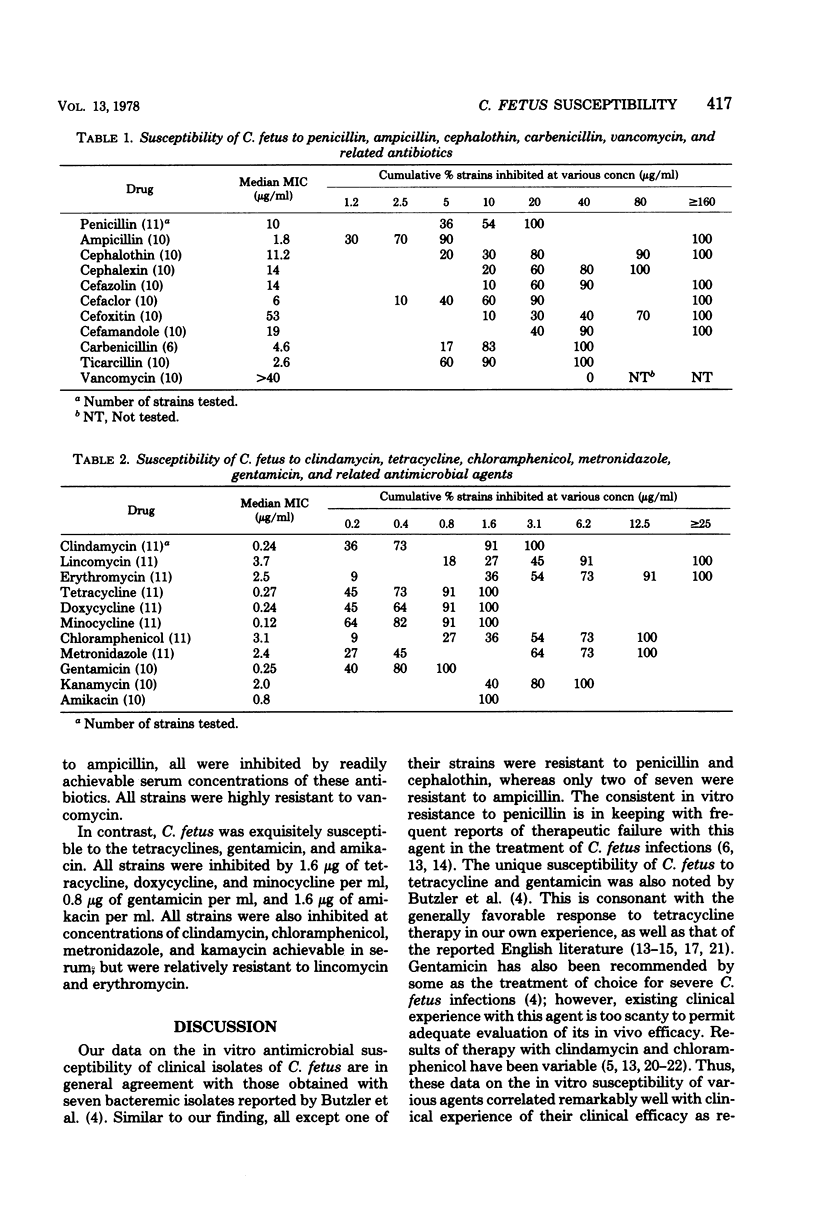
Abstract
In vitro susceptibility of 11 recent clinical isolates of Campylobacter fetus to 22 antimicrobial agents was determined by an agar dilution technique. Unlike most obligate anaerobic gram-negative bacilli, C. fetus isolates tested were relatively resistant to penicillin and cephalosporins, but exquisitely susceptible to tetracyclines and aminoglycosides. All strains were also inhibited at concentrations achievable in serum by clindamycin, chloramphenicol, metronidazole, carbenicillin, ticarcillin, and with rare exceptions, ampicillin. They were variably susceptible to lincomycin and erythromycin and highly resistant to vancomycin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bokkenheuser V. Vibrio fetus infection in man. I. Ten new cases and some epidemiologic observations. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Apr;91(4):400–409. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J., Sautter R. Campylobacter fetus septicemia with concurrent salpingitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):72–75. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.72-75.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Dekeyser P., Lafontaine T. Susceptibility of related vibrios and Vibrio fetus to twelve antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):86–89. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper I. A., Slee K. J. Human infection by Vibrio fetus. Med J Aust. 1971 Jun 12;1(24):1263–1267. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1971.tb92386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDEN A. N. Vibrio fetus meningitis in a newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1962 Jul;61:33–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(62)80226-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. I., Dye M., Carne H. The selective toxicity of antimicrobial nitroheterocyclic drugs. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):135–145. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernie D. S., Ware D. A., Park R. W. The effect of the nitroimidazole drug dimetridazole on microaerophilic campylobacters. J Med Microbiol. 1977 May;10(2):233–240. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-2-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin B., Ulmer D. D. Human infection with vibrio fetus. West J Med. 1974 Mar;120(3):200–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson C. H., Sack G. E. Neurology of Vibrio fetus infection. Neurology. 1971 Mar;21(3):307–309. doi: 10.1212/wnl.21.3.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILO C., HAGEMANN P. O., MARZI J. SEPTIC ARTHRITIS AND BACTEREMIA DUE TO VIBRIO FETUS: REPORT OF AN UNUSUAL CASE AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE. Am J Med. 1965 Jun;38:962–971. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O. Human infections with Vibrio fetus and a closely related vibrio. J Infect Dis. 1957 Sep-Oct;101(2):119–128. doi: 10.1093/infdis/101.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb H., Bettag J. L., Yung N. K., King S., Bronsky D. Vibrio fetus endocarditis. Report of 2 cases. Am Heart J. 1966 Mar;71(3):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(66)90479-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. W., Morris J. G. Effect of metronidazole on hydrogen production by Clostridium acetobutylicum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(3):225–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00425200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soonattrakul W., Andersen B. R., Bryner J. H. Raw liver as a possible source of Vibrio fetus septicemia in man. Am J Med Sci. 1971 May;261(5):245–249. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197105000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Treatment of anaerobic infections with metronidazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):672–675. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S. R., Chow A. W., Guze L. B. Spontaneous peritonitis of cirrhosis due to Campylobacter fetus. Gastroenterology. 1976 Aug;71(2):311–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toala P., McDonald A., Kass E. H. Septicemia caused by Vibrio fetus. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Aug;126(2):306–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesely D., MacIntyre S., Ratzan K. R. Bilateral deep brachial vein thrombophlebitis due to vibrio fetus. Arch Intern Med. 1975 Jul;135(7):994–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


