecture of floral characteristics in other species. Here, we detected two QTLs for anthocyanin concentration that together explained a large portion of the variance in the F2 population (total ∼37% Table 2). While QTL mapping studies, especially those with limited sample sizes, may tend to overestimate effect sizes (Beavis, 1998), a number of other studies that have quantified flower color in mapping populations have generally detected few loci of large effect on the trait as well (for example, Bradshaw et al., 1995; Bouck et al., 2007; reviewed in Galliot et al., 2006). We also detected two QTLs for nectar guide area that explained ∼35% of the variation in the trait (Table 2), which is similar to the findings of Bouck et al. (2007) in a cross between the other two Louisiana Iris species (I. brevicaulis and I. fulva). In contrast to floral color differences between species, differences in other aspects of floral morphology appear to be influenced by a larger number of minor QTLs (Fishman et al., 2002; Bouck et al., 2007; Kim and Rieseberg, 1999; reviewed in Galliot et al., 2006; but see Bradshaw et al., 1995). Here, we similarly detected between 0 and 4 QTLs for each morphological trait, with an average of 0.11±0.03 proportion of the variance explained by each of these loci.
The large effect of the color loci and the relatively small effect of the morphological loci suggest that the color difference between species may be accomplished with relatively few substitutions, while more mutational steps lay between the divergent morphologies of closely related species (reviewed in Galliot et al., 2006). Understanding the genetic architecture of floral traits and pollinator visitation allows an investigation of the loci that are under selection by pollinators (for example, Bradshaw and Schemske, 2003). The genetic architecture of floral differences and the effect of these differences on pollinator visitation have been studied in few systems. In Mimulus and Petunia, mutations with large effect on color (carotenoids and anthocyanins, respectively) also have a large effect on pollinator visitation (Bradshaw and Schemske, 2003; Hoballah et al., 2007). In analyses of pollinator visitation in experimental arrays of Louisiana Iris, pollinator preference QTLs overlapped with brightness and hue QTLs of relatively small effect in a backcross population between Iris fulva and I. brevicaulis (Martin et al., 2008). The current mapping population has an advantage over the I. brevicaulis × I. fulva mapping population for examining pollinator preferences, because I. nelsonii and I. hexagona have near-identical flowering phenologies. Iris fulva and I. brevicaulis have highly divergent flowering times (the peak flowering times of these species are shifted by approximately a month; Martin et al., 2007), which potentially results in experimental arrays that are offered to the pollinators differing throughout the field season, or the ‘training' of pollinators to prefer certain floral traits over time.
Summary and conclusions
We have shown that I. nelsonii, a homoploid hybrid, has a genome that is highly collinear with its progenitor species, which comports with the relatively high fertility observed when F1 hybrids are produced between I. nelsonii and its parents. This suggests that barriers other than karyotypic rearrangements were largely responsible for the early establishment of this species. Indeed, Randolph (1966) posited that ecological barriers were likely important in reducing gene flow between I. nelsonii and its progenitors, and Taylor et al. (2011) have shown that, in fact this hybrid taxon responds differently to abiotic environmental factors than its parental species. This mapping population and the newly-created map presented here will enable us to examine the genetic architecture of ecological divergence between I. nelsonii and I. hexagona. Pollinator isolation is a potentially strong ecological barrier between I. nelsonii and I. hexagona, and we are now in the position to perform pollinator array experiments to examine the genetic architecture of pollinator isolation between these species, and to determine whether the genetic architecture of the floral traits examined here reflects that of pollinator isolation.
Data archiving
Genotype and phenotype data have been deposited at Dryad (doi:10.5061/dryad.6cn04).
Acknowledgments
We thank M Arnold for the plant material. M Shaw, M Ramirez, J Matlock and J Fugette assisted in data collection. Thank you to the Dharmasiri lab at Texas State University-San Marcos for allowing use of their equipment, and to M Arnold, C Nice, J Ott, and K Whitney for helpful discussions. We also thank S Tang for providing map files for creation of the supplemental comparison map. This work was funded by the National Science Foundation (DEB-0816905, DEB-0949424 and DGE-0742306).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Heredity website (http://www.nature.com/hdy)
Supplementary Material
References
- Arnold ML. Iris nelsonii (Iridaceae): origin and genetic composition of a homoploid hybrid species. Am J Bot. 1993;80:577–583. doi: 10.1002/j.1537-2197.1993.tb13843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold ML, Hamrick JL, Bennett BD. Allozyme variation in Louisiana irises: a test for introgression and hybrid speciation. Heredity. 1990;65:297–306. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold ML, Martin NH. Hybrid fitness across time and habitats. Trends in Ecology and Evolution. 2010;25:530–536. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2010.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavis W.1998QTL analyses: power, precision, and accuracyIn: Paterson AH, (ed)Molecular Dissection of Complex Traits CRC Press Boca Raton; 145–162. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett BD, Grace JB. Shade tolerance and its effect on the segregation of two species of Louisiana Iris and their hybrids. Am J Bot. 1990;77:100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Bouck A, Peeler R, Arnold ML, Wessler SR. Genetic mapping of species boundaries in Louisiana irises using IRRE retrotransposon display markers. Genetics. 2005;171:1289–1303. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.044552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouck A, Wessler SR, Arnold ML. QTL analysis of floral traits in Louisiana Iris hybrids. Evolution. 2007;61:2308–2319. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw HD, Schemske DW. Allele substitution at a flower colour locus produces a pollinator shift I monkeyflowers. Nature. 2003;426:176–178. doi: 10.1038/nature02106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw HD, Wilbert SM, Otto KG, Schemske DW. Genetic mapping of floral traits associated with reproductive isolation in monkeyflowers (Mimulus) Nature. 1995;376:762–765. [Google Scholar]
- Buerkle CA, Morris RJ, Asmussen MA, Rieseberg LH. The likelihood of homoploid hybrid speciation. Heredity. 2000;84:441–451. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2540.2000.00680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buerkle CA, Rieseberg LH. The rate of genome stabilization in homoploid hybrid species. Evolution. 2008;62:266–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright DA, Troggio M, Velasco R, Gutin A. Genetic mapping in the presence of genotyping errors. Genetics. 2007;176:2521–2527. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.063982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casellas J, Gularte RJ, Farber CR, Varona L, Mehrabian M, Schadt EE, et al. Genome scans for transmission ratio distortion regions in mice. Genetics. 2012;191:247–259. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.135988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A, Lasher LK, Reefer JE. A maximum likelihood method for estimating genome length using genetic linkage data. Genetics. 1991;128:175–182. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill GA, Doerge RW. Empirical threshold values for quantiatitve trait mapping. Genetics. 1994;138:963–971. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.3.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyne JA, Orr HA. Patterns of speciation in Drosophila. Evolution. 1989;43:362–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1989.tb04233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyne JA, Orr HA. ‘Patterns of speciation in Drosophila' revisited. Evolution. 1997;51:295–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1997.tb02412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyne JA, Orr HA. Speciation. Sinauer Sunderland, MA; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Doerge RW, Churchill GA. Permutation tests for multiple loci affecting a quantitative character. Genetics. 1996;142:285–294. doi: 10.1093/genetics/142.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don RH, Cox PT, Wainwright BJ, Baker K, Mattick J. ‘Touchdown' PCR to circumvent spurious priming during gene amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991;19:4008. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.4008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emms SK, Arnold ML. Site-to-site differences in pollinator visitation patterns in a Louisiana iris hybrid zone. Oikos. 2000;91:568–578. [Google Scholar]
- Fishman L, Aagaard J, Tuthill JC. Toward the evolutionary genomics of gametophytic divergence: patterns of transmission ratio distortion in monkeyflower (Mimulus) hybrids reveal a complex genetic basis for conspecific pollen precedence. Evolution. 2008;62:2958–2970. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2008.00475.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman L, Kelly AJ, Morgan E, Willis JH. A genetic map in the Mimulus guttatus species complex reveals transmission ratio distortion due to heterospecific interactions. Genetics. 2001;159:1701–1716. doi: 10.1093/genetics/159.4.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman L, Kelly AJ, Willis JH. Minor quantitative trait loci underlie floral traits associated with mating system divergence in Mimulus. Evolution. 2002;56:2138–2155. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2002.tb00139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galliot C, Stuurman J, Kuhlemeier C. The genetic dissection of floral pollination syndromes. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2006;9:78–82. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2005.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwillie C, Ritland C, Ritland K. The genetic basis of floral traits associated with mating system evolution in Leptosiphon (Polemoniaceae): an analysis of quantitative trait loci. Evolution. 2006;60:491–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant V. Plant Speciation. Columbia University Press New York; 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Gross BL, Rieseberg LH. The ecological genetics of homoploid hybrid speciation. J Hered. 2005;96:241–252. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esi026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall MC, Willis JH. Transmission ratio distortion in intraspecific hybrids of Mimulus guttatus. Genetics. 2005;170:375–386. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.038653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoballah ME, Gubitz T, Stuurman J, Broger L, Barone M, Mandel T, et al. Single gene-mediated shift in pollinator attraction in Petunia. Plant Cell. 2007;19:779–790. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.048694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm S. A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scan J Statist. 1979;6:65–70. [Google Scholar]
- James JK, Abbott RJ. Recent, allopatric, homoploid hybrid speciation: the origin of Senecio squalidus (Asteraceae) in the British Isles from a hybrid zone on Mount Etna, Sicily. Evolution. 2005;59:2533–2547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiggins CD, Salazar C, Linares M, Mavarez J. Hybrid trait speciation and Heliconius butterflies. Phil Trans R Soc B. 2008;363:3047–3054. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juenger T, Purugganan M, Mackay TFC. Quantitative trait loci for floral morphology in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics. 2000;156:1379–1392. doi: 10.1093/genetics/156.3.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karrenberg S, Lexer C, Rieseberg L. Reconstructing the history of selection during homoploid hybrid speciation. Amer Nat. 2007;169:725–737. doi: 10.1086/516758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S-C, Rieseberg LH. Genetic architecture of species differences in annual sunflowers: implications for adaptive trait introgression. Genetics. 1999;153:965–977. doi: 10.1093/genetics/153.2.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koevoets T, Niehuis O, van de Zande L, Beukeboom LW. Hybrid incompatibilities in the parasitic wasp genus Nasonia: negative effects of hemizygosity and the identification of transmission ratio distortion loci. Heredity. 2012;108:302–311. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2011.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z, Nakazoto T, Salmaso M, Burke JM, Tang S, Knap SJ, et al. Extensive chromosomal repatterning and the evolution of sterility barriers in hybrid sunflower species. Genetics. 2005;171:291–303. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.042242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, et al. MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics. 1987;1:174–181. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln SE, Daly MJ, Lander ES. Constructing Genetic Maps with MAPMAKER/EXP 3.0 Manual. Whitehead Institute Cambridge, MA; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mallett J. Hybrid speciation. Nature. 2007;446:279–283. doi: 10.1038/nature05706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone JH, Fontenot BE. Patterns of reproductive isolation in toads. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e3900. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin NH, Bouck AC, Arnold ML. The genetic architecture of reproductive isolation in Louisiana irises: flowering phenology. Genetics. 2007;175:1803–1812. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.068338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin NH, Sapir Y, Arnold ML. The genetic architecture of reproductive isolation in Louisiana irises: pollination syndromes and pollinator preferences. Evolution. 2008;62:740–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2008.00342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle LC, Olson MS, Tiffin P. Patterns of reproductive isolation in three angiosperm genera. Evolution. 2004;58:1195–1208. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2004.tb01700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randolph LF. Iris nelsonii, a new species of Louisiana Iris of hybrid origin. Baileya. 1966;14:143–169. [Google Scholar]
- Randolph LF, Mitra J, Nelson IS. Cytotaxonomic studies of Louisiana Irises. Bot Gazette. 1961;123:125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Rasband WS.1997–2011ImageJ U. S. National Institutes of Health Bethesda, Maryland, USA; http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ . [Google Scholar]
- Rieseberg LH. Crossing relationships among ancient and experimental sunflower hybrid lineges. Evolution. 2000;54:859–865. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2000.tb00086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieseberg LH, Raymond O, Rosenthal DM, Lai Z, Livingstone K, Nakazato T, et al. Major ecological transitions in wild sunflowers facilitated by hybridization. Science. 2003;301:1211–1216. doi: 10.1126/science.1086949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieseberg LH, Van Fossen C, Desrochers AM. Hybrid speciation accompanied by genomic reorganization in wild sunflowers. Nature. 1995;375:313–316. [Google Scholar]
- Rieseberg LH, Willis JH. Plant speciation. Science. 2007;317:910–914. doi: 10.1126/science.1137729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salazar C, Baxter SW, Pardo-Diaz C, Wu G, Surridge A, Linares M, et al. Genetic evidence for hybrid trait speciation in Heliconius butterflies. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1000930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopece G, Widmer A, Cozzolino S. Evolution of postzygotic reproductive isolation in a guild of deceptive orchids. Amer Nat. 2008;171:315–326. doi: 10.1086/527501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemshorn KC, Reed FA, Nolte AW, Tautz D. Rapid formation of distinct hybrid lineages after secondary contact of two fish species (Cottus sp.) Mol Ecol. 2011;20:1475–1491. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang S, Okashah RA, Cordonnier-Pratt MM, Pratt LH, Johnson VE, Taylor CA, et al. EST and EST-SSR marker resources for Iris. BMC Plant Biol. 2009;9:72. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-9-72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang S, Okashah RA, Knapp SJ, Arnold ML, Martin NH. Transmission ratio distortion results in asymmetric introgression in Louisiana Iris. BMC Plant Biol. 2010;10:48. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor SJ, AuBuchon KJ, Martin NH. Identification of Floral Visitors of Iris nelsonii. Southeastern Naturalist. 2012;11:141–144. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor SJ, Willard RW, Shaw JP, Dobson MC, Martin NH. Differential response of the homoploid hybrid species Iris nelsonii (Iridaceae) and its progenitors to abiotic habitat conditions. Am J Bot. 2011;98:1309–1316. doi: 10.3732/ajb.1100012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton AR. Mechanisms of speciation - a population genetic approach. Ann Rev Ecol Syst. 1981;12:23–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng Z-B.2011Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5 Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC; . ( http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm ). [Google Scholar]
- Wilken DH. A simple method for estimating anthocyanin concentrations in tissue extracts. Phytochemical Bulletin. 1982;15:7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng Z-B. Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics. 1994;136:1457–1468. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.4.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.