Background: Despite the pivotal role of NKCC2 in blood pressure homeostasis, the mechanisms underlying its membrane trafficking remain poor.
Results: Substitutions of 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049 motifs result in ER retention of NKCC2.
Conclusion: NKCC2 surface expression is controlled by multiple di-leucine like motifs.
Significance: Elucidating the molecular mechanisms of the motif-facilitated ER export may help to develop therapeutic strategies targeting NKCC2 transport from the ER to the cell surface.
Keywords: Cell Surface, ER Quality Control, Membrane, Sodium Transport, Trafficking, ER Export, NKCC2
Abstract
Mutations in the apical Na-K-2Cl co-transporter, NKCC2, cause type I Bartter syndrome, a life-threatening kidney disease. Yet the mechanisms underlying the regulation of NKCC2 trafficking in renal cells are scarcely known. We previously showed that naturally occurring mutations depriving NKCC2 of its distal COOH-terminal tail and interfering with the 1081LLV1083 motif result in defects in the ER exit of the co-transporter. Here we show that this motif is necessary but not sufficient for anterograde trafficking of NKCC2. Indeed, we have identified two additional hydrophobic motifs, 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049, that are required for ER exit and surface expression of the co-transporter. Double mutations of 1038LL1039 or 1048LI1049 to di-alanines disrupted glycosylation and cell surface expression of NKCC2, independently of the expression system. Pulse-chase analysis demonstrated that the absence of the terminally glycosylated form of NKCC2 was not due to reduced synthesis or increased rates of degradation of mutant co-transporters, but was instead caused by defects in maturation. Co-immunolocalization experiments revealed that 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 were trapped mainly in the ER as indicated by extensive co-localization with the ER marker calnexin. Remarkably, among several analyzed motifs present in the NKCC2 COOH terminus, only those required for ER exit and surface expression of NKCC2 are evolutionarily conserved in all members of the SLC12A family, a group of cation-chloride co-transporters that are targets of therapeutic drugs and mutated in several human diseases. Based upon these data, we propose abnormal anterograde trafficking as a common mechanism associated with mutations depriving NKCC2, and also all other members of the SLC12A family, of their COOH terminus.
Introduction
The bumetanide-sensitive Na-K-2Cl co-transporter (NKCC2)3 in the apical membrane of thick ascending limb (TAL) cells, is the pacemaker of TAL sodium chloride reabsorption (1). Consequently, the activity of this co-transporter has a strong impact on final urinary salt excretion, consequently influencing long-term blood pressure levels (2). Loss-of-function mutations in the NKCC2 gene, SLC12A1, cause type I Bartter's syndrome (BS1), a life-threatening disease featuring arterial hypotension along with electrolyte abnormalities (3). Opposite to genetic inactivation of NKCC2, enhanced activity of NKCC2 has been linked to salt-sensitive hypertension and hypertensive disorders in humans and in rodent models (4). Moreover, recent studies revealed that rare mutations in the NKCC2 gene protect against hypertension in otherwise healthy individuals in the general population (5–7). NKCC2 activity appears, therefore, to be an important component of the renal machinery controlling Na homeostasis and blood pressure. All these findings emphasize the need to analyze the molecular mechanisms involved in the regulation of NKCC2 to gain insights into the pathophysiology of salt retention. Currently, our knowledge of the molecular mechanisms underlying the regulation of NKCC2 proteins in renal cells remains very poor, mainly because of the difficulty in expressing the co-transporter protein in epithelial cells (8, 9). To completely understand the functional regulation of NKCC2 and to identify novel and effective targets for BS1 or some forms of essential hypertension, we must unveil the molecular determinants underlying membrane trafficking of NKCC2 in a mammalian cell background, and understand how these regulatory factors orchestrate the journey of the co-transporter from the moment of its synthesis until its export to the cell surface.
To function properly, NKCC2 must be correctly targeted to the cell surface and expressed in numbers that allow TAL cells to respond appropriately to physiological or pathological challenges. Similar to other integral membrane proteins, the preparation for appropriate trafficking starts as NKCC2 protein is inserted into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and continues as the protein passes through the Golgi and the trans-Golgi network (10–12). During the journey through the secretory pathway, multiple sorting elements within a single protein are required to achieve delivery to the appropriate cell surface. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER), early in the biosynthetic secretory pathway, acts as an important determinant of the amount of a protein that reaches the plasma membrane (10, 11), whereas the Golgi apparatus acts as a sorting center to direct proteins to the plasma membrane (12, 13). All these processes are dictated by specific targeting signals coded into the amino acid sequence of the protein itself (14, 15). For instance, specific sequence elements for surface expression have been identified for the ionotropic glutamate receptor 2 (16), the inwardly rectifying potassium channel (17, 18) and the dopamine D1 receptor (19). The trafficking elements found in these proteins are required for their efficient ER export. Mutations in the sequences of these sorting signals result in protein retention in the ER without affecting assembly and folding. Moreover, these forward trafficking elements control the steady-state surface density of these proteins in the cell. In contrast to these proteins, very little is known about the molecular determinant of ER export signals and thus cell surface expression of NKCC2. Indeed, so far only one report has dealt with this phenomenon (20). Therefore, it is clear that we have not, so far, even scratch the surface of the regulation of NKCC2 ER export.
NKCC2 belongs to the super family of electroneutral cation-coupled chloride (CCC) co-transporters (SLC12A), which contains nine members in vertebrates (1). They are mainly composed of two Na+-dependent chloride co-transporters (NKCC1 and NKCC2), a Na+-Cl− co-transporter (NCC), four Na+-independent K+-Cl− co-transporters (KCC1, KCC2, KCC3, and KCC4 (2). The CCCs are very similar to one another, sharing 25–75% amino acid identity. They exhibit similar hydropathy profiles with 12 transmembrane domains, an NH2 terminus of variable length, and a long cytoplasmic COOH terminus (2). Both amino and COOH termini of the CCC family face the cytosol. The COOH-terminal domain of these co-transporter proteins is the predominant cytoplasmic region, and therefore it is likely to be a major factor in their intracellular trafficking. In agreement with this notion, several studies have found evidence that residues near the end of the intracellular COOH terminus of Slc12A family members are required for their proper cellular processing. For instance, Sabath et al. (21) found that several COOH-terminal truncation and point mutants in NCC exhibited impaired processing to the plasma membrane. Similarly, Parvin et al (22) showed evidence that truncating the COOH terminus of NKCC1 typically results in recombinant proteins that form intracellular aggregates. More recently, we reported that truncating the distal region of NKCC2 COOH terminus results in ER retention and subsequent loss of cell surface expression (20). Within this distal region, we identified an LLV conserved motif that is required for ER exit and surface expression of NKCC2 (20). Here, we report that this motif is necessary but not sufficient to mediate the ER export of the co-transporter. Indeed, we have now identified two additional highly conserved hydrophobic motifs, 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049, that dictate the ER exit of NKCC2. Loss of these motifs disrupts glycosylation and cell surface expression of NKCC2. Moreover, the high evolutionarily conservation of the two additional hydrophobic motifs among all members of the cation-chloride co-transporter family provides further support of their regulatory role in vivo.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Materials
All chemicals were obtained from Sigma unless otherwise noted. Penicillin and streptomycin were from Invitrogen.
Plasmid Constructions and Site-directed Mutagenesis
The cDNAs encoding mouse NKCC2 were fused at the amino-terminal end of the Myc (Myc-NKCC2). Site-directed mutagenesis method was performed according to the QuickChange protocol (QuickChange Site Directed Mutagenesis Kit; Stratagene) were performed using wild-type Myc-NKCC2 construct as template. Double amino acid mutations to alanines were performed using the following primers: 1)1038LL1039: 5′-cgactgaacgaggccgcacaggaacactccagagccg-3′ (sense) and 5′-cggctctggagtgttcctgtgcggcctcgttcagtcgc-3′ (reverse). 2) 1048LI1049: 5′-cagag ccgccaacgccgccgtgttgagccttccag-3′ (sense) and 5′-ctggaaggctcaacacggcggcgttggcggctctg-3′ (reverse). 3) 1050VL1051: 5′- gccaacctcatcgcggcgagccttccagtggc-3′ (sense) and 5′-gccactggaaggctcgccgcgatgaggttggc-3′ (reverse). 4) 1064LL1065: 5′- caagaaaaggatctatttcggatgcggcgtacatggcgtgga (sense) and 5′-tccacgccatgtacgccgcatccgaaatagatccttttcttg-3′ (reverse). 5) 1072IL1073/AA: 5′-ggcgtggttagaagccgcgaccaagaaccttcctcctg-3′ (sense) and 5′-caggaggaaggttcttggtcgcggcttctaaccacgcc-3′ (reverse). 6) 853KKAG856/AAAG: 5′- cgaggcttgtttgcggcggccggcaagctgaacattacc (sense) and 5′-ggtaatgttcagcttgccggccgccgcaaacaagcctcg-3′(reverse). 7) 866KKDG869/AADG: 5′- caagccagcccccgcggcagacggcaacatcagcag (sense) and 5′-ctgctgatgttgccgtctgccgcgggggctggcttg-3′(reverse). 8) 895KKQK898/AAQG: 5′- cagcgctcagtttaaagcggcgcagggaaaaggcacgattg (sense) and 5′-caatcgtgccttttccctgcgccgctttaaactgagcgctg-3′(reverse). 9) 930KKWK933/AAWK: 5′- cccatatatcttgactctcagagcagcatggaaagattgtaagt (sense) and 5′- acttacaatctttccatgctgctctgagagtcaagatatatggg-3′(reverse). All mutations were confirmed by sequencing.
Cell Culture
Opossum kidney (OKP) cells were grown in DMEM complemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Invitrogen), penicillin (100 units/ml), and streptomycin (100 units/ml) at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. Human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells were maintained in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. For DNA transfection, cells were grown to 60–70% confluence on plastic culture dishes and then were transiently transfected for 5 h with plasmids using the Lipofectamine Plus kit according to the manufacturer's instructions (Invitrogen). For cycloheximide chase experiments, 16 h post-transfection, cycloheximide (20 μg/ml) was added to the culture medium, and cells were harvested at indicated time. Cells for control and experimental groups are always derived from the same flask and passage and studied on the same day.
Protein Preparation, Immunoblotting, and Immunoprecipitation
Forty-eight hours post-transfection, cells were washed three times with cold PBS and lysed in 0.2 or 0.5 ml of lysis buffer (120 mm Tris/Hepes, pH 7.4, 150 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA, 3 mm KCl, 1% (v/v) Triton X-100) containing protease inhibitors (Complete 1697498; Roche Applied Science). Samples were harvested and centrifuged at 16,000 rpm for 15 min at 4 °C. Protein expression levels were assessed after normalizing and loading equal amounts of total protein for 7.5% SDS-PAGE separation and Western blotting with anti-Myc antibodies. For immunoprecipitation, cells were solubilized with lysis buffer containing 0.4 m NaCl, 0.5 mm EGTA, 1.5 mm MgCl2, 10 mm Hepes, pH 7.9, 5% (v/v) glycerol, 0.5% (v/v) Nonidet P-40, and protease inhibitors (Complete; Roche Applied Science). Immunoprecipitation was carried out using anti-Myc antibody followed by affinity purification using protein G-agarose beads (Dynal). After incubation with protein G-agarose beads for 1 h at room temperature, the immunocomplex was washed three times in PBS (Invitrogen). The protein samples were boiled in loading buffer, run on gradient 7.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gels, and probed with primary antibodies of interest and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody, according to standard procedures. Proteins were visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence detection (PerkinElmer Life Sciences), following the manufacturer's instructions.
Immunocytochemistry
Forty-eight hours post-transfection, confluent cells were washed twice with PBS, pH 8, 1 mm MgCl2, and 0.1 mm CaCl2. Cells were incubated at 4 °C for 1 h in PBS2+ (pH 8, 1 mm MgCl2, and 0.1 mm CaCl2), containing 1 mg/ml NHS-biotin. Cells were rinsed three times in rinsing solution with 100 mm glycine and reincubated at 4 °C in the same solution for 10 min. Then they were washed three times with PBS2+. Cells were fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 20 min at room temperature, incubated with 50 mm NH4Cl, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 for 1 min and incubated with DAKO (antibody diluent with background-reducing components) for 30 min to block nonspecific antibody binding. Fixed cells were incubated for 1 h at room temperature with the primary antibodies at the appropriate dilution in DAKO. Mouse anti-Myc, and rabbit anti-calnexin were visualized with Texas Red-coupled secondary antibodies, and fluorescein isothiocyanate-coupled IgG antibodies, respectively. Cells were then washed with PBS and mounted with Vectashield.
Measurement of Intracellular pH and Na-K-2Cl Co-transporter Activity
Measurement of cytoplasmic pH (pHi) was accomplished in cells grown to confluence on coverslips using the intracellularly trapped pH-sensitive dye 2′,7′-bis(carboxyethyl)-5,6-carboxyfluorescein. pHi was estimated from the ratio of fluorescence with excitation wavelengths of 495 and 450 nm and emission wavelength of 530 nm (Horiba Jobin Yvon, Longjumeau, France). Calibration of the 2′,7′-bis (carboxyethyl)-5,6-carboxyfluorescein excitation ratio was accomplished using the nigericin technique. Forty-eight hours post-transfection, Na-K-2Cl cotransport activity was measured as bumetanide-sensitive NH4 influx, as previously described (20, 23, 24). Cells were first bathed at 37 °C in a CO2-free Hepes/Tris-buffered medium containing 135 mm NaCl, 10 mm Hepes (pH 7.4), 5 mm KCl, 1 mm MgCl2, 0.8 mm KH2PO4, 0.2 mm K2HOP4, 1 mm CaCl2, and 10 mm BaCl2 to measure base-line pHi. 20 mm NH4Cl was then added to the medium, inducing a very rapid initial cellular alkalinization followed by a pHi recovery. The initial rate of intracellular pH recovery (dpHi/dt) was measured over the first 20 s of records, as reported earlier (20, 23, 24). The ΔpHi caused by NH4Cl addition was used to calculate the cell buffer capacity, which was not different between the studied groups (data not shown). Therefore, the Na-K-2Cl co-transporter activity is expressed as dpHi/dt.
Pulse-Chase Assays
After 24 h, OKP or HEK 293 cells transiently transfected with plasmid DNA using Lipofectamine reagent (Invitrogen) were incubated in cysteine- and methionine-free DMEM starvation media for 1 h. Starvation medium was removed and replaced with DMEM labeling medium containing [35S]methionine/cysteine labeling mix. After 1 h, cells were rinsed three times with PBS and another three times with normal growth medium and returned to normal growth medium for the duration of chase to the specified time points. Cells were washed twice with ice-cold PBS and incubated on ice for 1 h in lysis buffer with a mixture of protease inhibitors, after which solubilized extracts were collected for immunoprecipitation. Proteins were immunoprecipitated with monoclonal anti-Myc antibody, resolved with SDS-PAGE, blotted onto nitrocellulose, and revealed by autoradiography.
Statistical Analyses
Results are expressed as mean ± S.E. Differences between means were evaluated using paired or unpaired t test or analysis of variance as appropriate. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Identification of Trafficking Signals in NKCC2 COOH-terminal Domain
We previously showed that NKCC2 proteins with the BS1 mutation Y998X, which lack the last 101 amino acids of the cytoplasmic COOH terminus, are retained at the endoplasmic reticulum when expressed in OKP or HEK cells (20). Within this region, we identified an ER exit motif composed of highly conserved residues, required for the maturation and subsequent surface expression of NKCC2 (20). However, besides this motif, other signals in the NKCC2 COOH terminus may also contribute to the trafficking and/or folding of the co-transporter. Consistent with this notion, sequence analysis of the last 101 amino acids revealed that this region of NKCC2 is enriched in di-leucine like motifs; 1038LL1039, 1048LI1049, 1050VL1051, 1064LL1065, and 1072IL1073 motifs (Fig. 1A). These adjacent hydrophobic residues have been reported to function as ER export signals and/or for cell surface targeting for several membrane proteins (25–27). To explore the potential role of these residues in the export of NKCC2 protein from the ER and/or cell surface expression of the co-transporter, we generated a series of mutants in which each di-leucine like motif was individually substituted by di-alanine in the context of full-length NKCC2. Moreover, because the ER quality control mechanism and the capacity of the ER export machinery may depend on the cell type, the study was conducted in two different renal cell lines, OKP and HEK cells. A Myc epitope-tagged wild-type or mutant variants of NKCC2 were transiently transfected into OKP cells and HEK cells, and the degree of protein processing was determined by immunoblot analysis of total proteins. In agreement with our previously published data (20, 23, 24), when wild-type NKCC2 is exogenously expressed in renal cultured cells, both the core (immature) and complex glycosylated (mature) forms are observed (Fig. 1, B and C), the latter being the more abundant (20, 23, 24). As illustrated in Fig. 1B, mutant proteins in which the 1050VL1051, 1064LL1065, or 1072IL1073 motifs had been substituted by alanines (1050AA1051, 1064AA1065, and 1072AA1073), were processed normally in OKP cells (Fig. 1B, lanes 3–5), indicating that these motifs do not play a crucial role in NKCC2 maturation. In contrast, mutation of 1038LL1039 or 1048LI1049 residues to alanines (1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049) eliminated the complex glycosylated (mature form) band (Fig. 1B, lanes 2 and 6). As can be seen in Fig. 1C, similar results were obtained in HEK cells. Taken together, these data indicate that, in addition to the 1081LLV1083 motif (20), 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049 motifs are also required for the normal post-translational processing of NKCC2.
FIGURE 1.
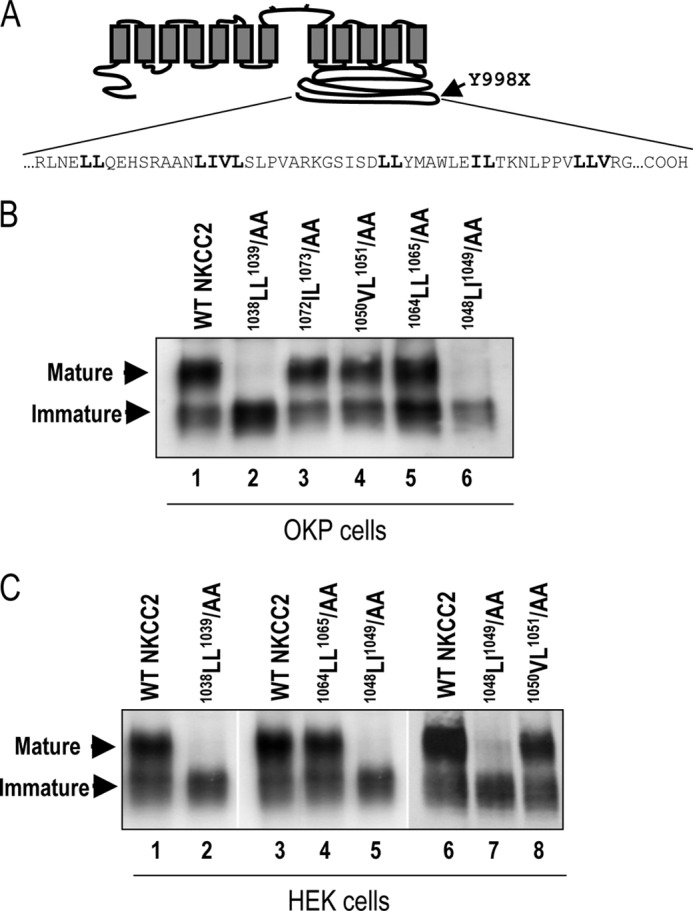
Identification of two additional trafficking signals in NKCC2 COOH-terminal domain. A, predicted topology of NKCC2. The distal region of NKCC2 COOH terminus, downstream from Y998X mutation (indicated by arrow) is enriched of di-leucine like motifs); 1038LL1039, 1048LI1049, 1050VL1051, 1064LL1065, and 1072IL1073. B, immunoblot analysis of OKP cells expressing wild-type or mutant NKCC2 proteins as indicated. Cells were transiently transfected with WT NKCC2 or mutated NKCC2 proteins; 1038AA1039, 1048AA1049, 1050AA1051, 1064AA1065, and 1072AA1073. Forty-eight hours post-transfection, total cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and probed by anti-Myc antibodies. The positions of the core (immature) and complex-glycosylated (mature) proteins are indicated. C, immunoblot analysis of HEK cells expressing wild-type or mutant NKCC2 proteins, as indicated, using anti-Myc antibodies.
Effect of 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 Mutations on NKCC2 Surface Expression
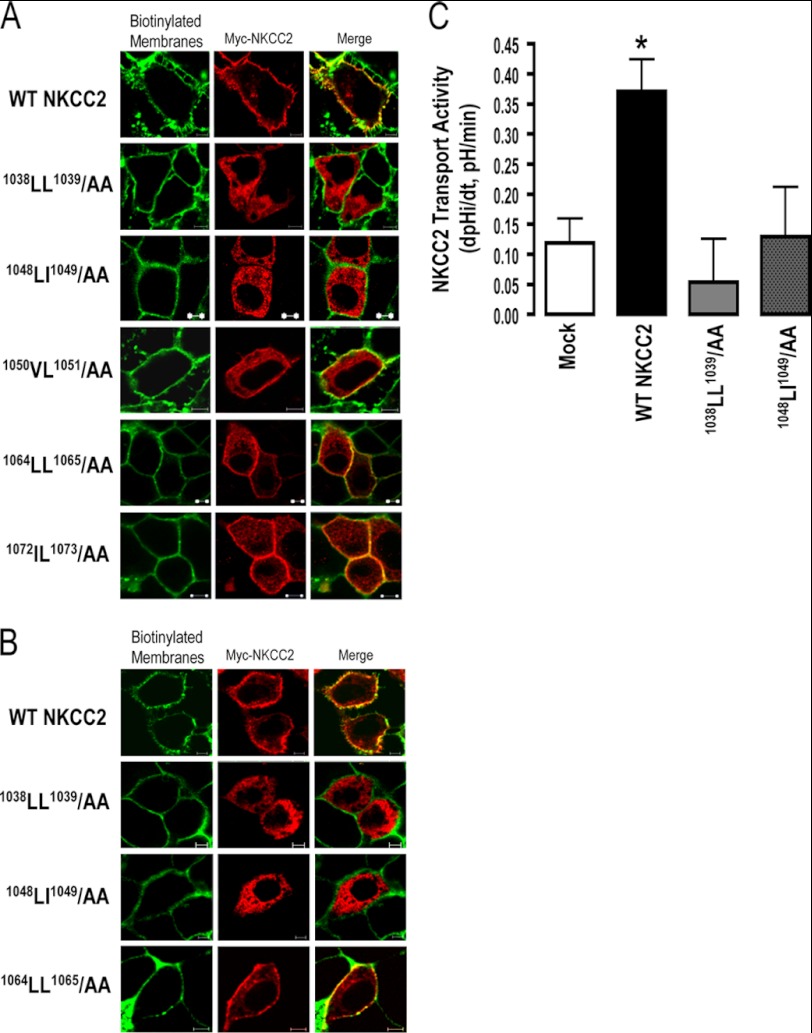
We previously demonstrated that only the complex-glycosylated and mature form of NKCC2 is able to reach the plasma membrane (20, 23). Given the absence of mature NKCC2 forms in cells expressing 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049, one would anticipate that these mutants are not delivered to the cell surface. Hence, we next investigated the effect of 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 mutations on NKCC2 cell surface expression. To this end, we compared the subcellular localization of wild-type NKCC2 and the mutant proteins using cells by immunostaining. Similar to WT NKCC2, immunocytochemistry analysis revealed that the staining of 1050AA1051, 1064AA1065, and 1072AA1073 proteins co-localized with biotinylated cell surface proteins (Fig. 2), indicating correct targeting of NKCC2 to the cell surface. In contrast, OKP cells transfected with 1038AA1039 or 1048AA1049 mutant NKCC2 displayed an immunofluorescence staining pattern that was more restricted to a perinuclear ER-like distribution. Indeed, these cells did not show any colocalization with biotinylated cell-surface proteins, indicating that these mutants were not expressed at the cell surface (Fig. 2A). Again, the effects of 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 mutations on NKCC2 are independent of the expression system given that similar results were obtained in HEK cells (Fig. 2B). On the basis of these data, we concluded that the two di-leucine-like motifs, 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049, are required for normal forward trafficking of mature proteins to the plasma membrane.
FIGURE 2.
1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 proteins are not expressed at the cell surface. Immunolocalization studies of wild-type and mutated NKCC2 proteins. Cells were transiently transfected with Myc-tagged wild-type and mutant NKCC2 proteins, as indicated. Forty-eight hours post-transfection, membrane proteins of confluent OKP cells (A) or HEK cells (B) were biotinylated at 4 °C with the biotinylation reagent sulfo-NHS-SS-biotin. Then the monolayers were fixed and stained for Myc tag NKCC2 protein (Texas red) and cell surface biotin (avidin-Cy2). The stained specimens were evaluated by confocal microscopy. Optical sections (xy) at the cell surface are depicted for Texas red (red) or Cy2 channel (green), and a merged channel. The yellow color (merged image) represents co-localization of NKCC2 with biotinylated membranes, and therefore indicates correct targeting to the cell surface. The white bars represent 5 μm. C, measurement of Na-K-2Cl co-transport activity in OKP cells expressing WT NKCC2 or mutant proteins; 1038LL1039/AA and 1048LI1049/AA. Mean initial rate of pHi recovery (dpHi/dt) from NH4+-induced alkaline load. Each bar represents the mean ± S.E. rates of cell pH recovery (dpHi/dt, pH units/min) under different experimental conditions (mock cells, cells expressing Myc-NKCC2, cells transfected with Myc-1038LL1039/AA and cells transfected with 1048LI1049/AA). *, p < 0.05 versus WT NKCC2 (Mock, n = 7; WT NKCC2, n = 6; 1038LL1039/AA, n = 8 and 1048LI1049/AA, n = 7).
Effect of 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 Mutations on NKCC2 Activity
In light of the action of 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 mutations on the NKCC2 surface level, we sought to determine whether this was associated with changes in NKCC2 co-transport activity. To address this, Na-K+ (NH4+)-2Cl transport activity was assessed by estimating the rate of intracellular acidification caused by entry into the cells of NH4+ via this transport mechanism after abrupt application of NH4Cl to the cells (20, 23, 24). In contrast to WT NKCC2, the NH4+ induced initial rate of pHi recovery in cells transfected with 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 was not significantly different from that of mock cells, indicating that mutants 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 did not express functional co-transporter protein (Fig. 2C). Together with the data illustrated on Fig. 2, A and B, these findings show evidence that 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049 are required for NKCC2 expression at the cell surface.
Localization of 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 Mutants in the ER
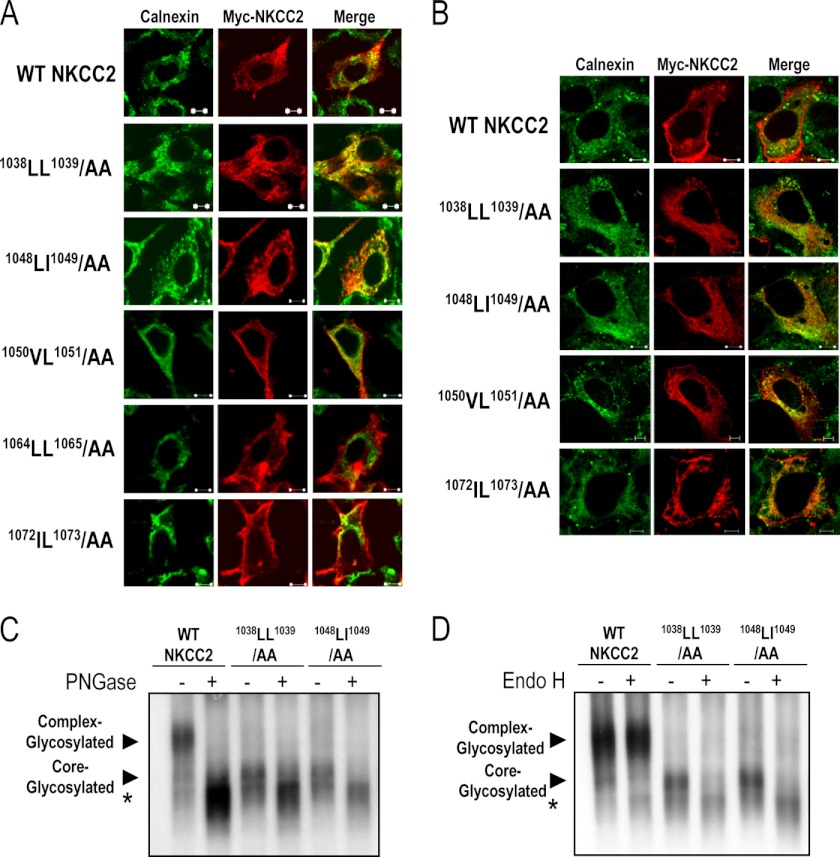
The above data suggest that mutation of 1038LL1039 or 1048LI1049 residues to alanine results in defective processing of NKCC2 from the ER to the Golgi and consequently in the absence of complex-glycosylated protein at the cell surface. On the basis of these observations, one would predict that the 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 mutants are retained in the ER. To test this hypothesis, the subcellular localization of wild-type NKCC2 and mutant NKCC2 proteins was compared with the distribution of calnexin, an ER marker. To this end, WT NKCC2, 1038AA1039, 1048AA1049, 1050AA1051, 1064AA1065, and 1072AA1073 mutants tagged with myc were transiently expressed in HEK293 cells (Fig. 3A) and OKP cells (Fig. 3B), and their subcellular distribution was revealed by microscopy. As anticipated, wild-type NKCC2 was essentially confined to the cell surface. Again, similar to WT NKCC2, 1050AA1051, 1064AA1065, and 1072AA1073 mutants were also localized at the cell surface (Fig. 3, A and B). Hence, for WT NKCC2, 1050AA1051, 1064AA1065, and 1072AA1073 proteins, cell surface expression surrounded the calnexin signal. In contrast, 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 completely lost their cell-surface expression pattern, and were instead confined to the perinuclear region of the transfected cells, with marked co-localization with calnexin (Fig. 3, A and B). In sum, these data indicate that the 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 mutants are largely retained in the ER and that 1038LL1039 and 1048LL1049 motifs are necessary to transport the protein from the ER to the cell surface.
FIGURE 3.
Substitutions of 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049 motifs results in ER retention. Transiently transfected HEK cells (A) or OKP cells (B) with wild-type or mutant NKCC2 proteins, as indicated, were fixed and permeabilized, and then cells were stained with mouse anti-Myc (Texas red; red)) and rabbit anti-calnexin (fluorescein isothiocyanate; green). Yellow, overlap between the Myc tag of NKCC2 protein (green) and the ER marker (red), representing co-localization of the proteins. The white bars represent 5 μm. C and D, glycosidase sensitivity of wild-type NKCC2, 1038LL1039/AA, 1048LI1049/AA proteins expressed in OKP cells. Total cell lysates of OKP cells expressing NKCC2 proteins were incubated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of peptide:N-glycosidase F (PGNase) or endoglycosidase H (Endo H) for 1 h at 37 °C. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and probed by anti-Myc antibodies. The positions of the core (immature) and complex-glycosylated (mature) proteins are indicated. *, non-glycosylated form of NKCC2.
To further confirm that 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 proteins were trapped in the ER, we evaluated their sensitivity to glycosidase digest. Peptide:N-glycosidase F removes all Asn-linked glycans, whereas endoglycosidase-H cleaves N-linked oligosaccharides on high mannose and hybrids (but not complex-type) oligosaccharides making it useful for examining the maturation of NKCC2 proteins as they move through the ER-Golgi compartments. As expected, the complex-glycosylated (mature) form of wild-type NKCC2 was sensitive to peptide:N-glycosidase F but not to endoglycosidase H (Fig. 3, C and D). Similar to the core-glycosylated (immature) form of wild-type NKCC2, 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 were sensitive to both endoglycosidase H and peptide:N-glycosidase F, (Fig. 3, C and D), indicating that 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 mutants were prevented from advancing beyond the ER to acquire endoglycosidase-H resistance. Together with the immunolocalization experiments, these data strengthen our conclusion that 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 mutants were unable to exit the ER.
The Di-leucine-like Motifs, 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049, Are Required for NKCC2 Maturation
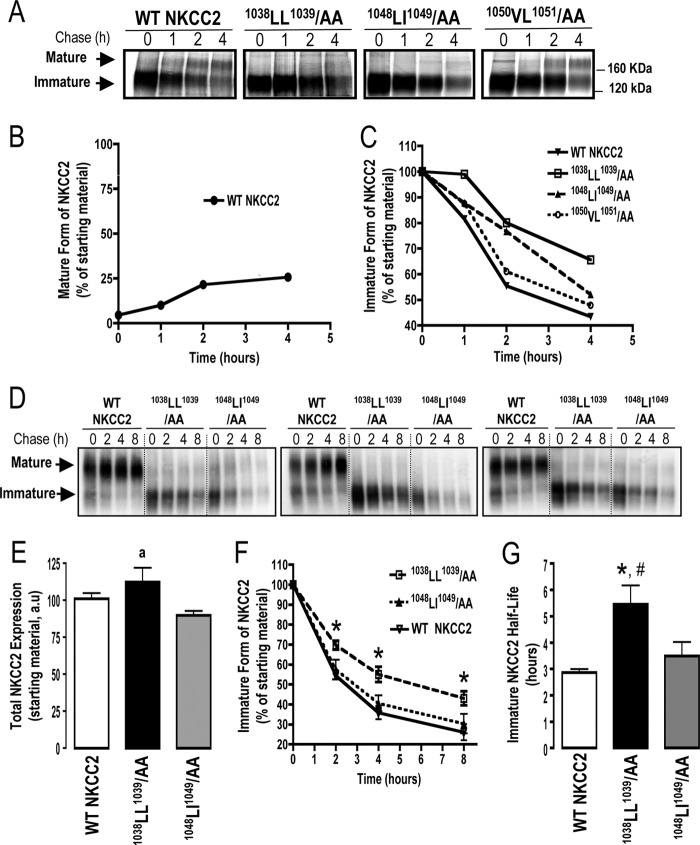
To determine if the ER localization of NKCC2 mutants reflected a defect in maturation, we analyzed the role of the identified di-leucine-like motifs in the stability and biosynthetic processing of NKCC2 by pulse-chase analysis, in which higher molecular mass maturation is marked by Golgi-mediated N-glycosylation of the NKCC2. In these experiments, cells transfected with Myc-tagged wild type or mutated NKCC2 proteins were labeled for 1 h with [35S]methionine/cysteine and chased with unlabeled methionine and cysteine at different time intervals between 1 and 4 h. The wild-type NKCC2 protein was initially synthesized as the core-glycosylated (immature) form, before being gradually converted to the complex-glycosylated (mature) form (Fig. 4A). As shown in Fig. 4B, the fractional conversion of the precursor to the mature form of NKCC2 is only about 26% (25.7 ± 0.1%, n = 3) after a 4 h chase period, implying that a majority of newly synthesized NKCC2 proteins was trapped in the ER and destined for degradation, a process that involves mainly the proteasome pathway (14, 20). These data indicate that the maturation of NKCC2 is a relatively slow and inefficient process and suggest that, similar to several transmembrane proteins (28–31), export from the ER constitutes the limiting step in the maturation and cell surface expression of the cotransporter. In kinetic analysis, the immature form of wild-type NKCC2 protein showed a progressive decrease with an estimated half-life of 3 h (Fig. 4C). Of note, the decrease represents the conversion of the immature to the mature form as well as the degradation of the immature form of NKCC2 protein. As expected, mutation of the 1050VL1051 motif had no obvious effect on NKCC2 maturation (Fig. 4, A and C). In contrast, although the 1038AA1039 and 1048AA1049 proteins were initially synthesized as the ∼120-kDa immature form at a level similar to that of wild-type NKCC2, the conversion to the mature form was barely detectable during the chase period in cells expressing these mutants (Fig. 4A), suggesting that mutations of 1038LL1039 and 1048LL1049 motifs block protein sorting from the ER. Interestingly, extrapolation of the decay curve obtained from the cells expressing NKCC2 mutants (Fig. 4C) yielded an estimated half-life of 4 and 6 h for 1048AA1049 and 1038AA1039, respectively, suggesting differences in their degradation rates. To corroborate these observations, we used the cycloheximide decay assay, as a second approach, to assess the half-life of the immature form of NKCC2. To this end, 16 h post-transfection, cycloheximide was added to block protein synthesis, and at various times after addition of cycloheximide, NKCC2 levels were monitored by Western blot. It is worth nothing that at the start of the chase period (t = 0), total NKCC2 protein levels were comparable between the three studied groups (Fig. 4, D and E), clearly confirming that a defect in protein expression is not responsible for the lack of cell surface targeting and transport activity observed at 48 h post-transfection in cells expressing 1048AA1049 and 1038AA1039 mutants (Figs. 2 and 3). In kinetic analysis, the immature form of wild-type NKCC2 protein displayed a progressive decline with a half-life of 2.9 h (2.9 ± 0.1 h, n = 6), which is in agreement with the pulse-chase analysis described above. As shown in Fig. 4, F and G, the half-life of the 1048AA1049 mutant (3.5 ± 0.5 h, n = 6) was not significantly different from that of immature WT NKCC2. In contrast to 1048AA1049, the 1038AA1039 mutant had, again, a slower rate of decay at different time points during the chase period (Fig. 4, F and G), with an estimated half-life of 5.5 h (5.5 ± 0.7 h, n = 6). Altogether, these data demonstrate that mutations of 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049 motifs clearly disrupt transport from the ER, thereby leading to a lack of cell surface expression and activity. Moreover, they indicate that whereas the two NKCC2 mutants fail to exit the ER, their distinct half-lives suggest that different mechanisms are involved in their ER-associated degradation.
FIGURE 4.
Mutations of 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049 motifs impair maturation of the co-transporter. A, pulse-chase analysis of wild-type and mutant NKCC2 proteins. 24 h post-transfection, OKP cells were metabolically labeled with [35S]methionine and [35S]cysteine for 1 h and chased with unlabeled methionine and cysteine for the indicated times. Proteins were then isolated by immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc antibodies, run on SDS-polyacrylamide gels, and revealed by autoradiography. B, time course of the appearance of mature WT NKCC2, the results are presented as relative intensity. C, quantitative analysis of immature WT NKCC2, 1038LL1039/AA, 1048LI1049/AA, and 1050VL1051 proteins was performed, and the results are presented as relative intensity. D, cycloheximide chase analysis of wild-type and mutant NKCC2 proteins. 16 h post-transfection, OKP cells transiently expressing WT NKCC2 or mutant proteins; 1038LL1039/AA and 1048LI1049/AA, were chased for the indicated time after addition of cycloheximide. Total cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and probed by anti-Myc antibodies. E, expression of total NKCC2 protein at the start of the chase period (t = 0). Each bar represents mean ± S.E. from six independent experiments. a, p = 0.064, versus WT NKCC2 and 1048LI1049/AA. F, time-dependent changes in the density of WT and mutated NKCC2 proteins. The density of the immature form of NKCC2 proteins was normalized to the density at time 0. Each point represents mean ± S.E. from six independent experiments, *, p < 0.05, versus WT NKCC2 and 1048LI1049/AA. G, bar graph shows the half-lives of wild-type and mutated NKCC2 proteins. Each bar represents mean ± S.E. from six independent experiments. *, p < 0.01 versus WT NKCC2. #, p < 0.05 versus 1048LI1049/AA.
Effect of Mutation of KKXX Motifs Present in NKCC2 C Terminus
The significance of our findings is that they indicate that naturally occurring BS1 mutations, such as Y998X and N984fs (32, 33), which deprive NKCC2 of its distal COOH-terminal tail and thus interfere with the previously reported 1081LLV1083 motif (20), and the two additional 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049 motifs identified in the present report, result in defects in the ER exit of the co-transporter. Altogether, our findings suggest that the last 101 AA of COOH terminus is an essential determinant of the ER export of NKCC2. However, one alternative explanation is that the role of the distal region of NKCC2 COOH terminus is to mask an ER retention signal present upstream from the Y998X mutation, which becomes exposed when BS1 mutations truncate the NKCC2 COOH terminus. To date, two well-characterized retention/retrieval signals, RXR and KKXX, have been found in the cytoplasmic tail of several transmembrane proteins (34–37). The RXR motif is not present in the NKCC2 COOH terminus. Moreover, although several KKXX motifs are present upstream from the Y998X mutation, the two-lysine residues of these motifs are not located at the third and fourth positions from the COOH terminus, and therefore are unlikely to be effective in ER retention (34, 35). To confirm this, we generated a series of mutants in which each the two-lysine residues of each motif was substituted by di-alanine in wild-type NKCC2 and mutant proteins; Y998X, 1038LL1039/AA, 1048LI1049/AA, and 1081LLV1083/AAA. As shown in Fig. 5A, mutating the 930KKWK933 motif, the closest KKXX motif to the end of COOH terminus, had no effect on WT NKCC2 processing, and failed to rescue the expression of complex-glycosylated forms of Y998X, 1038LL1039/AA, 1048LI1049/AA, and 1081LLV1083/AAA proteins. Likewise, mutations of the two-lysine residues of 853KKAG856, 866KKDG869, and 895KKQK898 motifs did not restore, even partially, the expression of complex-glycosylated form of the mutant proteins (Fig. 5B). Taken together, these findings suggest that the defect in protein maturation and ER exit is unlikely to be due to the exposure of an ER retention signal in mutated NKCC2 proteins.
FIGURE 5.
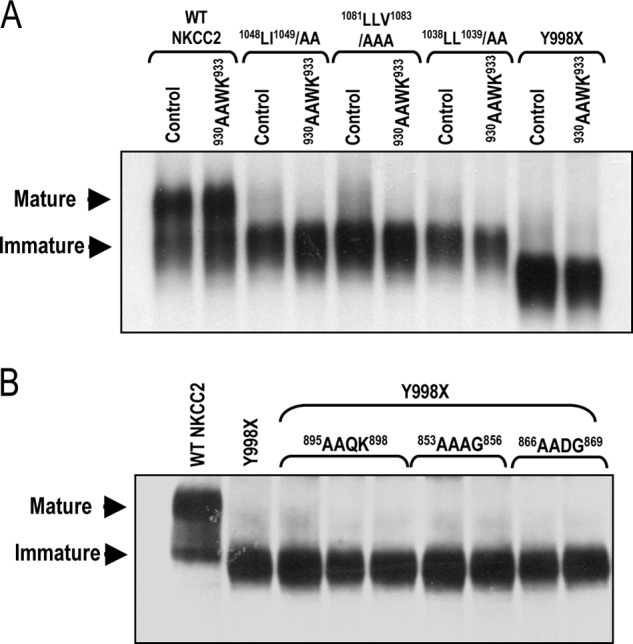
Mutations of KKXX motifs have no effect on NKCC2 maturation. Immunoblot analysis of OKP (A) cells or HEK cells (B) expressing wild-type or mutant NKCC2 proteins. Cells were transiently transfected with wild-type NKCC2 or mutated NKCC2 proteins, as indicated. Total cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and probed by anti-Myc antibodies. The positions of the core (immature) and complex-glycosylated (mature) proteins are indicated.
Hydrophobic 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049 Motifs Are Highly Conserved in the COOH-terminal Tails of Cation Chloride Co-transporters
Amino acid residues, which play important roles in protein function, are often conserved. Consistent with this, we previously showed the trihydrophobic motif 1081LLV1083, required for the maturation and subsequent surface expression of NKCC2, is highly conserved (20). Thus, we sought to examine whether the two di-leucine like motifs identified in the present study were also conserved among the members of the CCC family. As shown in Fig. 6, the result revealed that the identity of each hydrophobic motif was fully conserved, or replaced with a di-leucine like/hydrophobic motif composed of valine and/or isoleucine residues, in the COOH-terminal tails of all members of the cation-chloride co-transporter family. Importantly, the two hydrophobic motifs were highly conserved not only between isoforms, but also during evolution. In contrast, 1050VL1051, 1064LL1065, and 1072IL1073 motifs, which are not indispensable for ER exit and surface expression for NKCC2 were much less conserved. Taken in concert, these data lend further support to the role of 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049 motifs in vivo, and strongly suggest that they may function as a common ER export signal for the cation chloride co-transporters.
FIGURE 6.
1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049 motifs are highly conserved. Sequence alignment of the COOH-terminal amino acids of mouse NKCC2 (amino acids 1134–1077) with those of other representative members of the SlcA12 family. All di-leucine like motifs analyzed in the present study are indicated in bold. Evolutionarily conserved di-leucine like motifs are indicated in green. See “Results” for additional details.
DISCUSSION
We have reported previously that the 1081LLV1083 hydrophobic motif within the COOH terminus of NKCC2 is required for its export from the ER (20), its maturation and its subsequent surface expression. Here, we identified two other motifs, 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049, that are required for export of NKCC2 from the ER. Mutation of 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049 to di-alanine results in expression of an immature protein that colocalizes in the ER with the chaperone protein, calnexin. We demonstrated that these residues are necessary for the exit of NKCC2 co-transporters from the ER. In contrast, di-leucine-like motifs 1050VL1051, 1064LL1065, and 1072IL1073 had no influence on this process indicating the existence of specific elements regulating the transport of NKCC2 protein from the ER.
The efficient sorting of membrane proteins to a variety of post-Golgi destinations is controlled by sorting motifs, which are short specific sequences in the protein cytoplasmic domain (38, 39). One type of signals is the so-called di-leucine/dihydrophobic motifs, in which one of the leucines can be replaced by isoleucine or valine, without loss of function (39–42). This motif has been shown earlier to mediate sorting in the TGN and targeting to endosomes and lysosomes or internalization from the plasma membrane (39, 41, 42). More recently, there have been several reports indicating that di-leucine like motifs, in particular when present in the COOH terminus, are also important for protein exit from the ER (25–27, 43). For instance, a role in protein transport from the ER to the plasma membrane was found for a COOH-terminal di-leucine motif in the case of vasopressin V2 (44) and 5-HT serotonin receptors (45). Likewise, we recently showed that an LLV/LLI motif present in the COOH-terminal tail of the kidney cation-chloride co-transporters, NKCC2 and NCC, are required for their ER exit and cell surface expression (20). Nezu et al. (46) also demonstrated that the same motif is indispensable for the ER exit of NKCC1. Here, we provide evidence for the presence of two additional di-leucine like motifs in NKCC2 COOH terminus that are required for ER exit of NKCC2. Indeed, independent di-alanine mutagenesis of either locus induced ER trapping of the co-transporter protein. 1038LL1039, 1048LI1049, and 1081LLV1083 motifs could coordinate together and/or with multiple regions of the COOH-terminal domain in addition to the distal region to promote NKCC2 ER sorting. However, one cannot rule out the possibility that these motifs act independently to promote protein sorting. With this regard, Kasai et al (47) reported that syntaxin 8 has two functionally distinct di-leucine-based motifs in its cytoplasmic domain that act independently in its protein sorting. Furthermore, the 1038LL1039, 1048LI1049, and 1081LLV1083 motifs may dictate distinct steps involved in NKCC2 export from the ER. Further studies are needed to better characterize these three di-leucine-based motifs and to better delineate the steps of the intracellular trafficking of NKCC2 in which these signals are involved.
In principle, the retention of NKCC2 protein in the ER can be due to at least three possibilities. The first possibility is the exposure of cryptic ER retention motifs in mutated proteins. For instance, Kupershmidt et al (48) reported that a key function of the COOH-terminal 104 amino acids of HERG is to mask an ER retention signal, which becomes exposed when mutations truncate the HERG COOH terminus. In the same way, BS1 mutations Y998X, which deprive NKCC2 of its COOH-terminal 101 amino acids containing the 1038LL1039, 1048LI1049, and 1081LLV1083 motifs, could retain the co-transporter in ER by exposing a retention signal normally masked in intact NKCC2 protein. However, sequence analysis did not reveal the presence of potentially functional ER retention signals, such as RXR, and KKXX motifs or KXKXX motifs (34–37) in the NKCC2 COOH terminus, suggesting that the exposure of an ER retention signal in the mutated protein is very unlikely to explain the defect in the co-transporter processing. The second possibility is that defective interactions between the di-leucine-like based motifs and components of the ER sorting machinery caused by di-alanine mutations were actually responsible for ER retention. The 1038LL1039, 1048LI1049, and 1081LLV1083 motifs may indeed belong to the family of adjacent bulky hydrophobic ER export signals (25, 26, 43). In this regard, all our attempts using co-immunoprecipitation have failed so far to detect an interaction in HEK cells, between wild-type NKCC2 and endogenously expressed Sec24 A-D, components of the COPII coat (49, 50) (data not shown). Similarly, Zhang et al (51) failed to detect the interaction between Sec24 and AT2R either by coimmunoprecipitation from cells transiently expressing both AT2R and Sec24 or by AT2R COOH-terminal glutathione S-transferase fusion protein pull-down assay. Moreover, although binding of the COPII Sec24 to the cytosolic tail of integral membrane proteins has been demonstrated, only weak interactions were reported (49, 52, 53). It is also worth mentioning that while it was initially thought that exit from the ER absolutely required COPII components, recent work has revealed that there is an increasing number of proteins that leave the ER in the absence of functioning COPII coat components (54–57). Hence, it remains to be clarified whether the COPII machinery plays a pivotal role in the ER exit of NKCC2. Moreover, the 1038LL1039, 1048LI1049, and 1081LLV1083 motifs may also provide interactive sites mediating the interaction of the co-transporter with selective and specific proteins, such as KChlPI for the Kv4 potassium channel (57), RAMP for the calcitonin receptor-like receptor (58) and RanBP2 for opsin (59), so as to facilitate their transport from the ER to the cell surface. Finally, one cannot discount the possibility that a folding defect in mutant NKCC2 is recognized by the ER quality control, leading therefore to the retention of the co-transporter in the ER. Interestingly, our pulse-chase and cycloheximide decay experiments revealed that 1038LL1039/AA and 1048LI1049/AA mutants have distinct protein half-lives. This difference in the rates of protein degradation may stem from the nature of the specific folding defects associated with each individual protein (60). Therefore, the fate of mutant forms of NKCC2 is presumably determined by subtle differences in folding that direct it to distinct machinery for ER associated degradation. However, based only on their rates of degradation, one cannot predict the degree of misfolding caused by 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049 mutations. Indeed, it was documented that some misfolded and unassembled proteins in the ER may have prolonged half-lives of more than 6–10 h (29, 61). In contrast, in the case of the delta subunit of the T cell receptor, the degradation of the protein in the ER is much faster (62). Likewise, whereas the mutation of the di-acidic ER export motif causes enhanced protein degradation of CFTR (63), mutating the COOH-terminal valine, another ER exit code, leads, in contrast, to a stabilization of Pmel17 protein (64). Whether our NKCC2 mutants are mainly conformation mutants, like the cystic fibrosis ΔF508 mutants (63), as opposed to relatively “pure” sorting mutants, similar to DAA for CFTR (63), remains to be determined. A complete understanding of the mechanisms by which the 1038LL1039, 1048LI1049 and 1081LLV1083 motifs control ER export of NKCC2 will be possible only with elucidation of the structure of the COOH terminus and identification of the proteins that bind to this part of the molecule. Nevertheless, regardless of the mechanisms underlying the inability of NKCC2 mutants to exit the ER, our results provide evidence that besides the 1081LLV1083 motif, the 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049 motifs are crucial determinants of NKCC2 forward trafficking to the cell surface.
Remarkably, similar to the 1081LLV1083 motif (20), the two di-leucine-like motifs, 1038LL1039 and 1048LI1049, are highly conserved in the COOH-terminal tails of all members of the cation chloride co-transporter family. Indeed, all three motifs are present in all members of the CCC transporters and are evolutionarily conserved from insect to human homologs. In contrast, all other analyzed di-leucine like motifs of NKCC2 COOH terminus, which are not indispensable for ER exit of the co-transporter, are not highly conserved. Likewise, the KKXX motifs that had no effect on NKCC2 maturation are not conserved among the members of the CCC family (data not shown). Taken together, all these findings further support the role the highly conserved hydrophobic 1081LLV1083, 1038LL1039, and 1048LI1049 motifs in the regulation of surface expression of NKCC2. Indeed, conservation analysis is one of the most widely used methods for predicting functionally important residues in protein sequences (65). Using this predictive and powerful approach, recent studies revealed that rare mutations in SLC12A1 and SLC12A3 protect against hypertension by reducing the activity of renal salt co-transporters NKCC2 and NCC, respectively (5–7). Hence, given the high conservation of the 1081LLV1083, 1038LL1039, and 1048LI1049 motifs, it is tempting to speculate that similar mechanisms govern the ER exit of the different members of the Slc12A family. This is of particular interest since members of the CCC family are known to play important roles in numerous physiological processes and are mutated in several human diseases such as Bartter, Gitelman, and Anderman syndromes (2, 66, 67). Consequently, these findings raise the possibility that loss of these conserved motifs may contribute to the generation of several diseases related not only to kidney functions, but also to processes in which the other CCC family members are involved, such as exocrine fluid secretion, hearing, olfaction, spermatogenesis, pain perception, visual processing, and other neuronal functions (2, 66–70).
In conclusion, our results reveal that sorting of NKCC2 protein from ER and expression at the cell surface are controlled by multiple di-leucine-like motifs located within the cytoplasmic tail of the co-transporter. It is now common knowledge that a number of human genetic diseases are attributable to perturbations in the sub-cellular trafficking of transport proteins (71). Therefore, elucidating the molecular basis of defects in trafficking and processing of NKCC2 may provide a helpful tool to illuminate completely new and unanticipated signals and pathways in the regulation not only of NKCC2, but also of all members of the SLC12 family. The exact characterization and identification of the molecular mechanisms underlying the targeting defect of the CCC co-transporters may provide a foundation for the development of therapeutic strategies by designing specific drugs to treat at least some of the symptoms that arise from their dysfunction.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Alain Doucet and Aurélie Edwards for helpful discussions and careful reading of the manuscript. We also thank Dr. Randy Schekman (University of California, Berkeley) for the kind gift of anti-SEC24 A–D antibodies.
This work was supported by grants from INSERM, Paris, France.
- NKCC2
- Na-K-2Cl co-transporter
- TAL
- thick ascending limb
- CCC
- cation chloride co-transporter
- OKP
- opossum kidney
- Aa
- amino acid(s)
- NCC
- Na-Cl co-transporter
- ER
- endoplasmic reticulum
- BS1
- Bartter syndrome type 1
- HEK
- human embryonic kidney
- pHi
- cytoplasmic pH
- NHS
- N-hydroxysuccinimide.
REFERENCES
- 1. Russell J. (2000) Sodium-potassium-chloride cotransport. Physiol. Rev. 80, 211–276 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Gamba G. (2005) Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of electroneutral cation-chloride cotransporters. Physiol. Rev. 85, 423–493 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Simon D. B., Karet F. E., Hamdan J. M., DiPietro A., Sanjad S. A., Lifton R. P. (1996) Bartter's syndrome, hypokalaemic alkalosis with hypercalciuria, is caused by mutations in the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter NKCC2. Nat. Genet. 13, 183–188 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Ares G. R., Caceres P. S., Ortiz P. A. (2011) Molecular regulation of NKCC2 in the thick ascending limb. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 301, F1143–F1159 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Monette M. Y., Rinehart J., Lifton R. P., Forbush B. (2011) Rare mutations in the human Na-K-Cl cotransporter (NKCC2) associated with lower blood pressure exhibit impaired processing and transport function. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 300, F840–F847 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Ji W., Foo J. N., O'Roak B. J., Zhao H., Larson M. G., Simon D. B., Newton-Cheh C., State M. W., Levy D., Lifton R. P. (2008) Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation. Nat. Genet. 40, 592–599 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Acuna R., Martinez-de-la-Maza L., Ponce-Coria J., Vazquez N., Ortal-Vite P., Pacheco-Alvarez D., Bobadilla N. A., Gamba G. (2011) J. Hypertens. 29, 475–483 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Isenring P., Jacoby S. C., Payne J. A., Forbush B., 3rd. (1998) Comparison of Na-K-Cl cotransporters. NKCC1, NKCC2, and the HEK cell Na-L-Cl cotransporter. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 11295–11301 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Mount D. B. (2006) Membrane trafficking and the regulation of NKCC2. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 290, F606–607 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Vitale A., Denecke J. (1999) The endoplasmic reticulum-gateway of the secretory pathway Plant Cell 11, 615–628 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Yeaman C., Grindstaff K. K., Nelson W. J. (1999) New perspectives on mechanisms involved in generating epithelial cell polarity. Physiol. Rev. 79, 73–98 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Caplan M. J. (1997) Membrane polarity in epithelial cells: protein sorting and establishment of polarized domains. Am. J. Physiol. 272, F425–F429 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Ellgaard L., Molinari M., Helenius A. (1999) Setting the standards: quality control in the secretory pathway. Science 286, 1882–1888 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Ellgaard L., Helenius A. (2003) Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 181–191 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Muth T. R., Caplan M. J. (2003) Transport protein trafficking in polarized cells. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 19, 333–366 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Kalandadze A., Wu Y., Fournier K., Robinson M. B. (2004) Identification of motifs involved in endoplasmic reticulum retention-forward trafficking of the GLT-1 subtype of glutamate transporter. J. Neurosci. 24, 5183–5192 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Ma D., Zerangue N., Lin Y. F., Collins A., Yu M., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. (2001) Role of ER export signals in controlling surface potassium channel numbers. Science 291, 316–319 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Zerangue N., Schwappach B., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. (1999) A new ER trafficking signal regulates the subunit stoichiometry of plasma membrane K(ATP) channels. Neuron 22, 537–548 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Bermak J. C., Li M., Bullock C., Zhou Q. Y. (2001) Regulation of transport of the dopamine D1 receptor by a new membrane-associated ER protein. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 492–498 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Zaarour N., Demaretz S., Defontaine N., Mordasini D., Laghmani K. (2009) A highly conserved motif at the COOH terminus dictates endoplasmic reticulum exit and cell surface expression of NKCC2. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 21752–21764 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Sabath E., Meade P., Berkman J., de los Heros P., Moreno E., Bobadilla N. A., Vázquez N., Ellison D. H., Gamba G. (2004) Pathophysiology of functional mutations of the thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter in Gitelman disease. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 287, F195–203 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Parvin M. N., Gerelsaikhan T., Turner R. J. (2007) Regions in the cytosolic C-terminus of the secretory Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl(-) cotransporter NKCC1 are required for its homodimerization. Biochemistry 46, 9630–9637 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Benziane B., Demaretz S., Defontaine N., Zaarour N., Cheval L., Bourgeois S., Klein C., Froissart M., Blanchard A., Paillard M., Gamba G., Houillier P., Laghmani K. (2007) NKCC2 surface expression in mammalian cells: down-regulation by novel interaction with aldolase B. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 33817–33830 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Zaarour N., Defontaine N., Demaretz S., Azroyan A., Cheval L., Laghmani K. (2011) Secretory carrier membrane protein 2 regulates exocytic insertion of NKCC2 into the cell membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 9489–9502 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Dong C., Filipeanu C. M., Duvernay M. T., Wu G. (2007) Regulation of G protein-coupled receptor export trafficking. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1768, 853–870 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Ren X. Q., Cheng S. B., Treuil M. W., Mukherjee J., Rao J., Braunewell K. H., Lindstrom J. M., Anand R. (2005) Structural determinants of α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor trafficking. J. Neurosci. 25, 6676–6686 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Bello V., Goding J. W., Greengrass V., Sali A., Dubljevic V., Lenoir C., Trugnan G., Maurice M. (2001) Characterization of a di-leucine-based signal in the cytoplasmic tail of the nucleotide-pyrophosphatase NPP1 that mediates basolateral targeting but not endocytosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 12, 3004–3015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Pietilä E. M., Tuusa J. T., Apaja P. M., Aatsinki J. T., Hakalahti A. E., Rajaniemi H. J., Petäjä-Repo U. E. (2005) Inefficient maturation of the rat luteinizing hormone receptor. A putative way to regulate receptor numbers at the cell surface. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 26622–26629 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Hurtley S. M., Helenius A. (1989) Protein oligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 5, 277–307 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Petaja-Repo U. E., Hogue M., Laperriere A., Walker P., Bouvier M. (2000) Export from the endoplasmic reticulum represents the limiting step in the maturation and cell surface expression of the human delta opioid receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 13727–13736 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Valentijn J. A., Fyfe G. K., Canessa C. M. (1998) Biosynthesis and processing of epithelial sodium channels in Xenopus oocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 30344–30351 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Adachi M., Asakura Y., Sato Y., Tajima T., Nakajima T., Yamamoto T., Fujieda K. (2007) Novel SLC12A1 (NKCC2) mutations in two families with Bartter syndrome type 1. Endocr. J. 54, 1003–1007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Vargas-Poussou R., Feldmann D., Vollmer M., Konrad M., Kelly L., van den Heuvel L. P., Tebourbi L., Brandis M., Karolyi L., Hebert S. C., Lemmink H. H., Deschênes G., Hildebrandt F., Seyberth H. W., Guay-Woodford L. M., Knoers N. V., Antignac C. (1998) Novel molecular variants of the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter gene are responsible for antenatal Bartter syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 62, 1332–1340 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Shin J., Dunbrack R. L., Jr., Lee S., Strominger J. L. (1991) Signals for retention of transmembrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum studied with CD4 truncation mutants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 1918–1922 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Vincent M. J., Martin A. S., Compans R. W. (1998) Function of the KKXX motif in endoplasmic reticulum retrieval of a transmembrane protein depends on the length and structure of the cytoplasmic domain. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 950–956 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Gassmann M., Haller C., Stoll Y., Abdel Aziz S., Biermann B., Mosbacher J., Kaupmann K., Bettler B. (2005) The RXR-type endoplasmic reticulum-retention/retrieval signal of GABAB1 requires distant spacing from the membrane to function. Mol. Pharmacol. 68, 137–144 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Ma D., Jan L. Y. (2002) ER transport signals and trafficking of potassium channels and receptors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 12, 287–292 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Trowbridge I. S., Collawn J. F., Hopkins C. R. (1993) Signal-dependent membrane protein trafficking in the endocytic pathway. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 9, 129–161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Sandoval I. V., Arredondo J. J., Alcalde J., Gonzalez Noriega A., Vandekerckhove J., Jimenez M. A., Rico M. (1994) The residues Leu(Ile)475-Ile(Leu, Val, Ala)476, contained in the extended carboxyl cytoplasmic tail, are critical for targeting of the resident lysosomal membrane protein LIMP II to lysosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 6622–6631 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Valdenaire O., Barret A., Schweizer A., Rohrbacher E., Mongiat F., Pinet F., Corvol P., Tougard C. (1999) Two di-leucine-based motifs account for the different subcellular localizations of the human endothelin-converting enzyme (ECE-1) isoforms. J. Cell Sci. 112, 3115–3125 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. (1992) A novel di-leucine motif and a tyrosine-based motif independently mediate lysosomal targeting and endocytosis of CD3 chains. Cell 69, 1143–1157 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Pond L., Kuhn L. A., Teyton L., Schutze M. P., Tainer J. A., Jackson M. R., Peterson P. A. (1995) A role for acidic residues in di-leucine motif-based targeting to the endocytic pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 19989–19997 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Nufer O., Guldbrandsen S., Degen M., Kappeler F., Paccaud J. P., Tani K., Hauri H. P. (2002) Role of cytoplasmic C-terminal amino acids of membrane proteins in ER export. J. Cell Sci. 115, 619–628 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Schülein R., Hermosilla R., Oksche A., Dehe M., Wiesner B., Krause G., Rosenthal W. (1998) A dileucine sequence and an upstream glutamate residue in the intracellular carboxyl terminus of the vasopressin V2 receptor are essential for cell surface transport in COS.M6 cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 54, 525–535 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Carrel D., Hamon M., Darmon M. (2006) Role of the C-terminal di-leucine motif of 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B serotonin receptors in plasma membrane targeting. J. Cell Sci. 119, 4276–4284 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Nezu A., Parvin M. N., Turner R. J. (2009) A conserved hydrophobic tetrad near the C terminus of the secretory Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter (NKCC1) is required for its correct intracellular processing. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 6869–6876 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Kasai K., Suga K., Izumi T., Akagawa K. (2008) Syntaxin 8 has two functionally distinct di-leucine-based motifs. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 13, 144–154 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Kupershmidt S., Yang T., Chanthaphaychith S., Wang Z., Towbin J. A., Roden D. M. (2002) Defective human Ether-à-go-go-related gene trafficking linked to an endoplasmic reticulum retention signal in the C terminus. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 27442–27448 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Miller E. A., Beilharz T. H., Malkus P. N., Lee M. C., Hamamoto S., Orci L., Schekman R. (2003) Multiple cargo binding sites on the COPII subunit Sec24p ensure capture of diverse membrane proteins into transport vesicles. Cell 114, 497–509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Wendeler M. W., Paccaud J. P., Hauri H. P. (2007) Role of Sec24 isoforms in selective export of membrane proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO Rep. 8, 258–264 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Zhang X., Dong C., Wu Q. J., Balch W. E., Wu G. (2011) Di-acidic motifs in the membrane-distal C termini modulate the transport of angiotensin II receptors from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell surface. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 20525–20535 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Mossessova E., Bickford L. C., Goldberg J. (2003) SNARE selectivity of the COPII coat. Cell 114, 483–495 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Wang X., Matteson J., An Y., Moyer B., Yoo J. S., Bannykh S., Wilson I. A., Riordan J. R., Balch W. E. (2004) COPII-dependent export of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator from the ER uses a di-acidic exit code. J. Cell Biol. 167, 65–74 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Reiterer V., Maier S., Sitte H. H., Kriz A., Rüegg M. A., Hauri H. P., Freissmuth M., Farhan H. (2008) Sec24- and ARFGAP1-dependent trafficking of GABA transporter-1 is a prerequisite for correct axonal targeting. J. Neurosci. 28, 12453–12464 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Schepetilnikov M. V., Manske U., Solovyev A. G., Zamyatnin A. A., Jr., Schiemann J., Morozov S. Y. (2005) The hydrophobic segment of Potato virus X TGBp3 is a major determinant of the protein intracellular trafficking. J. Gen. Virol. 86, 2379–2391 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Nickel W., Seedorf M. (2008) Unconventional mechanisms of protein transport to the cell surface of eukaryotic cells. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 24, 287–308 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Hasdemir B., Fitzgerald D. J., Prior I. A., Tepikin A. V., Burgoyne R. D. (2005) Traffic of Kv4 K+ channels mediated by KChIP1 is via a novel post-ER vesicular pathway. J. Cell Biol. 171, 459–469 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. McLatchie L. M., Fraser N. J., Main M. J., Wise A., Brown J., Thompson N., Solari R., Lee M. G., Foord S. M. (1998) RAMPs regulate the transport and ligand specificity of the calcitonin-receptor-like receptor. Nature 393, 333–339 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Ferreira P. A., Nakayama T. A., Pak W. L., Travis G. H. (1996) Cyclophilin-related protein RanBP2 acts as chaperone for red/green opsin. Nature 383, 637–640 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Brodsky J. L. (2007) The protective and destructive roles played by molecular chaperones during ERAD (endoplasmic-reticulum-associated degradation). Biochem. J. 404, 353–363 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Li P., Ninomiya H., Kurata Y., Kato M., Miake J., Yamamoto Y., Igawa O., Nakai A., Higaki K., Toyoda F., Wu J., Horie M., Matsuura H., Yoshida A., Shirayoshi Y., Hiraoka M., Hisatome I. (2011) Reciprocal control of hERG stability by Hsp70 and Hsc70 with implication for restoration of LQT2 mutant stability. Circ. Res. 108, 458–468 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bonifacino J. S., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. (1988) Degradation from the endoplasmic reticulum: disposing of newly synthesized proteins. Cell 54, 209–220 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Roy G., Chalfin E. M., Saxena A., Wang X. (2010) Interplay between ER exit code and domain conformation in CFTR misprocessing and rescue. Mol. Biol. Cell 21, 597–609 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Theos A. C., Berson J. F., Theos S. C., Herman K. E., Harper D. C., Tenza D., Sviderskaya E. V., Lamoreux M. L., Bennett D. C., Raposo G., Marks M. S. (2006) Dual loss of ER export and endocytic signals with altered melanosome morphology in the silver mutation of Pmel17. Mol. Biol. Cell 17, 3598–3612 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Capra J. A., Singh M. (2007) Predicting functionally important residues from sequence conservation. Bioinformatics 23, 1875–1882 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Delpire E., Lu J., England R., Dull C., Thorne T. (1999) Deafness and imbalance associated with inactivation of the secretory Na-K-2Cl co-transporter. Nat. Genet. 22, 192–195 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Delpire E., Mount D. B. (2002) Human and murine phenotypes associated with defects in cation-chloride cotransport. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 64, 803–843 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Delpire E. (2000) Cation-Chloride Cotransporters in Neuronal Communication. News Physiol. Sci. 15, 309–312 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Gavrikov K. E., Nilson J. E., Dmitriev A. V., Zucker C. L., Mangel S. C. (2006) Dendritic compartmentalization of chloride cotransporters underlies directional responses of starburst amacrine cells in retina. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 18793–18798 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Kaneko H., Putzier I., Frings S., Kaupp U. B., Gensch T. (2004) Chloride accumulation in mammalian olfactory sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. 24, 7931–7938 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Howell G. J., Holloway Z. G., Cobbold C., Monaco A. P., Ponnambalam S. (2006) Cell biology of membrane trafficking in human disease. Int. Rev. Cytol. 252, 1–69 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]