Abstract
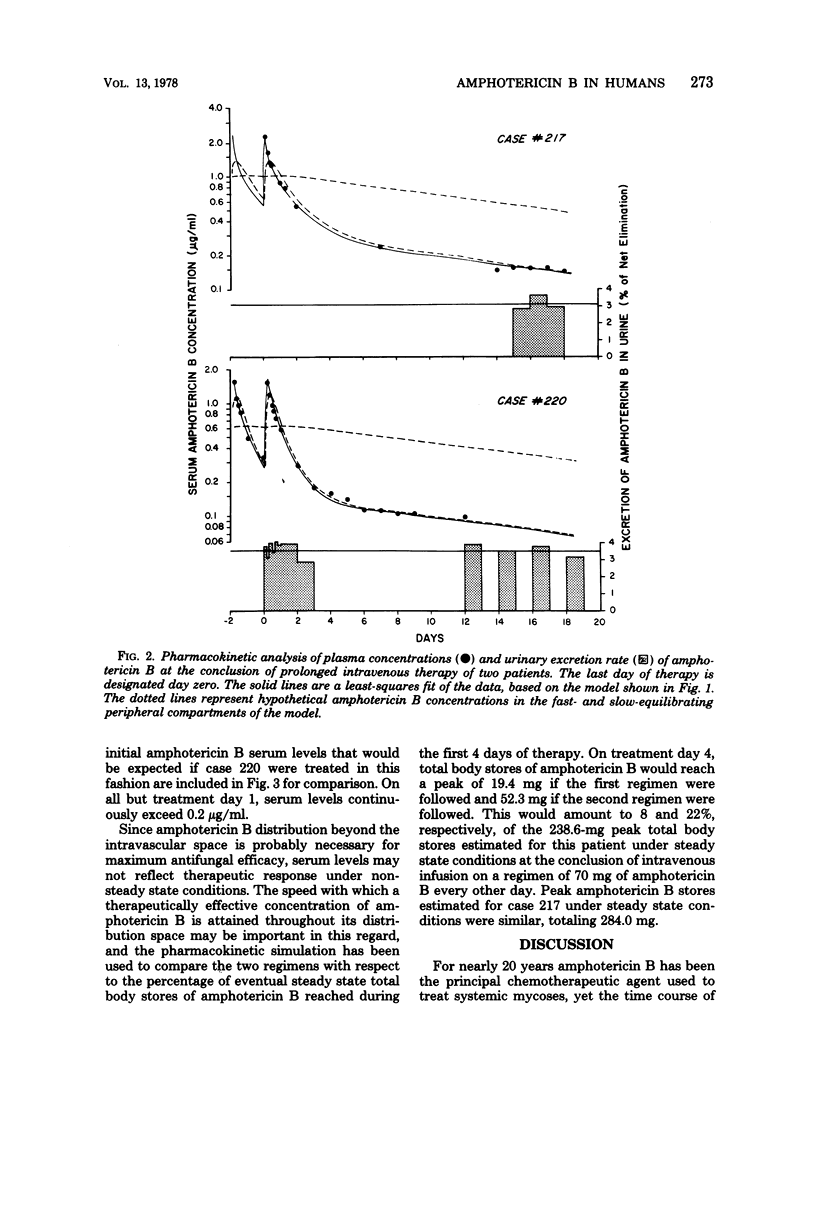
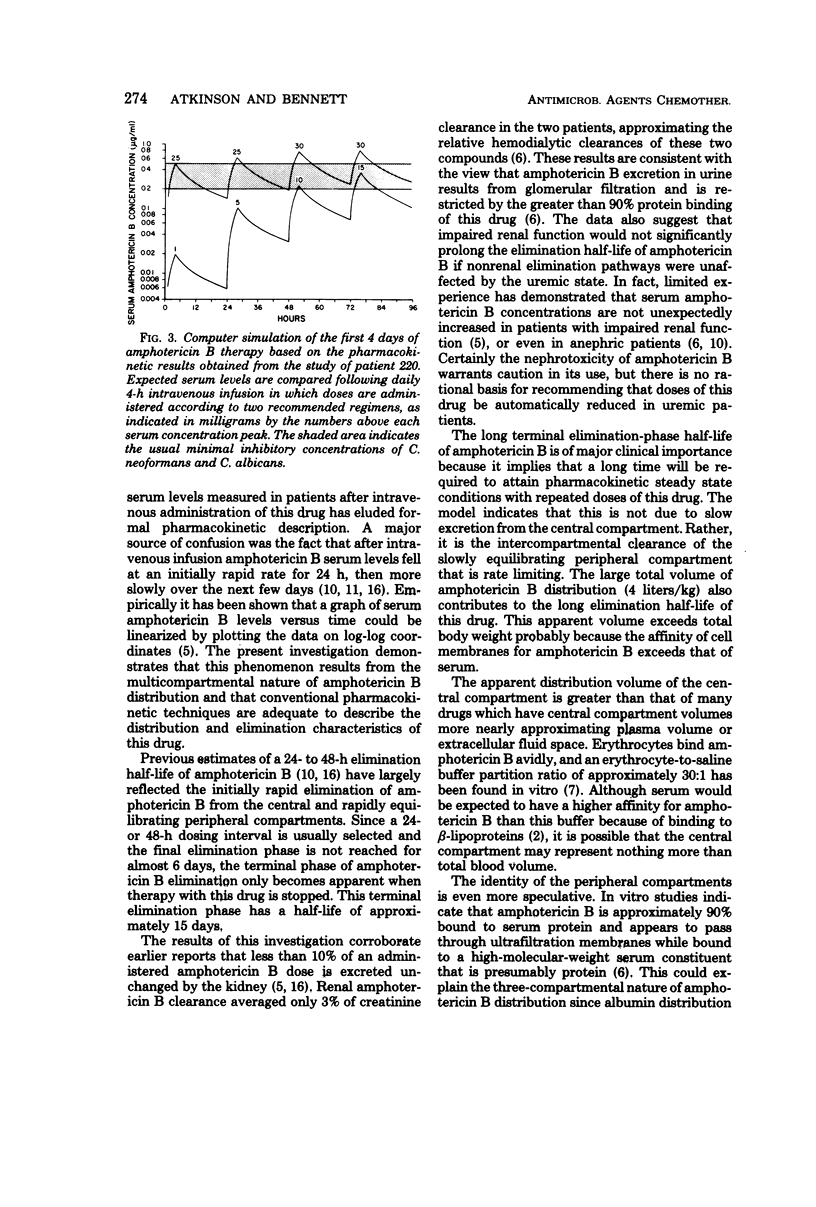
The pharmacokinetics of amphotericin B were studied in two patients at the conclusion of long-term therapy for disseminated histoplasmosis. The distribution kinetics of this drug were adequately described by a three-compartment mamillary model with a total distribution volume averaging 4 liters/kg. The elimination phase half-life of amphotericin B was approximately 15 days, reflecting slow release of amphotericin B from a peripheral compartment. In accordance with previous reports, renal excretion accounted for only 3% of total amphotericin B elimination. The pharmacokinetic model for one of the patients also was used to compare the simulated amphotericin B serum levels that would be expected if initial therapy followed two recommended regimens.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson A. J., Jr, Bindschadler D. D. Pharmacokinetics of intrathecally administered amphotericin B. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Jun;99(6):917–924. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.99.6.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. E. Chemotherapy of systemic mycoses (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 3;290(1):30–32. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401032900107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindschadler D. D., Bennett J. E. A pharmacologic guide to the clinical use of amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):427–436. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block E. R., Bennett J. E., Livoti L. G., Klein W. J., Jr, MacGregor R. R., Henderson L. Flucytosine and amphotericin B: hemodialysis effects on the plasma concentration and clearance. Studies in man. Ann Intern Med. 1974 May;80(5):613–617. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-5-613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. T., Cotlove E. Increased permeability of human erythrocytes induced by amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):341–350. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Spickard A., Rogers D. E., Koenig M. G. Treatment of disseminated mycotic infectioons. A new approach to amphotericin B therapy. Am J Med. 1968 Sep;45(3):405–418. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman H. A., Hamilton J. D., Gutman R. A. Amphotericin B therapy in an anephric patient. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):302–305. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. T., Jr, Bates J. H., Abernathy R. S. Amphotericin B serum concentrations during therapy. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jun;19(6):955–959. doi: 10.1128/am.19.6.955-959.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jusko W. J., Gretch M. Plasma and tissue protein binding of drugs in pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab Rev. 1976;5(1):43–140. doi: 10.3109/03602537608995839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOURIA D. B. Some aspects of the absorption, distribution, and excretion of amphotericin B in man. Antibiotic Med Clin Ther (New York) 1958 May;5(5):295–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. R., Atkinson A. J., Jr, Wellman H. N., Goldsmith R. E. The effect of diphenylhydantoin on thyroxine metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1266–1279. doi: 10.1172/JCI106339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrier D., Gibaldi M. Clearance and biologic half-life as indices of intrinsic hepatic metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Oct;191(1):17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



