Abstract
Identification of regulatable mechanisms by which transcription factor NF-E2 p45-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is repressed will allow strategies to be designed that counter drug resistance associated with its up-regulation in tumours that harbour somatic mutations in Kelch-like ECH-associated protein-1 (Keap1), a gene that encodes a joint adaptor and substrate receptor for the Cul3-Rbx1/Roc1 ubiquitin ligase. We now show that mouse Nrf2 contains two binding sites for β-transducin repeat-containing protein (β-TrCP), which acts as a substrate receptor for the Skp1-Cul1-Rbx1/Roc1 ubiquitin ligase complex. Deletion of either binding site in Nrf2 decreased β-TrCP-mediated ubiquitylation of the transcription factor. The ability of one of the two β-TrCP-binding sites to serve as a degron could be both increased and decreased by manipulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) activity. Biotinylated-peptide pull-down assays identified DSGIS338 and DSAPGS378 as the two β-TrCP-binding motifs in Nrf2. Significantly, our pull-down assays indicated that β-TrCP binds a phosphorylated version of DSGIS more tightly than its non-phosphorylated counterpart, whereas this was not the case for DSAPGS. These data suggest that DSGIS, but not DSAPGS, contains a functional GSK-3 phosphorylation site. Activation of GSK-3 in Keap1-null mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), or in human lung A549 cells that contain mutant Keap1, by inhibition of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) – protein kinase B (PKB)/Akt pathway markedly reduced endogenous Nrf2 protein and decreased to 10-50% of normal the levels of mRNA for prototypic Nrf2-regulated enzymes, including the glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic and modifier subunits, glutathione S-transferases Alpha-1 and Mu-1, heme oxygenase-1 and NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase-1. Pre-treatment of Keap1−/− MEFs or A549 cells with the LY294002 PI3K inhibitor or the MK-2206 PKB/Akt inhibitor increased their sensitivity to acrolein, chlorambucil and cisplatin between 1.9-fold and 3.1-fold, and this was substantially attenuated by simultaneous pre-treatment with the GSK-3 inhibitor CT99021.
Keywords: Nrf2, β-TrCP, GSK-3, oxidative stress, drug resistance, ubiquitylation
Introduction
NF-E2 p45-related factor 2 (Nrf2)1 is a cap‘n’collar (CNC) basic-region leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor that serves as a master regulator of redox homeostasis (1). It is activated by thiol-reactive agents, and plays a fundamental role in cellular adaptation to oxidative stress because of its ability to transactivate genes that contain an antioxidant response element (ARE) in their promoter regions (2,3).
Nrf2 is principally controlled through protein ubiquitylation, which targets it for proteasomal degradation (4-6). The N-terminal Nrf2-ECH homology (Neh)2 domain of Nrf2 contains an ETGE motif to which Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) binds with high affinity, and a DLG motif to which Keap1 binds with low affinity (7,8); Keap1 is a dimeric protein that serves jointly as an ubiquitin ligase adaptor and substrate receptor (9). Under normal redox homeostatic conditions, the two subunits of Keap1 bind simultaneously the ETGE and DLG motifs in Nrf2 and allow Cul3-Rbx1/Roc1, i.e. the cullin-ring-ligase CRLKeap1, to ubiquitylate the transcription factor (10,11). However, upon treatment of cells with inducing agents (such as sulforaphane or tert- butylhydroquinone) the activity of Keap1 is inhibited, CRLKeap1 no longer ubiquitylates Nrf2, the CNC-bZIP protein accumulates in the nucleus, and ARE-driven genes become transcriptionally activated (12,13).
Often, Nrf2 is up-regulated in tumours of the head and neck, liver, lung, ovary and stomach through loss of its repression by Keap1. This can arise as a consequence of somatic mutations or epigenetic changes that either diminish the activity of Keap1 or reduce its expression (14-20). Alternatively, Nrf2 may evade repression by Keap1 as a consequence of somatic mutations in the ETGE and DLG motifs of the CNC-bZIP factor, or by overexpression of the Nrf2 gene (21-23). As constitutive activation of Nrf2 in tumours is associated with increased resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs and a higher rate of cell proliferation, it is desirable to identify Keap1-independent mechanisms by which the CNC-bZIP factor can be repressed. One such example is provided by the presence of two regions within the Neh6 domain of Nrf2 (in mouse Nrf2 these are residues 329-339 and 363-379) that support turnover of the CNC-bZIP protein even when Keap1 is inactivated (24). It has also been found that glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) inhibits Nrf2 by preventing nuclear accumulation of the CNC-bZIP factor (25-27). Recently, evidence has been provided that GSK-3-catalysed phosphorylation of the Neh6 domain in Nrf2 creates a phosphodegron to which the substrate receptor β-transducin repeat-containing protein (β-TrCP)2 is recruited (28); β-TrCP contains an F-box domain that interacts with the Skp1 adaptor protein, and a WD40 domain that binds substrates (29). Collectively, these findings suggest that the phosphodegron created by GSK-3 enables ubiquitylation of Nrf2 by the Skp1-Cul1-Rbx1/Roc1 core E3 complex, i.e. SCFβ-TrCP.
Whilst progress has been made in understanding how the N-terminal degron within the Neh6 domain of Nrf2 operates, the molecular mechanism by which the other degron in Neh6 functions is not known. It has also not not been examined whether Nrf2 can be down-regulated by activation of its Neh6-based degrons. It is important to explore this possibility as it might provide a strategy to counter Nrf2-mediated drug resistance.
Results
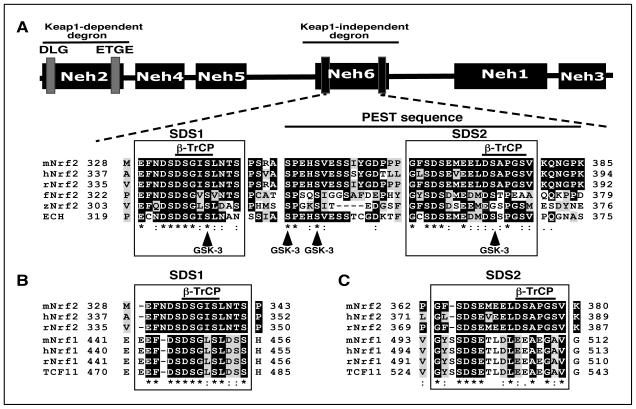
To gain a better understanding of which amino acids within Neh6 direct degradation of Nrf2 protein, a sequence alignment from different species was undertaken. Figure 1A shows that the Neh6 domain contains two regions that are highly conserved across vertebrates. One of these, called SDS1, is located in mouse Nrf2 between amino acids 329-342 in the N-terminal portion of Neh6 and contains a putative DSGIS338 non-canonical β-TrCP-binding site (ref. 28)3. The second region, designated SDS2, is located in mouse Nrf2 between amino acids 363-379 in the C-terminal portion of Neh6 and contains a possible β-TrCP-binding site formed by DSEME370 and a more likely β-TrCP-binding site involving DSAPGS378. Both SDS1 and SDS2 contain putative GSK-3 phosphorylation sites. The SDS2 region is situated within a possible PEST sequence that lies between amino acids 347-380 (6). As shown in Figure 1B, the SDS1 region is conserved in acidic domain-2 of NF-E2 p45-related factor 1 (Nrf1). The putative DSGIS β-TrCP binding site within SDS1 of Nrf2 is represented by DSGLS in Nrf1, and the latter has recently been reported to recruit β-TrCP (30). Although the SDS2 region is represented in the Neh6-like domain of Nrf1, the potential DSEME and DSAPGS β-TrCP binding sites are poorly conserved (Figure 1C).
Figure 1.
The Neh6 domain of Nrf2 comprises two conserved regions that include putative β-TrCP binding sites and a potential PEST sequence.
A) Amino acid sequences corresponding to the Neh6 domain of Nrf2 from mouse (m), human (h), rat (r), frog (f), and zebrafish (z), along with that of ECH (i.e. chicken Nrf2) have been aligned using the T-Coffee tool (at http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/tcoffee/). White letters on a black background represent residues that are identical across at least half of the species studied, and black letters on a grey background are conserved residues. The two boxes designated SDS1 and SDS2 contain sequences enriched with Ser and Asp residues. The solid horizontal bar over residues corresponding to 347 and 385 in mouse Nrf2 depicts a potential PEST sequence that is enriched with Pro, Glu, Ser and Thr residues (6). Within the SDS1 and SDS2 boxes, a solid horizonal bar is shown above sequences that represent putative β-TrCP binding sites. The residues that are predicted to be phosphorylated by GSK-3, based on the Scansite program (at http://scansite.mit.edu), are shown at the bottom as vertical arrows.
B) Amino acid sequences of the SDS1 region in the Neh6 domain of mNrf2, hNrf2 and rNrf2 have been aligned with a similar region in the acidic domain-2 of mNrf1, hNrf1, rNrf1 and TCF11, a splice variant of Nrf1 (the protein shown is the human factor).
C) Amino acid sequences of the SDS2 region in the Neh6 domain of mNrf2, hNrf2 and rNrf2 have been aligned with a similar region in the Neh6-like domain of mRn1, hNrf1, rNrf1 and TCF11.
The stability and activity of Nrf2 is controlled through two separate sequences within its Neh6 domain
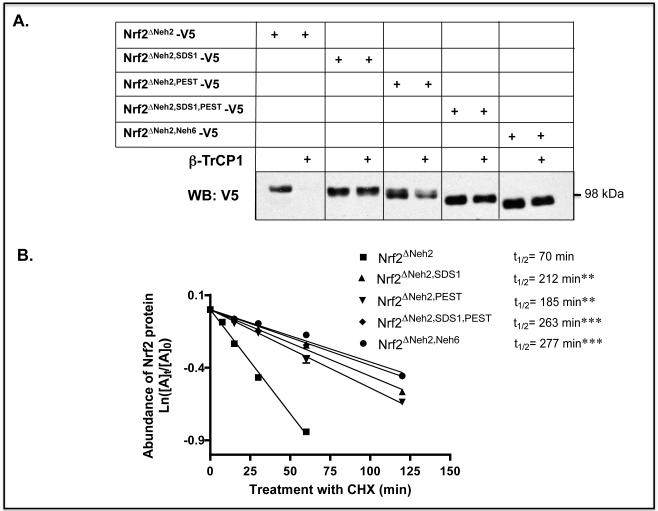
The degron activity of different regions within Neh6 was studied by examining the stability of various Nrf2 deletion mutants, all of which lacked the N-terminal Neh2 domain. Deletion of the SDS1 region or the PEST sequence increased the stability of Nrf2ΔNeh2-V5 in Keap1−/− mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells (Figure 2A), with the half-life estimated to increase from 70 min for Nrf2ΔNeh2-V5 to about 212 and 185 min for Nrf2ΔNeh2,SDS1-V5 and Nrf2ΔNeh2,PEST-V5, respectively (Figure 2B). Deletion of both SDS1 and PEST further increased the half-life of Nrf2ΔNeh2-V5 to 263 min. Moreover, forced co-expression of β-TrCP1 with Nrf2ΔNeh2-V5 in Keap1-null MEFs greatly diminished the amount of the mutant CNC-bZIP protein detected by immunoblotting (Figure 2A). By contrast, forced expression of the adaptor protein had only a small effect on the abundance of Nrf2ΔNeh2,SDS1-V5 in Keap1−/− MEFs, whereas it decreased modestly the level of Nrf2ΔNeh2,PEST-V5. Deletion of both SDS1 and PEST, or deletion of the entire Neh6 domain within Nrf2ΔNeh2-V5, rendered the compound mutant CNC-bZIP protein insensitive to destabilization by forced expression of β-TrCP.
Figure 2.
Repression of Nrf2 by β-TrCP is abolished by deletion of two separate regions within its Neh6 domain.
A) Keap1−/− MEFs were transfected for 24 h with pcDNA3.1 expression vectors encoding V5-tagged mouse Nrf2ΔNeh2 or related mutants that lack SDS1, PEST or the entire Neh6 domain, along with either an empty pcDNA4-FLAG plasmid or a pcDNA4-βTrCP1-FLAG plasmid. Twenty-four h later, the cells were serum-depleted by transfer to Delbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) containing 0.5% fetal bovine serum (FBS) for 16 h, after which whole cell lysates were prepared and ectopic Nrf2 measured by Western blotting using mouse anti-V5 antibodies.
B) Keap1−/− MEFs were transfected with the same Nrf2ΔNeh2-V5, Nrf2ΔNeh2,SDS1-V5, Nrf2ΔNeh2,PEST-V5 and Nrf2ΔNeh2,Neh6-V5 expression vectors used in panel A. Following transfection, the MEFs were serum-depleted for 16 h before they were treated with CHX for various periods of time and the relative amounts of ectopic mutant Nrf2 measured by Western blotting. Results that were significantly higher than the Nrf2ΔNeh2 control with P values of 0.01-0.001 or <0.001 are indicated with double (**) or triple (***) asterisk signs, respectively.
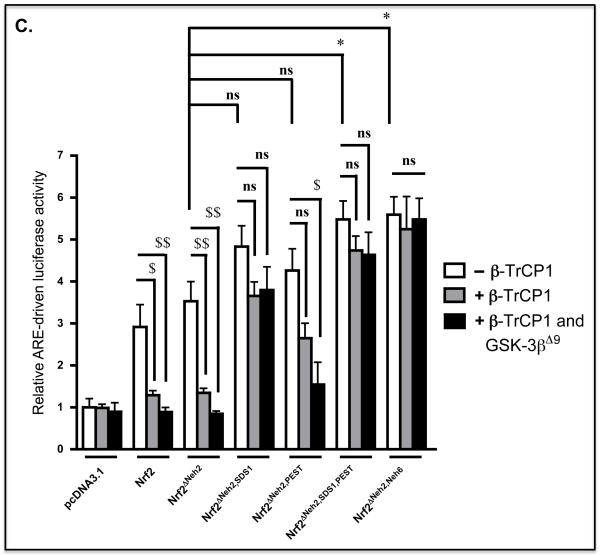
C) COS1 cells were co-transfected with an empty pcDNA3.1 expression vector or one encoding various mutant mouse Nrf2 proteins (as indicated at the bottom of the figure) along with the murine quinone reductase-based P-1016/nqo1-Luc reporter construct (2) and the pRL-TK Renilla control plasmid. At the same time, the cells were also transfected with combinations of empty vectors and pcDNA4-βTrCP1-FLAG and pCGN/GSK-3βΔ9 as indicated. Equal amounts of DNA were transfected into COS1 cells in the different experimental groups. After overnight transfection, the cells were serum-depleted for 16 h, before ARE-driven luciferase activity was measured. All results were normalized to Renilla luciferase activity. The data are presented as follows: cells transfected with empty pcDNA4 expression vector in open bars; cells transfected with pcDNA4-FLAG and pcDNA4-βTrCP1-FLAG in grey bars; cells transfected with pcDNA4-βTrCP1-FLAG and pCGN/GSK-3βΔ9 solid black bars. Results in which ectopic expression of compound mutant forms of Nrf2 stimulated an increase in ARE-driven luciferase activity with a P value of 0.05-0.01, relative to that produced by Nrf2ΔNeh2-V5, are indicated by a single asterisk (*). Results in which the stimulation of ARE-driven luciferase activity produced by Nrf2 or its mutants was reduced through forced expression of β-TrCP1 or forced co-expression of β-TrCP and GSK-3βΔ9 with a P value of 0.05-0.01 or <0.005 are indicated by $ or $$$, respectively.
In order to assess the functional significance of the reduction in steady-state Nrf2 protein levels affected by forced expression of β-TrCP, the ability of Nrf2ΔNeh2-V5-based mutants to transactivate an ARE-luciferase reporter gene, based on the promoter of mouse NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase-1 (Nqo1) (2), was examined in COS1 cells (Figure 2C). An expression vector for Nrf2ΔNeh2-V5 produced a 3.5-fold increase in relative luciferase activity. However, this increase was almost completely abolished on co-transfection with an expression vector for β-TrCP, and was further decreased upon expression of constitutively active GSK-3βΔ9. Following transfection with an expression vector for Nrf2 lacking both Neh2 and the SDS1 region (Nrf2ΔNeh2,SDS1), an increase in luciferase activity of 4.8-fold was observed (compared with a 3.5-fold increase stimulated by Nrf2ΔNeh2), and this was reduced to a ~3.6-fold increase in activity upon co-expression of β-TrCP. By contrast with Nrf2 and Nrf2ΔNeh2, the activity of Nrf2ΔNeh2,SDS1 was not inhibited by GSK-3βΔ9 (Figure 2C). Transfection with an expression vector for Nrf2ΔNeh2 lacking the PEST sequence produced an approximate 4-fold increase in luciferase activity that was reduced to a 2.5-fold increase in reporter activity on co-expression of β-TrCP. However, unlike Nrf2ΔNeh2,SDS1, the reduction in the luciferase activity produced by the Nrf2ΔNeh2,PEST mutant that occurred on co-expression of β-TrCP was further decreased by GSK-3βΔ9 (Figure 2C). Transfection of COS1 cells with an expression vector for Nrf2 lacking Neh2 and both SDS1 and PEST sequences produced an approx. 5.5-fold increase in luciferase activity, and this increase was not inhibited by ectopic expression of β-TrCP and GSK-3βΔ9.
Nrf2 contains two separate β-TrCP binding regions within its Neh6 domain
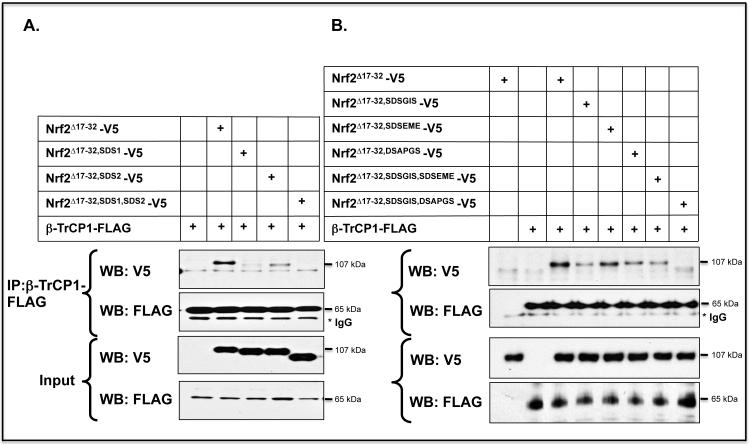
The above data suggest that the PEST sequence in the Neh6 domain contains a degron that interacts with β-TrCP. In order to locate the degron more accurately, Nrf2 expression constructs were made in which the PEST sequence was deleted in two halves, N-PEST347-362 and SDS2 (i.e. C-PEST363-379). Using COS1 cells, the contributions made by SDS1 and SDS2 to the association of Nrf2 with β-TrCP1 were compared by co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) of ectopic V5-tagged Nrf2 deletion mutants with FLAG-tagged β-TrCP1. Western blotting of material precipitated with anti-FLAG antibody revealed that the association between Nrf2 and β-TrCP was markedly reduced on deletion of either the SDS1 or SDS2 regions (Figure 3A), whereas deletion of N-PEST347-362 did not influence the association between Nrf2 and β-TrCP1 (data not shown).
Figure 3.
Transcription factor Nrf2 contains two separate sequences in its Neh6 domain to which β-TrCP can bind.
A) COS1 cells were co-transfected with pcDNA3.1 expression plasmids encoding V5-tagged mouse Nrf2Δ17-32 or mutants lacking SDS1, SDS2, or SDS1 and SDS2, along with pcDNA4-βTrCP1-FLAG. Empty pcDNA3.1 vector was included in the transfection mixture to normalize the amount of DNA to which cells were exposed. Following overnight transfection, the cells were serum-depleted for 16 h by transfer to DMEM containing 0.5% FBS before whole cell lysates were prepared. An aliquot (10%) of the lysate was withdrawn as the input sample, and the remainder was used for the pull-down assay that employed an antibody against FLAG as described in Materials and Methods.
B) COS1 cells were co-transfected for 24 h with an expression vector for mouse Nrf2Δ17-32-V5, or its mutants lacking SDSGIS338, SDSEME370 and DSAPGS378, either individually or as double deletion mutants, along with an expression plasmid for FLAG-tagged β-TrCP1. As in panel A, β-TrCP1 was pulled-down after the cells had been subjected to 16 h serum-depletion using antibodies against FLAG, and the Nrf2 mutants that co-immunoprecipitated with β-TrCP1 were detected by immunoblotting with antibodies against the V5 epitope.
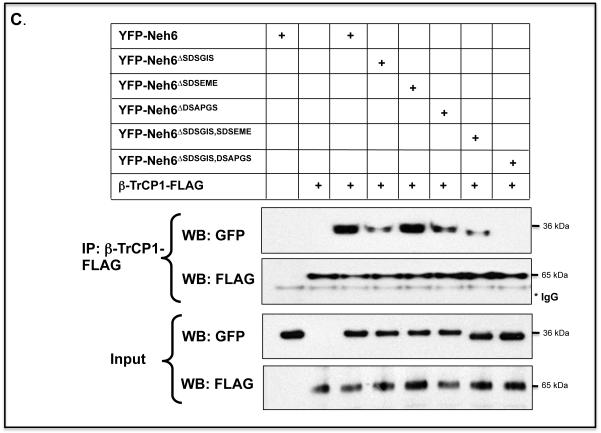
C) COS1 cells were co-transfected with expression vectors for a YFP-Neh6 fusion protein, or YFP-Neh6 protein lacking SDSGIS338, SDSEME370 or DSAPGS378, or combinations thereof, along with an expression plasmid for FLAG-tagged β-TrCP1. The Neh6 domain mutants that co-immunoprecipitated with β-TrCP1 were detected by immunoblotting with antibodies against GFP.
The co-IP assay was also performed to investigate the significance of putative β-TrCP recognition sites within the SDS1 and SDS2 regions in the Neh6 domain of Nrf2. Deletion of the SDSGIS338 peptide from within SDS1 of the murine CNC-bZIP factor resulted in a dramatic decrease in the amount of mutant Nrf2 precipitated with β-TrCP (Figure 3B). By contrast, deletion of the SDSEME370 peptide within SDS2 did not influence the association of Nrf2 with β-TrCP, whereas deletion of the DSAPGS378 peptide within SDS2 caused a significant reduction in the amount of the CNC-bZIP protein pulled-down with β-TrCP. These results support the hypothesis that both SDSGIS338 and DSAPGS378 motifs in the Neh6 domain are recognised by β-TrCP whereas SDSEME370 is not bound by β-TrCP.
A separate co-IP assay was used to test whether the Neh6 domain is sufficient to allow Nrf2 to interact with β-TrCP. We created an EYFP-Neh6 fusion protein, along with mutants that lacked the SDSGIS338, SDSEME370 and DSAPGS378 peptide sequences, and examined whether they could be precipitated with β-TrCP. The assay revealed that β-TrCP pulled-down EYFP-Neh6. Deletion of either SDSGIS or DSAPGS significantly reduced the amount of EYFP-Neh6 that could co-IP with β-TrCP but deletion of SDSEME did not diminish the amount of EYFP-Neh6 precipitated with β-TrCP (Figure 3C).
GSK-3 activity influences the association between Neh6 and β-TrCP
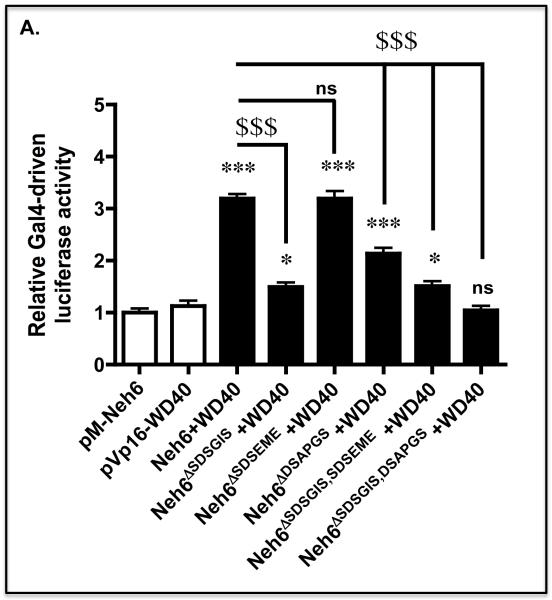
We created a mammalian two-hybrid assay to further examine the interactions between the Neh6 domain of mouse Nrf2 and the WD-40 domain of β-TrCP1 that comprised Gal4(DBD)-Neh6 and Gal4(AD)-WD40 fusion proteins along with a Gal4-driven luciferase reporter gene. As shown in Figure 4A, co-expression of the Gal4(DBD)-Neh6 and Gal4(AD)-WD40 fusion proteins in COS1 cells along with the Gal4 PTKUAS-Luc reporter plasmid, produced an approximate 3.2-fold increase in luciferase activity, when compared with the activity obtained upon expression of either Gal4(DBD)-Neh6 or Gal4(AD)-WD40 alone. Most significantly, deletion of the SDSGIS and DSAPGS peptides from the murine Neh6 domain decreased induction of luciferase activity from 3.2-fold to just 1.5-fold and 2.1-fold, respectively.
Figure 4.
A peptide sequence in the SDS1 region of the Neh6 domain allows Nrf2 to interact with β-TrCP in a GSK-3-dependent manner.
A) COS1 cells were co-transfected with expression vectors encoding the Gal4 DNA-binding domain fused to the Neh6 domain (i.e. Gal4(DBD)-Neh6), or expression vectors for Gal4(DBD)-Neh6 containing individual or combined deletion of the SDSGIS338, SDSEME370 and DSAPGS378 hexapeptides along with an expression vector for the Gal4 activating domain fused to the substrate-binding WD40 domain of β-TrCP1 (Gal4(AD)-WD40) and the reporter plasmids PTKUAS-Luc and pRL-TK Renilla. Forty-eight h later the cells were serum-depleted for 16 h by transfer to DMEM containing 0.5% FBS, after which time Gal4-driven luciferase activity was measured. Significant increases in Gal4-driven reporter gene activity, relative to that produced by pM-Neh6 alone, with P values of 0.01-0.001 or <0.001 are indicated above the histogram bars by ** or ***, respectively. Significant decreases in reporter gene activity relative to that produced by Neh6 + WD40 with P values <0.001 are indicated by $$$ on a horizontal line from Neh6 with a vertical line directed at the relevant data points.
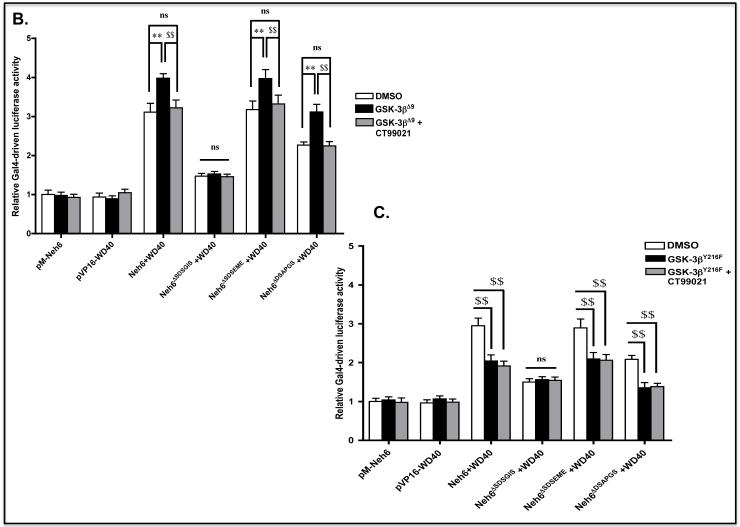
B) COS1 cells were co-transfected with expression vectors for Gal4(DBD)-Neh6, Gal4(DBD)-Neh6ΔSDSGIS, Gal4(DBD)-Neh6ΔSDSEME or Gal4(DBD)-Neh6ΔDSAPGS and the expression plasmid for Gal4(AD)-WD40. At the same time, the COS1 cells were transfected with the reporter plasmids P TKUAS-Luc and pRL-TK Renilla, along with either an empty expression vector or one encoding GSK-3βΔ9. Following 48 h transfection, the COS1 cells were serum-depleted for 16 h, during which time a portion was treated with 5 μM CT99021 for 2 h or with 0.1% DMSO vehicle control. The cells were then harvested, lysed and Gal4-driven luciferase activity measured. Differences in reporter gene activity produced by a given two-hybrid pair that were observed upon either expression of GSK-3βΔ9 or treatment with CT99021 with P values of 0.01-0.001 (increase **, or decrease $$) are indicated by the linked lines above the histogram bars.
C) COS1 cells were transfected with expression vectors as described in panel B, but a plasmid encoding GSK-3βY216F substituted for that encoding GSK-3βΔ9.
When constitutively active GSK-3βΔ9 was included in the mammalian two-hybrid assay, we found that Gal4-driven luciferase activity in cells expressing Gal4(DBD)-Neh6 increased from 3.2-fold to 4.0-fold (Figure 4B). Ectopic GSK-3βΔ9 did not however increase Gal4-driven luciferase activity in cells expressing Gal4(DBD)-Neh6 that lacked SDSGIS. By contrast, GSK-3βΔ9 increased Gal4-driven luciferase activity from about 2.3-fold to 3.1-fold in cells expressing Gal4(DBD)-Neh6that lacked DSAPGS. When the kinase-dead GSK-3βY216F mutant was included in the mammalian two-hybrid assay, Gal4-driven luciferase activity in cells expressing Gal4(DBD)-Neh6 lacking SDSGIS was again unaltered by forced expression of the GSK-3 protein (Figure 4C).
GSK-3 alters the abundance of a Neh6-containing fusion protein through a single peptide sequence
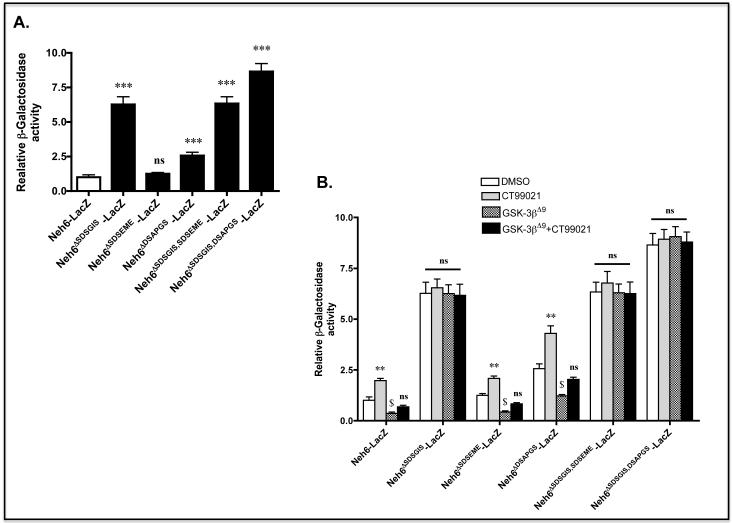
To test whether GSK-3 activity influences the degron activities of the SDSGIS or DSAPGS sequences, we created an expression vector for a Neh6(LacZ)-V5 fusion protein and deletion mutants that lack the two motifs. Transfection of COS1 cells with an expression vector for Neh6(LacZ)-V5 gave a level of β-gal activity that was clearly discernable from background. By contrast with ‘wild-type’ Neh6(LacZ)-V5, a fusion protein lacking SDSGIS gave a 6.2-fold increase in β-gal activity and one lacking DSAPGS gave a 2.5-fold increase in activity (Figure 5A).
Figure 5.
The abundance of a Neh6-LacZ fusion protein is controlled by two peptide sequences and by GSK-3
A) COS1 cells were co-transfected with a pcDNA3.1 expression vector for a V5-tagged fusion protein comprising Neh6 coupled at its C-terminus to LacZ (i.e. Neh6(LacZ)-V5), or expression vectors for Neh6(LacZ)-V5 bearing individual or combined deletion of the SDSGIS338, SDSEME370 and DSAPGS378 hexapeptides from the Neh6 domain along with an expression plasmid for βTrCP1-FLAG and pRL-TK Renilla as a transfection control. As further controls, COS1 cells were transfected with the expression plasmid for Neh6(LacZ)-V5 alone, or were co-transfected with expression plasmids for LacZ-V5 and β-TrCP1-FLAG; all of these included the Renilla transfection control plasmid. After 24 h transfection, the cells were serum-depleted for 16 h before β-gal activity was measured and results normalised against Renilla. Enzyme activity results that are significantly higher than that produced by Neh6-LacZ with a P value of <0.001 are indicated by ***.
B) COS1 cells were co-transfected with the expression plasmids for Neh6(LacZ)-V5, or its mutants, and β-TrCP1-FLAG as above along with the expression vector for GSK-3βΔ9. Thereafter, the cells were transferred to medium containing 0.5% FBS for 16 h, and were then treated with 5 μM CT99021 or 0.1% DMSO vehicle control for 2 h before being harvested and β-gal activity measured. The β-galactosidase activity was normalised against Renilla. The significance of changes in β-gal activity following treatment with CT99021 and/or ectopic expression of GSK-3βΔ9 for an individual Neh6-LacZ fusion protein is indicated above the histogram bars as outlined in Materials and Methods.
Treatment of COS1 cells that expressed ectopic ‘wild-type’ Neh6(LacZ)-V5 with the GSK-3 inhibitor CT99021 increased β-gal activity ~2.0-fold when compared with COS1 cells expressing the ‘wild-type’ fusion protein that had been treated with vehicle alone (Figure 5B). Treatment of COS1 cells that expressed ectopic Neh6ΔSDSGIS(LacZ)-V5 with the GSK-3 inhibitor did not increase β-gal activity over that observed in vehicle-treated cells. Treatment of cells that expressed ectopic Neh6ΔDSAPGS(LacZ)-V5 with the CT99021 GSK-3 inhibitor increased β-gal activity an additional 1.8-fold when compared with cells expressing the same fusion protein that had been treated with vehicle alone.
GSK-3 activity increases ubiquitylation of Nrf2 through a single peptide in the Neh6 domain
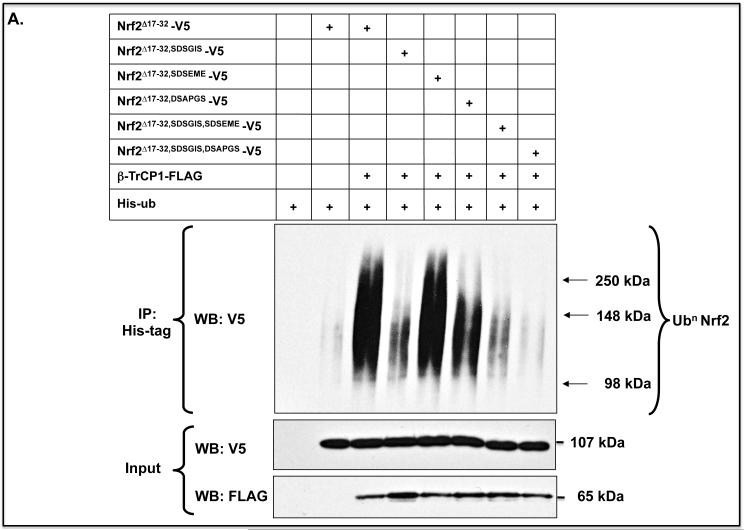
An in-vivo ubiquitylation assay was performed to assess the biological significance of the two β-TrCP binding motifs in the Neh6 domain. Expression constructs for Nrf2Δ17-32-V5 with or without the SDSGIS338 or DSAPGS378 peptides were co-transfected into COS1 cells with FLAG-tagged β-TrCP and pHisUb. Deletion of either the SDSGIS338 or DSAPGS378 peptide within Nrf2 led to a significant decrease in its ubiquitylation (Figure 6A). Moreover, combined deletion of both peptide sequences resulted in complete inhibition of ubiquitylation.
Figure 6.
β-TrCP-mediated ubiquitylation of Nrf2 involves two separate peptide motifs in the Neh6 domain
A) COS1 cells were co-transfected for 24 h with a pcDNA3.1 expression vector encoding V5-tagged mouse Nrf2Δ17-32, or mutants lacking SDSGIS338, SDSEME370 or DSAPGS378, along with expression plasmids for HisUb and β-TrCP1-FLAG. As controls, the cells were transfected with empty expression vectors, pHisUb alone or pcDNA3.1-Nrf2Δ17-32-V5 without pcDNA4-βTrCP1-FLAG. Following transfection, the cells were serum-depleted for 16 h, after which whole cell lysates were prepared in phosphate-buffered saline. To allow loading to be assessed, a 10% portion of the lysate was retained as input. The remainder of each sample was used to purify His-tagged protein separately using Ni2+-agarose beads, and the total amount of ubiquitylated Nrf2 protein in each sample was determined by Western blotting with anti-V5 antibodies. The input samples were also immunoblotted with anti-V5 and anti-FLAG antibodies to confirm equal loading of Nrf2 and β-TrCP1.
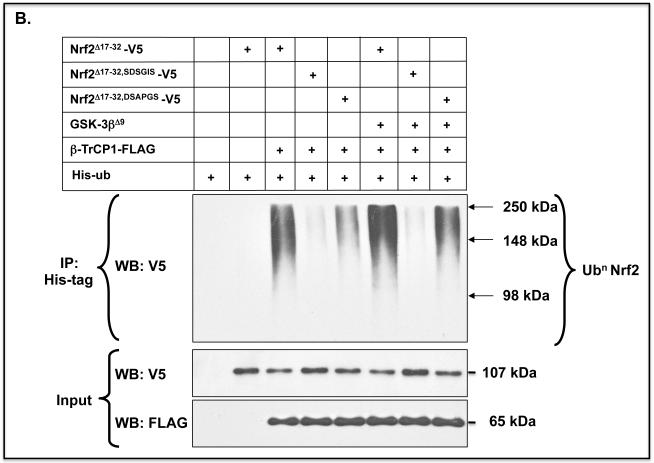
B) The same ubiquitylation assay was performed for Nrf2Δ17-32-V5, Nrf2Δ17-32,SDSGIS-V5 and Nrf2Δ17-32,DSAPGS-V5 as in panel A, but on this occasion the Nrf2 expression constructs were co-transfected into COS1 cells with an expression vector for either GSK-3βΔ9 or an empty vector.
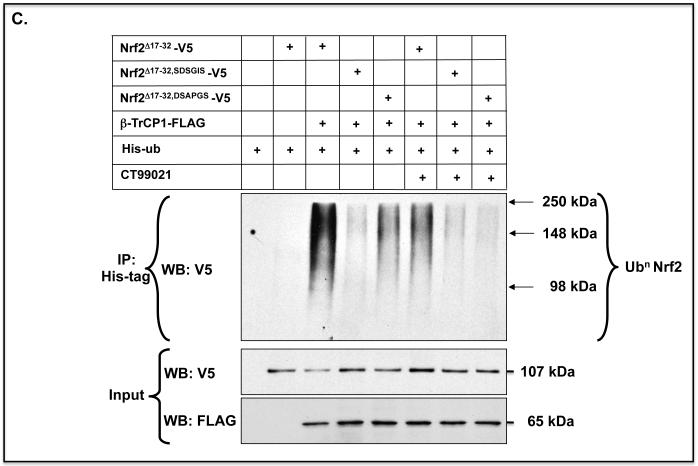
C) The same ubiquitylation assay was performed for Nrf2Δ17-32-V5, Nrf2Δ17-32,SDSGIS-V5 and Nrf2Δ17-32,DSAPGS-V5 as in panel A, but in this case the COS1 cells were treated with 5 μM CT99021 to inhibit GSK-3.
Forced expression of constitutively active GSK-3βΔ9 increased ubiquitylation of Nrf2Δ17-32-V5 that contained the SDSGIS338 motif but not those mutants that lacked it (Figure 6B). Moreover, the GSK-3 inhibitor CT99021 only inhibited ubiquitylation of Nrf2Δ17-32-V5 forms that contained the SDSGIS338 sequence (Figure 6C). Thus, ubiquitylation of Nrf2 through the SDSGIS sequence is influenced by GSK-3 whereas ubiquitylation of Nrf2 through the DSAPGS378 sequence occurs independently of the kinase.
Phosphorylation of the DSGIS338 motif in the Neh6 domain of Nrf2 increases binding by β-TrCP
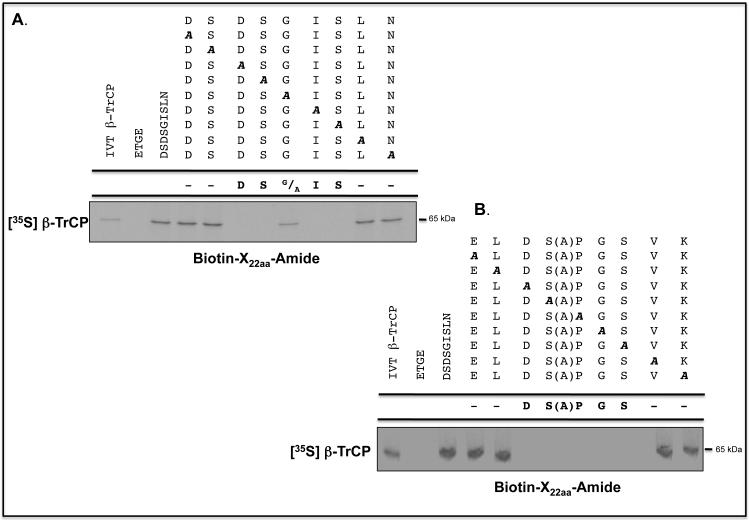
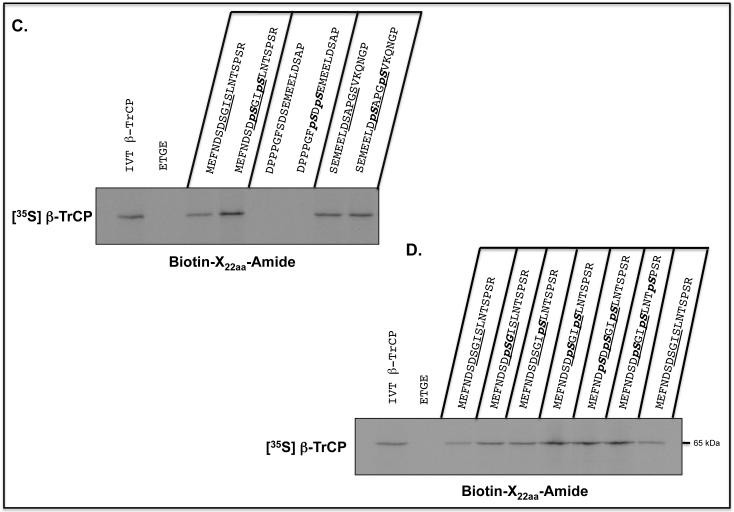
To define the sequences in the Neh6 domain of Nrf2 to which β-TrCP binds, a biotinylated-peptide pull-down assay was carried out. A series of scanning mutants were synthesised across the (SGSG)-328MEFNDSDSGISLNTSPSR345 and (SGSG)-367SEMEELDSAPGSVKQNGP384 peptides in which NDSDSGISLN340 and ELDSAPGSVK380 sequences (with the residues previously deleted in Neh6 shown in bold italics), respectively, were each replaced individually with Ala; the Ala-375 residue was left unchanged. As shown in Figures 7A and B, the pull-down assay indicated that the sequences DSGIS338 and DSAPGS378 represent the core destruction motifs to which β-TrCP binds.
Figure 7.
β-TrCP binds both phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated Nrf2-derived peptides containing the DSGIS and DSAPGS sequences.
Biotinylated-peptides, designed around sequences in the SDS1 and SDS2 regions of the Neh6 domain in mouse Nrf2, were coupled with Streptavidin, which had first been immobilized on agarose beads, and used in pull-down assays to identify those that were bound by in vitro translated [35S]methionine-labelled β-TrCP1. A biotinylated ETGE-containing peptide, representing residues 73-90 of mouse Nrf2, was used as a negative control.
A) Ala-scanning substitutions were introduced into the (SGSG)MEFNDSDSGISLNTSPSR peptide between residues equivalent to Asp-332 and Asn-340 in the Neh6 domain (the residues changed are shown underlined). Each of the peptides was used in the pull-down assay, and autoradiography was used to identify β-TrCP1 that bound the peptides. As a control, lane 1 contained total [35S]methionine-labelled in vitro translated protein. Lane 2 shows [35S]methionine-labelled protein pulled-down by the ETGE peptide. Lane 3 shows [35S]methionine-labelled protein pulled-down by the wild-type 22-mer peptide, and lanes 4-12 show protein pulled down by the peptides with Ala substitutions across residues 332-340.
B) Ala-scanning substitutions were introduced into the (SGSG)SEMEELDSAPGSVKQNGP peptide between residues equivalent to Glu-371 and Ser-374 and Pro-376 and Lys-380 in the Neh6 domain (the residues changed are shown underlined). As above, lane 1 represents total [35S]methionine-labelled in vitro translated protein, lane 2 shows protein pulled-down by the ETGE peptide, lane 3 shows protein pulled-down by the wild-type 22-mer peptide. Lanes 4-7 show [35S]methionine-labelled protein pulled down by the peptides with Ala substitutions across residues 371-374, and lanes 8-12 show protein pulled down by peptide with Ala substitutions across residues 376-380.
C) The biotinylated-peptide pull-down assay was used to test whether double phosphorylation of the peptides increased their binding by β-TrCP; the phosphorylated residues are indicated in bold italics in the peptide shown above the gel. Lane 1 represents total [35S]methionine-labelled in vitro translated protein, and lane 2 shows protein pulled down by the ETGE-containing peptide based on the Neh2 domain. Lanes 3 and 4 show the protein pulled-down by DSGIS- and DpSGIpS-containing peptides. Lanes 5 and 6 show that the SDSEME- and pSDpSEME-containing peptides did not pull-down protein. Lanes 7 and 8 show the protein pulled-down by DSAPGS- and DpSAPGpS-containing peptides.
D) The effect of individual phosphorylation of Ser-333, Ser-335, Ser-338 and Ser-342 across the DSGIS-containing peptide on binding by β-TrCP was examined by pull-down assay. Lane 1 shows total [35S]methionine-labelled in vitro translated protein, and lane 2 shows protein pulled-down by the ETGE-containing peptide based on the Neh2 domain. Lanes 3 and 9 show protein bound to the non-phosphorylated DSGIS-containing peptide. Lanes 4-8 show the protein bound to the DSGIS-containing peptide in which only Ser-335 is phosphorylated, only Ser-338 is phosphorylated, both Ser-335 and Ser-338 are phosphorylated, Ser-333, Ser-335 and Ser-338 are phosphorylated, and Ser-335, Ser-338 and Ser-342 had been phosphorylated, respectively.
The peptide pull-down assay was next employed to test whether binding of β-TrCP to peptides containing DSGIS or DSAPGS was influenced by phosphorylation. An increase in binding between the immobilized DSGIS-containing peptide and β-TrCP was observed on phosphorylation of Ser-335 and Ser-338, giving DpSGIpS (Figure 7C). By contrast, no increase in binding between the immobilized DSAPGS-containing peptide and β-TrCP was observed on phosphorylation of Ser-374 and Ser-378, giving DpSAPGpS.
The biotinylated-peptide pull-down assay was also used to test whether the increase in binding of β-TrCP to phosphorylated DSGIS was due to either Ser-335 and/or Ser-338. The data in Figure 7D indicate that β-TrCP binds DSGIS-containing peptides with a single phosphorylation at either Ser-335 or Ser-338 better than the unphosphorylated peptide. Moreover, relative to the di-phosphorylated peptide at Ser-335 and Ser-338 (i.e. DpSGIpS338), β-TrCP did not show a further increase in binding towards tri-phosphorylated peptides with additional phosphoserines at positions 333 or 342.
Activation of GSK-3 decreases Nrf2 protein levels and increases sensitivity to anti-cancer drugs
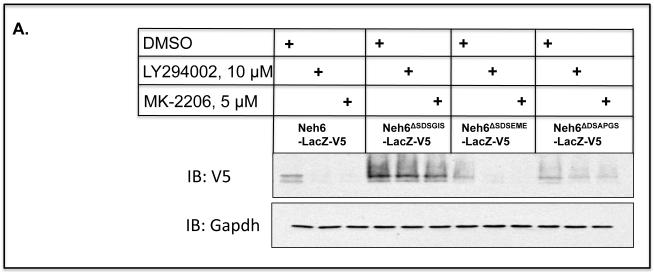
GSK-3α and GSK-3β are negatively regulated by phosphorylation of their Ser-21 and Ser-9 residues, respectively (31,32). We hypothesised that augmenting the activity of GSK-3α/β by blocking phosphorylation of Ser-21/Ser-9 might down-regulate Nrf2, as a consequence of maximizing phosphorylation of the DSGIS motif and thus its turnover via SCFβ-TrCP. To test this idea, we used inhibitors to prevent protein kinase B (PKB)/Akt from inactivating GSK3α/β; LY294002 was used to inhibit the upstream phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and MK-2206 was used to inhibit the proximal PKB/Akt. Treatment of COS1 cells that had been transfected with an expression plasmid encoding Neh6(LacZ)-V5 for 8 h with 10 μM LY294002 or 5 μM MK-2206 decreased the amount of the V5-tagged ‘wild-type’ Neh6-LacZ fusion protein by 80% (Figure 8A). However, the amount of the V5 epitope detected from the Neh6ΔSDSGIS(LacZ)-V5 mutant was not affected by LY294002 or MK-2206. As anticipated, the levels of both Neh6ΔSDSEME(LacZ)-V5 and Neh6ΔDSAPGS(LacZ)-V5 were diminished by LY294002 or MK-2206. These observations suggest that the PI3K-PKB/Akt pathway regulates Nrf2 activity via the DSGIS motif.
Figure 8.
Nrf2 is down-regulated by prevention of the inhibitory phosphorylation of GSK-3
A) COS1 cells were transfected with a pcDNA3.1 expression vector for a V5-tagged fusion protein comprising Neh6(LacZ)-V5 or Neh6(LacZ)-V5 bearing individual deletion of the SDSGIS338, SDSEME370 and DSAPGS378 from the Neh6 domain for 24 h. Twenty-four h later the cells were serum depleted by transfer to DMEM containing 0.1% (v/v) FBS for a further 16 h before the cells were treated with either 10 μM LY294002, 5 μM MK-2206 or with vehicle (0.1% (v/v) DMSO) in media containing 0.1% (w/v) FBS for 8 h. Whole-cell lysates were harvested and proteins were resolved in SDS-PAGE and gels were immuno-blotted with the indicated antibodies. The antibody that recognised phospho-GSK-3β (Ser-9) was from Abcam (ab30619). Gapdh was used as an internal control.
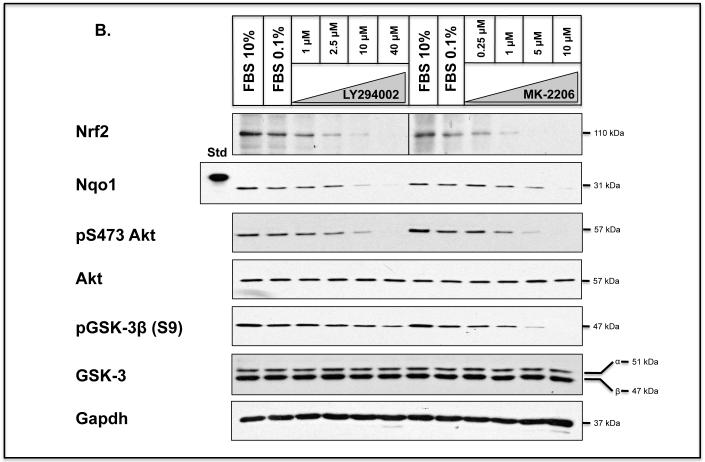
B) Keap1−/− MEFs were seeded in 60 mm petri-dishes in DMEM containing 10% FBS 24 h prior to serum depletion (0.1% FBS) for a further 16 h. Thereafter, the cells were treated for 8 h with 1.0, 2.5, 10 or 40 μM LY294002 or 0.25, 1.0, 5.0 or 10 μM MK-2206, all of which were dissolved in DMSO to a final concentration of 0.1% (by vol), in media containing 0.1% (w/v) FBS; 0.1% (v/v) DMSO was used as vehicle control. Whole-cell lysates were harvested and proteins were resolved in SDS-PAGE and gels were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Gapdh was used as a sample loading control.
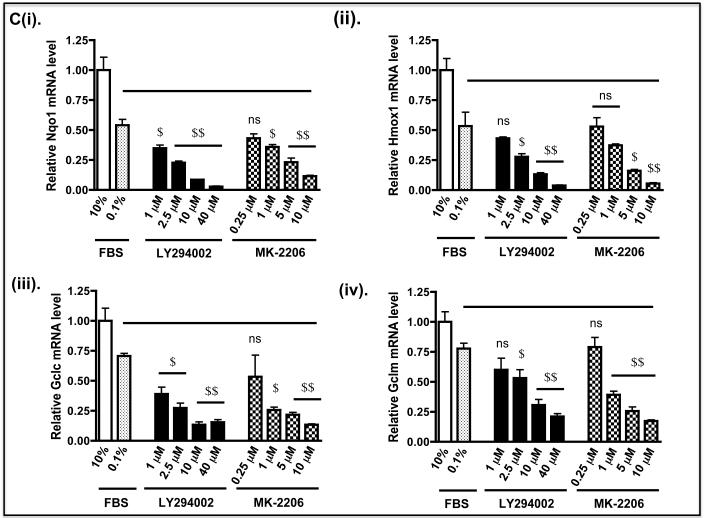
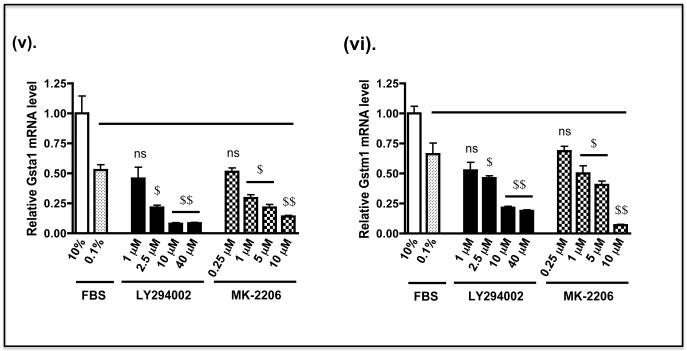
C) Keap1−/− MEFs were grown in 60 mm petri-dishes in DMEM containing 10% FBS 24 h prior to serum depletion (0.1% FBS) for 16 h, as described in panel B above. The fibroblasts were then treated with LY294002 or MK-2206 in medium containing 0.1% FBS, at the doses indicated, for 2 h before they were transferred to fresh medium containing 0.1% FBS for 6 h. Thereafter, the fibroblasts were harvested, total RNA extracted, and mRNA for Nqo1, Hmox1, Gclc, Gclm, Gsta1 and Gstm1 measured by TaqMan chemistry as described by Higgins et al (61). The solid horizontal bar indicates that mRNA levels in MEFs treated with kinase inhibitors in medium containing 0.1% FBS were compared with MEFs treated with DMSO vehicle control in medium containing 0.1% FBS.
To test whether activation of GSK-3 in Keap1−/− MEFs results in a loss of endogenous Nrf2 protein, we treated the fibroblasts with LY294002 or MK-2206. Treatment of the knockout MEFs with increasing concentrations of either LY294002 or MK-2206 for 8 h resulted in a substantial decrease in the amount of Nrf2 protein at the higher doses of inhibitor (Figure 8B). The reduction in Nrf2 protein levels coincided with a decrease in inhibitory phosphorylation of GSK-3β at Ser-9, and loss of activating phosphorylation of PKB/Akt at Ser-473. These data suggest failure to inhibit GSK-3 by its N-terminal phosphorylation is associated with increased turn-over of the CNC-bZIP transcription factor.
The biochemical consequence of Nrf2 down-regulation in Keap1−/− MEFs by LY294002 or MK-2206 was examined by measuring expression of endogenous ARE-driven genes. At the doses used, we found treatment of fibroblasts with LY294002 for 2 h followed by transfer to fresh medium containing 0.1% FBS for a further 6 h produced marginally greater decreases in mRNA levels for Nqo1, heme oxygenase-1 (Hmox1), glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic (Gclc) and modifier (Gclm) subunits, and glutathione S-transferase Alpha-1 (Gsta1) and Mu-1 (Gstm1) subunits than did MK-2206 (Figure 8C). Specifically, the mRNA species for Nqo1, Hmox1, Gclc, Gclm, Gsta1 and Gstm1 were reduced by 10 μM LY294002 to 18%, 28%, 21%, 24%, 16% and 36% of control levels, respectively, whereas the same mRNAs were decreased by 5 μM MK-2206 to 42%, 33%, 32%, 33%, 42% and 61% of control, respectively.
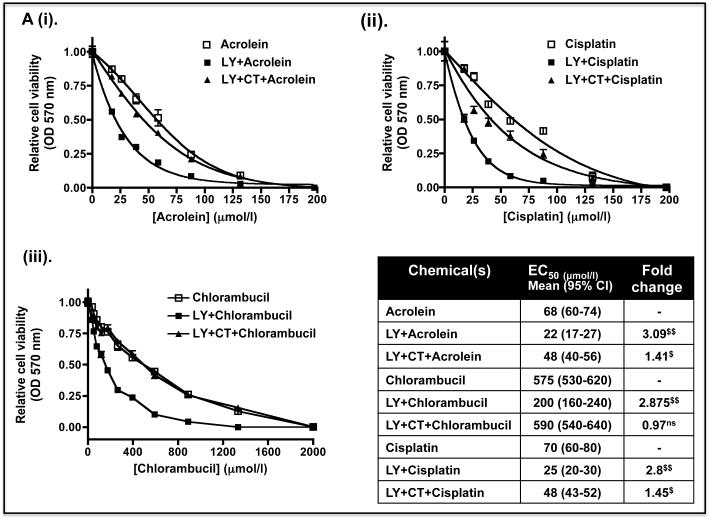
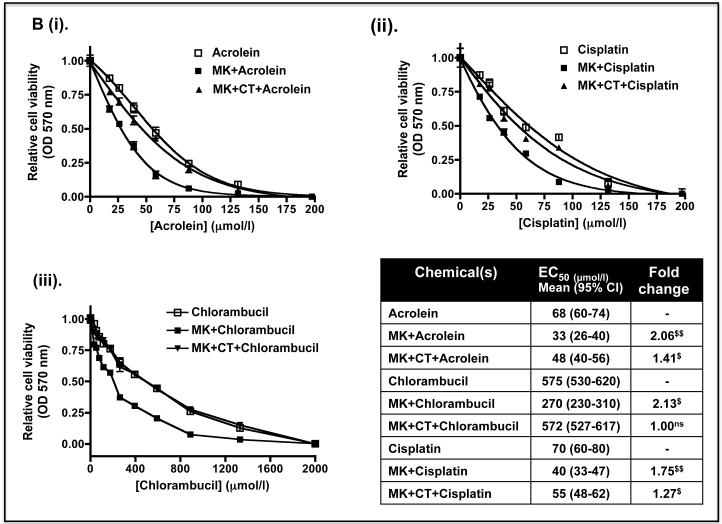
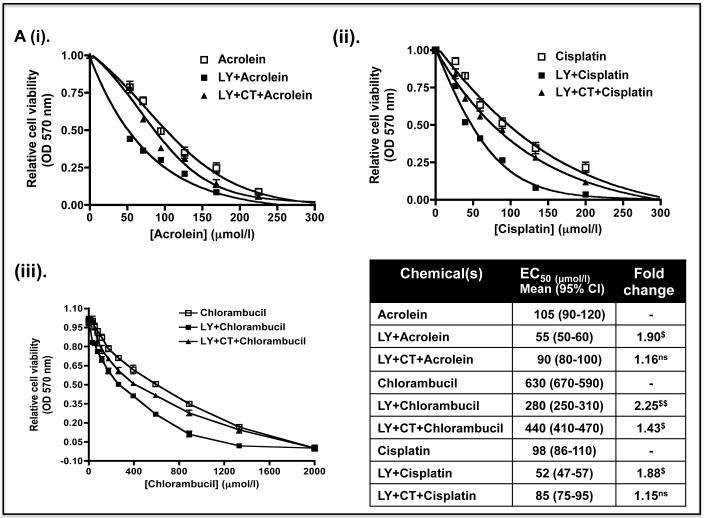
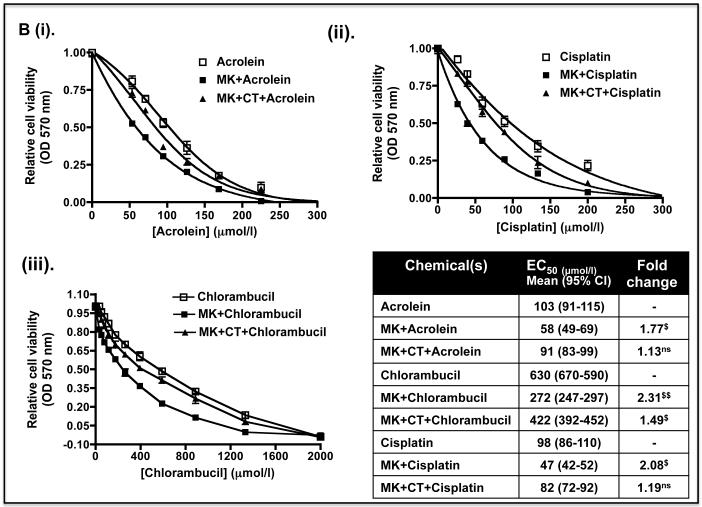
To test whether the decreases in Nrf2 protein and its target genes caused by LY294002 and MK-2206 might increase sensitivity to anticancer drugs, Keap1−/− MEFs were pre-treated with 10 μM LY294002 or 5 μM MK-2206 for 8 h before the fibroblasts were exposed to increasing doses of acrolein, cisplatin or chlorambucil. Figure 9A shows that the EC50 dose of acrolein, cisplatin and chlorambucil was 68, 575 and 70 μmol/l in Keap1−/− MEFs that had not been pre-treated with either LY294002 or MK-2206. However, the EC50 values for acrolein, cisplatin and chlorambucil were reduced to 22, 200 and 25 μmol/l, respectively, when they were pre-treated with the PI3K inhibitor. Figure 9B shows that the EC50 dose of acrolein, cisplatin and chlorambucil was reduced to 33, 270 and 40 μmol/l when the fibroblasts were pre-treated with the PKB/Akt inhibitor MK-2206. Thus, pre-treatment of Keap1−/− MEFs with LY294002 or MK-2206 can increase their sensitivity towards acrolein, cisplatin and chlorambucil between 1.8-fold and 3.1-fold. Inclusion of the GSK-3 inhibitor CT99021 with the kinase inhibitor pre-treatment regimen abolished the increased sensitivity to chlorambucil conferred by LY294002 or MK-2206. However, CT99021 only partially countered the increased sensitivity towards acrolein and cisplatin conferred by LY294002 or MK-2206. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that the increased sensitivity caused by LY294002 or MK-2206 towards chlorambucil requires de-repression of GSK-3 activity, whereas this is only partially true for acrolein and cisplatin.
Figure 9.
The sensitivity of Keap1−/− MEFs to anti-cancer drugs is increased by prevention of inhibitory phosphorylation of GSK-3
Keap1-null MEFs (1.32 × 104) were seeded in 96-well microtitre plates 24 h prior to serum depletion (0.1% FBS) for a further 16 h. The cells were then pre-treated for 8 h with (A) 10 μM LY29400 2 or 10 μM LY294002 plus 5 μM CT99021 (B) 5 μM MK-2206 or 5 μM MK-2206 plus 5 μM CT99021 in media containing 0.1% (w/v) FBS; in both (A) and (B) the kinase inhibitors were dissolved in DMSO to a final concentration of 0.1% (by volume). Thereafter, the MEFs were challenged for 48 h with increasing doses of acrolein (dissolved in ethanol), cisplatin (dissolved in media), chlorambucil (dissolved in DMSO) or a constant amount of vehicle control in media containing 0.1% (w/v) FBS. Finally, MTT was added to each of the wells and cell viability assessed by reduction of the dye (OD570), as described in the Materials and Methods section. The relative viability of Keap1−/− MEFs following exposure to different concentrations of acrolein, cisplatin or chlorambucil is shown as mean values ± SEM from three separate experiments. The EC50 dose represents the effective concentration of acrolein, cisplatin or chlorambucil required to reduce the viability of Keap1-null MEFs to 50% of maximum; the EC50 results shown in the table are mean values, with standard deviation as the 95% confidence interval presented in parenthesis. The statistical significance of differences in EC50 of Keap1-null MEFs for acrolein, cisplatin or chlorambucil with or without pre-treatment with LY294002 and/or CT99021, or MK-2206 and/or CT99021 were calculated by Two-Way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-tests.
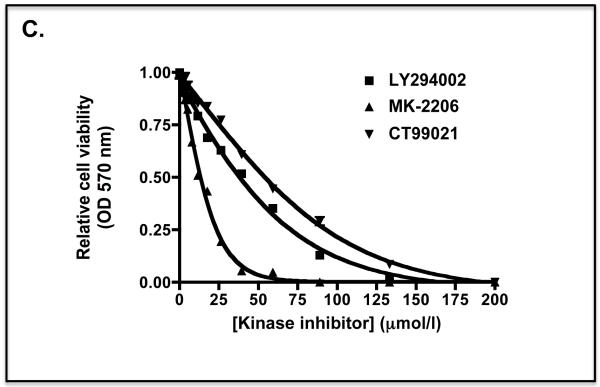
C) The MTT curve for Keap1-null MEFs treated for 48 h with different doses of LY294002 or MK-2206 in medium containing 0.1% FBS is shown as a control.
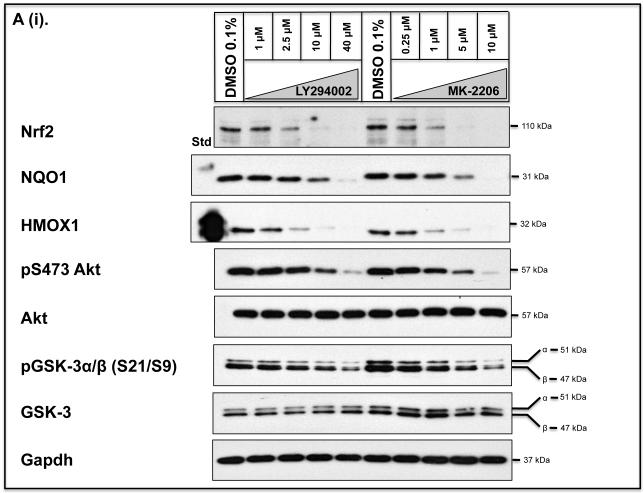
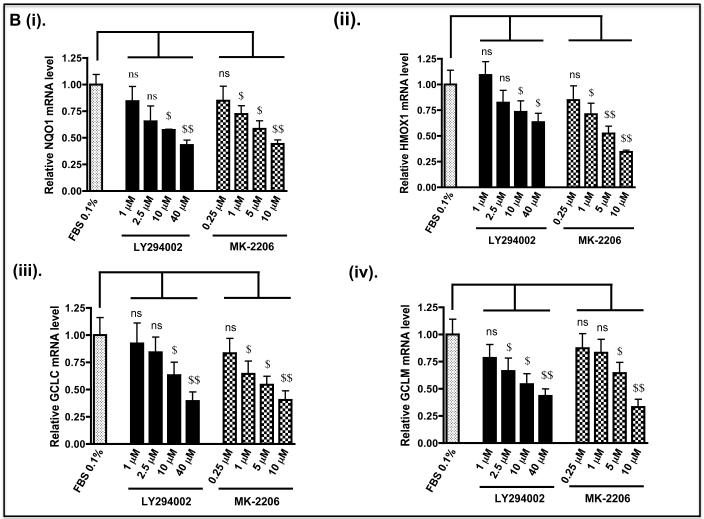
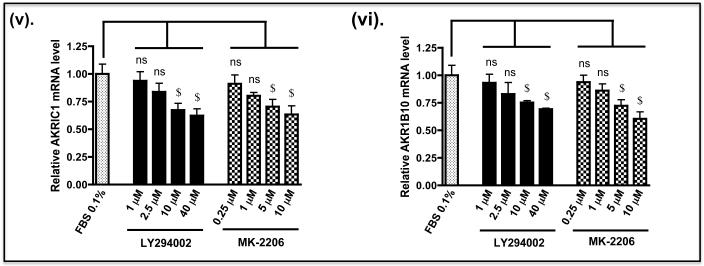
As the above experiments were performed in Keap1-null MEFs, we also examined whether de-repression of GSK-3 might decrease the expression of Nrf2-target genes in human cells with mutant Keap1, and render them more sensitive to anticancer drugs. To this end we examined human pulmonary epithelial A549 cells as they have been reported to harbour Keap1 encoding a protein with a Gly to Cys change at amino acid 333 (14) and to exhibit hypermethylation of the Keap1 promoter (17). Figure 10A shows that treatment of A549 cells with LY294002 or MK-2206 decreased significantly the level of Nrf2 protein and this was associated with both a decrease in activating phosphorylation of Ser-473 in PKB/Akt and a loss of inhibitory phosphorylation of GSK-3 β at Ser-9. Following treatment of A549 cells with LY294002 or MK-2206, the amount of mRNA for NQO1, HMOX1, GCLC and GCLM was decreased to 10%-50% of normal (Figure 10B). However, the decrease in mRNA for aldo-keto reductase (AKR) 1B10 and AKR1C1, both of which are members of the human ARE-gene battery (3), was not so obvious. As was the case with Keap1−/− MEFs, treatment of A549 cells with LY294002 or MK-2206 increased the sensitivity of the human lung cells to acrolein, cisplatin and chlorambucil (Figure 11).
Figure 10.
Down-regulation of Nrf2 in human lung A549 cells decreases expression of cytoprotective genes
A) A549 cells were seeded and grown in DMEM that contained 10% FBS for about 24 h before transfer to DMEM containing 0.1% FBS for 16 h. The cells were then treated for 8 h with various doses of either LY294002 or MK-2206 in DMEM containing 0.1% FBS, as indicated, before lysates were prepared and the levels of individual proteins measured by Western blotting. The antibody that recognised both phospho-GSK-3α (Ser-21) and phospho-GSK-3β (Ser-9) was from Cell Signalling (#9331).
B) A549 cells were grown as described above. After serum depletion for 16 h, they were treated for 2 h with various doses of LY294002 or MK-2206 and transferred to fresh DMEM containing 0.1% FBS for a further 6 h before being harvested. Messenger RNA levels were measured by TaqMan RT-PCR.
Figure 11.
The sensitivity of A549 cells to chemotherapeutic agents is increased by inhibition of the PI3K-PKB/Akt pathway
A549 cells were seeded and grown in 96-well plates for 24 h before being subjected to serum depletion (in 0.1% FBS) for 16 h.
A) The A549 cells were then pretreated for 8 h with LY294002, or LY294002 plus CT99021, before they were challenged with various doses of acrolein, cisplatin or chlorambucil for 48 h and cytotoxicity measured using the MTT assay.
B) The A549 cells were pretreated with MK-2206, or MK-2206 plus CT99021, for 8 h before being exposed to acrolein, cisplatin or chlorambucil for 48 h and MTT cytotoxicity testing performed.
C) An MTT curve for A549 cells treated for 48 h with different doses of LY294002, MK-2206 or CT99021 in medium containing 0.1% FBS is shown as a control.
Discussion
Many short-lived regulatory proteins that contribute to tumourigenesis are controlled by ubiquitylation via SCFβ-TrCP (33). Originally, β-catenin and IκBα were identified as substrates for SCFβ-TrCP and shown to contain similar destruction motifs, with the consensus sequence DSGΦXS (where Φ is a hydrophobic residue, and X is any amino acid), to which β-TrCP binds following their phosphorylation by GSK-3 (34,35). Herein we report the identification of two non-identical binding motifs for β-TrCP within the Neh6 domain of Nrf2. One of these is the non-prototypic sequence DSGIS, which is conserved in vertebrate species, and has been observed previously in the erythropoietin receptor (36) and in the Yes-associated protein (YAP) transcription coactivator (37). The second β-TrCP-binding site in Nrf2 is the peptide sequence DSAPGS, which has not been identified before. It does however resemble the destruction motifs in the Cdc2 inhibitory kinase Wee1A (i.e. DSAFQE) and in the NF-κB 2 gene product p100 (i.e. DSAYGS) (38,39). Both the DSGIS and DSAPGS motifs in the Neh6 domain of Nrf2 are each sufficient to enable ubiquitylation of the CNC-bZIP protein by SCFβ-TrCP.
GSK-3 activity antagonises Nrf2 (25), and this has been postulated to entail the formation of a phosphodegron that is recognised by β-TrCP (28). The present study indicates that the DSGIS destruction motif in Nrf2 is influenced by GSK-3 whereas the DSAPGS motif is not. Our in vitro biotinylated peptide pull-down assay indicated that non-phosphorylated DSGIS- and DSAPGS-containing peptides are recognised by β-TrCP suggesting that GSK-3 activity is not essential for SCFβ-TrCP ubiquitylation of Nrf2. However, the pull-down assay also revealed that phosphorylated DSGIS-containing peptides are bound more avidly by β-TrCP than the non-phosphorylated peptide, whereas this was not the case for the DSAPGS-containing peptide. These findings are consistent with the mammalian two-hybrid experiment, which showed that the interaction between Nrf2-derived proteins containing the DSGIS peptide and the β-TrCP substrate adaptor (or its WD-40 domain) was diminished, but not abolished, by treatment with the GSK-3 inhibitor CT99021.
Through creating a phosphodegron in Nrf2 that is recognized by SCFβ-TrCP, it seems that GSK-3 provides a pivotal control hub by which the CNC-bZIP factor can be both up- and down-regulated. The activity of GSK-3α/β is positively regulated by phosphorylation of a “T-loop” Tyr residue (Tyr-279 in GSK-3α, Tyr-216 in GSK-3β) and negatively regulated by phosphorylation of an N-terminal Ser residue (Ser-21 in GSK-3α, Ser-9 in GSK-3β) (40). Also, GSK-3β is inactivated by p38 MAPK-mediated phosphorylation of Ser-389 and Thr-390, and by ERK-mediated phosphorylation of Thr-43. PKB/Akt represents an important negative regulator of GSK-3α/β, and in this study we have used the PKB/Akt inhibitor MK-2206 and the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 to increase GSK-3 activity, and thus down-regulate Nrf2. It is well documented that GSK-3 can be inhibited by the actions of ERK, p38 MAPK, PI3K and PKC (40). Interestingly, these kinases have been reported to influence ARE-driven gene expression (41-47) but it remains unclear whether they alter Nrf2 activity by direct or indirect mechanisms (48). Notably, Rojo et al (49) have proposed that the phytochemical nordihydroguaiaretic acid stimulates Nrf2-mediated induction of ARE-driven genes by activating the PI3K-PKB/Akt pathway, which in turn inhibits GSK-3 and prevents formation of the Neh6-phosphodegron recognised by SCFβ-TrCP. We now propose that ERK, p38 MAPK and PKC may all similarly regulate Nrf2 indirectly by inhibiting GSK-3. In addition, a ‘priming’ kinase is required to phosphorylate a substrate before GSK-3 is able to carry out further modifications (50). In the case of Nrf2, the identity of the ‘priming’ kinase is unknown, but this represents another point at which formation of the DpSGIpS phosphodegron might be controlled.
A key question concerns the relationship between β-TrCP and Keap1. Whilst both CRLKeap1and SCFβ-TrCP function independently, it is not known to what extent each influences the expression of Nrf2-target genes under normal homeostatic conditions. Furthermore, it is unclear to what extent SCFβ-TrCP restrains the expression of Nrf2-target genes when inducing agents inhibit CRLKeap1. One possibility is that CRLKeap1 and SCFβ-TrCP have tissue-specific effects with the activity of the latter being influenced by metabolism and proliferation. Another is that Keap1 and β-TrCP regulate Nrf2 in different sub-cellular compartments. It is widely accepted that Keap1 is located primarily in the cytoplasm (51). By contrast it is possible that β-TrCP regulates Nrf2 predominantly in the nucleus. Discrepancies unfortunately exist regarding the sub-cellular localization of the β-TrCP1 and β-TrCP2 isoforms and their splice variants (β-TrCP1α, β-TrCP1β, β-TrCP2α, β-TrCP2β and β-TrCP2γ) (52,53). Interestingly, other components of the ubiquitylation machinery, including Cdc34, Skp1 and Cul-1, have been identified within the nucleus (54). Therefore it is likely that degradation of Nrf2 by SCFβ-TrCP is, at least in part, a nuclear event.
Activation of the Neh6 phosphodegron in Nrf2 that is created by GSK-3 represents a strategy by which overexpression of the CNC-bZIP factor might be countered in drug-resistant tumours with somatic mutations in Keap1. However, down-regulation of Nrf2 is likely to sensitize normal tissues to the toxic effects of anticancer agents, and therefore therapeutic selectivity needs to be considered carefully before embarking on this approach. We envisage that down-regulation of Nrf2 might provide therapeutic selectivity in the treatment of tumours that endure a higher burden of reactive oxygen species (ROS) than normal tissues. Specifically, tumours harbouring oncogenic Ras, Bcr-Abl or Myc produce relatively high levels of ROS (55), and at least some of these are likely to be dependent on Nrf2 for survival (23). It might be imagined that tumours harbouring oncogenes that increase ROS production would be more susceptible than normal tissues to apoptosis stimulated by oxidative stress, and that this potential vulnerability could be increased further by the administration of drugs that increase ROS levels.
In conclusion, we have demonstrated that the Neh6 domain of Nrf2 contains two distinct destruction motifs, the activity of one of which, DSGIS, is increased by GSK-3 activity (see Figure 12 for a model). Thus, in tumours in which Nrf2 is constitutively up-regulated, stimulation of the DSGIS degron by activation of GSK-3 represents a potentially useful therapeutic approach to overcome drug resistance and inhibit cell proliferation.
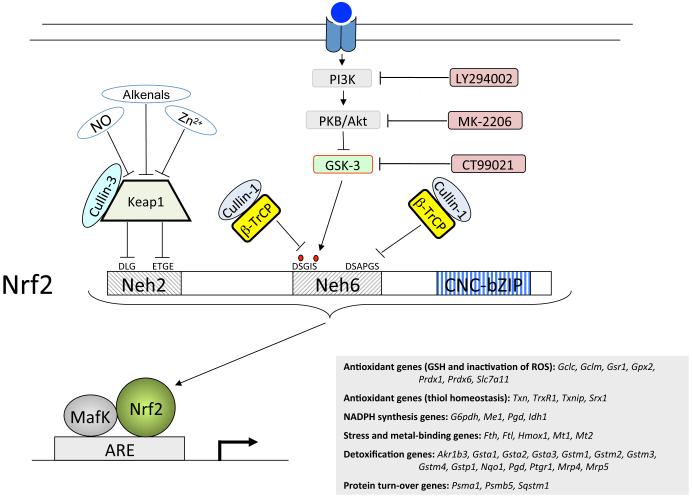
Figure 12.
Repression of Nrf2 by β-TrCP occurs in both a GSK-3-dependent and a GSK-3-independent manner
Nrf2 is subject to dual regulation by Keap1 and β-TrCP. The cartoon shows that Nrf2 is repressed by Keap1 though DLG and ETGE motifs in its Neh2 domain, both of which are required for ubiquitylation of the CNC-bZIP protein by Cul3-Rbx1. By contrast, Nrf2 is repressed by β-TrCP though DSGIS and DSAPGS motifs in its Neh6 domain, each of which is sufficient for ubiquitylation of the CNC-bZIP protein by Cul1-Rbx1. Phosphorylation of the DSGIS motif increases its degron activity, and this is positively regulated by GSK-3. The GSK-3 inhibitor CT99021 decreases the degron activity of the DSGIS destruction motif whereas PI3K and PKB/Akt inhibitors increase the degron activity of the DSGIS motif. By contrast, the DSAPGS destruction motif is not influenced by GSK-3 activity.
Materials and Methods
Chemicals
The GSK-3 inhibitor CT99021 was synthesized as described elsewhere (56). Other chemicals were commercially available.
Expression plasmids
Expression plasmids for C-terminally V5-tagged wild-type mouse Nrf2 (Nrf2-V5) and Nrf2Δ17-32-V5 (i.e. pcDNA3.1/V5mNrf2 and pcDNA3.1/V5mNrf2Δ17-32) have been described previously (4,24). We created the following deletions within pcDNA3.1/V5mNrf2 by site-directed mutagenesis (SDM) using primers listed in Table 1 in the Supplemental Material: Δ3-96 (called ΔNeh2), Δ300-385 (called ΔNeh6), Δ329-342 (called ΔSDS1), Δ333-338 (called ΔSDSGIS), Δ347-362 (called ΔN-PEST), Δ350-380 (called ΔPEST), Δ363-379 (called ΔC-PEST or ΔSDS2), Δ365-370 (called ΔSDSEME) and Δ373-378 (called ΔDSAPGS).
An expression plasmid for a YFP-Neh6 fusion protein was created by ligating the cDNA encoding amino acids 300-380 of mouse Nrf2 into the BamHI/XbaI site in the pEYFP-C1 plasmid (Clontech) to yield a vector for YFP fused at its C-terminus to the N-terminal end of Neh6 called pEYFP-C1/mNeh6. This plasmid was used as a template to generate deletion mutants within Neh6 by SDM.
An expression construct for N-terminally hexahistidine-Xpress tagged mouse β-TrCP1 protein (pcDNA4/HisMaxBmβTrCP1) was generated by PCR of the mouse β-TrCP1 coding region in IMAGE clone 3491843 using oligonucleotides bearing mismatches that introduced BamHI and XhoI sites, and following restriction the product was ligated into pcDNA4/HisMaxB (Invitrogen). In order to create an expression vector for a C-terminal FLAG-tagged form of β-TrCP1, the DYKDDDDK epitope was engineered into the β-TrCP1 TAA stop codon within pcDNA4/HisMaxBmβTrCP1 and the nonsense codon was reintroduced immediately C-terminal to the epitope, giving pcDNA4/HisMaxBmβTrCP1-FLAG. An expression construct for mouse β-TrCP1 that uses the T7 promoter was created by subcloning the cDNA for β-TrCP1 into the BamHI/XhoI site of pcDNA3 to give pcDNA3/HismβTrCP1.
For mammalian two-hybrid experiments, cDNA encoding amino acids 300-380 of mouse Nrf2, and the various deletion mutants therein, were ligated into the BamHI/EcoRI site in pcDNA3.1/Gal4D-V5 (57) to give a plasmid encoding the Gal4 DNA-binding domain fused at its C-terminus to Neh6 (i.e. Gal4(DBD)-Neh6), which was called pcDNA3.1/Gal4(DBD)-Neh6. The cDNA encoding amino acids 303-581 of mouse β-TrCP1, comprising the WD-40 domain, was ligated into the BamHI/HindIII site in the Gal4 activation domain plasmid pVP16, giving the plasmid pV16/WD40 that encoded Gal4(AD)-WD40.
For LacZ reporter experiments, cDNA encoding amino acids 290-410 of mouse Nrf2, and various deletion mutants, were ligated into the KpnI/BamHI site in pcDNA3.1/V5-His/lacZ. A nuclear localization signal, RKKKRKV, from SV40 was engineered to be contiguous with both the C-terminus of amino acids 290-410 from Nrf2 and the N-terminus of LacZ, giving the plasmid pcDNA3.1/V5mNeh6-NLS-LacZ that encoded a Neh6-LacZ-V5 fusion protein.
Expression vectors for N-terminally HA-tagged constitutively active GSK-3βΔ9 (pCGN/GSK-3βΔ9) and N-terminally HA-tagged kinase-dead GSK-3βY216F (pCGN/GSK-3βY216F) have been reported previously (58,59).
Cell biology
Keap1−/− MEF, COS1 and A549 cells were routinely grown in Delbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium containing 10% FBS (28). The ability of various Nrf2-V5 mutant proteins to co-IP with FLAG-tagged β-TrCP1 was assessed by standard methods (7). ARE-driven reporter gene expression was determined as described previously (2). In vivo ubiquitylation was determined by the method of Treier et al (60). MTT cytotoxicity testing was performed as described elsewhere (61).
Mammalian two-hybrid assay
COS1 cells were co-transfectased with expression vectors for Gal4(DBD)-Neh6, or one of its deletion mutants, and Gal4(AD)-WD40 protein along with the Gal4-driven luciferase reporter plasmid PTKUAS-Luc and the pRL-TK Renilla Luciferase reporter vector that was used to control for transfection efficiency (57). Approximately 48 h after transfection, the cells were serum-depleted by transfer to media containing 0.5% FBS for 16 h before luciferase activity was measured. Results were normalized to the Renilla luciferase luminescence.
Peptide binding assay
The ability of β-TrCP1 to bind peptides designed around possible destruction motifs in the Neh6 domain of Nrf2 was examined by a peptide pull-down assay (62). The peptides studied comprised 22 amino acids, each including the tetra-peptide SGSG sequence at the N-terminus that was coupled to Biotin, and the remainder representing amino acids 327-344, 359-376 or 367-384 from mouse Nrf2; see Tables 2 and 3 in the Supplemental Material. In the assay, [35S]methionine-labelled mouse β-TrCP1, produced from pcDNA3/HismβTrCP1 using a TNT Quick Coupled Transcription/Translation System (Promega), was tested for its ability to adsorb to the above synthetic peptides that had been biotinylated and coupled to Streptavidin-agarose beads overnight. The in vitro translated and labelled β-TrCP1 protein was allowed to interact for 120 min at 4°C with the immobilized peptides, and after extensive washing the relative amount of protein bound to given aliquots of the beads was determined by measurement of the amount of [35S]methionine-labelled protein of correct size when examined by autoradiography following SDS/PAGE.
Protein and mRNA analyses
Immunoblotting was performed by standard methods. Antibodies that cross-react with phospho Ser-9 of GSK-3β (ab30619) were from Abcam, and those that recognise both phospho Ser-21 of GSK-3 α and phospho Ser-9 of GSK-3β (#9331) were from Cell Signalling. Antibodies against Nrf2, Nqo1 and Hmox1 have been described previously (2,7,49). Other antibodies were readily available from commercial sources. Measurement of mRNA levels in Keap1-null MEFs and A549 cells was carried out by TaqMan reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) as described previously (2,61,63).
Statistical analyses
The significance of results was assessed using GraphPad Prism 5 software and either One-Way ANOVA or Two-Way ANOVA, Newman-Keuls Multiple Comparison Test. Mean ± SD results in which the P value was >0.05 were deemed to be not significant (ns). Increases in the mean ± SD results for which the P values were between 0.05 and 0.01, between 0.01 and 0.001, or <0.001 are indicated by single, double, or triple asterisks (*), respectively. Similarly, the significance of decreases in mean ± SD results is indicated by single, double, or triple dollar signs ($).
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to Professor Masayuki Yamamoto for supplying Keap1-null MEFs, and thank Dr Akira Kikuchi for the gift of the pCGN/GSK-3βΔ9 and pCGN/GSK-3βY216F expression plasmids. We thank Professor Ronald T. Hay and Dr David W. Meek for valuable advice in establishing the peptide pull-down assay, and Dr Albena T. Dinkova-Kostova and Professor C. Roland Wolf for helpful suggestions. We gratefully acknowledge Tenovus Scotland (T07/39), the Association for International Cancer Research (09-0254) and Cancer Research UK (C4909/A9990; C4909/A13786) for funding this work.
Grant support: This work was funded by Tenovus Scotland (T07/39), the Association for International Cancer Research (09-0254) and Cancer Research UK (C4909/A9990; C4909/A13786).
Footnotes
Nrf2 is sometimes referred to as NF-E2-like 2 (nfe2l2).
Note that two mammalian β-TrCP paralogues exist (i.e. β-TrCP1 and β-TrCP2) which possess similar properties. In this paper we have employed the general term β-TrCP, rather than defining the isoform, unless specific experimental details are described.
Throughout this paper expression constructs encoding mouse Nrf2 have been studied, and thus the numbering of amino acids is based on the murine CNC-bZIP transcription factor.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary information
This describes the oligonucleotide primers used to create expression vectors (Table 1) and peptides used to define sequences in the Neh6 domain of Nrf2 that can be bound by β-TrCP (Tables 2 and 3). This is available at the Oncogene website.
Contacts
Sudhir Chowdhry: Phone: +44 (0)1382 632788. S.Chowdhry@dundee.ac.uk, Yiguo Zhang: Phone: +44 (0)1382 425617. y.z.zhang@dundee.ac.uk, Michael McMahon: Phone: +44 (0)1382 660111. m.j.m.mcmahon@dundee.ac.uk, Calum Sutherland: Phone: +44 (0)1382 632507. c.d.sutherland@dundee.ac.uk, Antonio Cuadrado: Phone: +34 915854383. antonio.cuadrado@uam.es, John D. Hayes: Phone: +44 (0)1382 632788. j.d.hayes@dundee.ac.uk
References
- 1.Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N, Biswal S. Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;47:89–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.46.120604.141046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nioi P, McMahon M, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Hayes JD. Identification of a novel Nrf2-regulated antioxidant response element (ARE) in the mouse NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 gene: reassessment of the ARE consensus sequence. Biochem J. 2003;374:337–348. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hayes JD, McMahon M, Chowdhry S, Dinkova-Kostova AT. Cancer chemoprevention mechanisms mediated through the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010;13:1713–1748. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McMahon M, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Hayes JD. Keap1-dependent proteasomal degradation of transcription factor Nrf2 contributes to the negative regulation of antioxidant response element-driven gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:21592–21600. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300931200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nguyen T, Sherratt PJ, Huang HC, Yang CS, Pickett CB. Increased protein stability as a mechanism that enhances Nrf2-mediated transcriptional activation of the antioxidant response element. Degradation of Nrf2 by the 26 S proteasome. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:4536–4541. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207293200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Stewart D, Killeen E, Naquin R, Alam S, Alam J. Degradation of transcription factor Nrf2 via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and stabilization by cadmium. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:2396–2402. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209195200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.McMahon M, Thomas N, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Hayes JD. Dimerization of substrate adaptors can facilitate cullin-mediated ubiquitylation of proteins by a “tethering” mechanism: a two-site interaction model for the Nrf2-Keap1 complex. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:24756–24768. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M601119200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tong KI, Padmanabhan B, Kobayashi A, Shang C, Hirotsu Y, Yokoyama S, et al. Different electrostatic potentials define ETGE and DLG motifs as hinge and latch in oxidative stress response. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27:7511–7521. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00753-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Petroski MD, Deshaies RJ. Function and regulation of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:9–20. doi: 10.1038/nrm1547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kobayashi A, Kang MI, Okawa H, Ohtsuji M, Zenke Y, Chiba T, et al. Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:7130–7139. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.16.7130-7139.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhang DD, Lo SC, Cross JV, Templeton DJ, Hannink M. Keap1 is a redox-regulated substrate adaptor protein for a Cul3-dependent ubiquitin ligase complex. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:10941–10953. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.24.10941-10953.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kobayashi M, Li L, Iwamoto N, Nakajima-Takagi Y, Kaneko H, Nakayama Y, et al. The antioxidant defence system Keap1-Nrf2 comprises a multiple sensing mechanism for responding to a wide range of chemical compounds. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29:493–502. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01080-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.McMahon M, Lamont DJ, Beattie KA, Hayes JD. Keap1 perceives stress via three sensors for the endogenous signaling molecules nitric oxide, zinc, and alkenals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:18838–18843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007387107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Singh A, Misra V, Thimmulappa RK, Lee H, Ames S, Hoque MO, et al. Dysfunctional KEAP1-NRF2 interaction in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS Med. 2006;3:e420. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Singh A, Boldin-Adamsky S, Thimmulappa RK, Rath SK, Ashush H, Coulter J, et al. RNAi-mediated silencing of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 gene expression in non-small cell lung cancer inhibits tumor growth and increases efficacy of chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2008;68:7975–7984. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ohta T, Iijima K, Miyamoto M, Nakahara I, Tanaka H, Ohtsuji M, et al. Loss of Keap1 function activates Nrf2 and provides advantages for lung cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 2008;68:1303–1309. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang R, An J, Ji F, Jiao H, Sun H, Zhou D. Hypermethylation of the Keap1 gene in human lung cancer cell lines and lung cancer tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;373:151–154. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Konstantinopoulos PA, Spentzos D, Fountzilas E, Francoeur N, Sanisetty S, Grammatikos AP, et al. Keap1 mutations and Nrf2 pathway activation in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:5081–5089. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Muscarella LA, Parrella P, D’Alessandro V, la Torre A, Barbano R, Fontana A, et al. Frequent epigenetics inactivation of KEAP1 gene in non-small cell lung cancer. Epigenetics. 2011;6:710–719. doi: 10.4161/epi.6.6.15773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yoo NJ, Kim HR, Kim YR, An CH, Lee SH. Somatic mutations of the KEAP1 gene in common solid cancers. Histopathology. 2012;60:943–952. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2012.04178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shibata T, Ohta T, Tong KI, Kokubu A, Odogawa R, Tsuta K, et al. Cancer related mutations in NRF2 impair its recognition by Keap1-Cul3 E3 ligase and promote malignancy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:13568–13573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806268105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jiang T, Chen N, Zhao F, Wang XJ, Kong B, Zheng W, et al. High levels of Nrf2 determine chemoresistance in type II endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70:5486–5496. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.DeNicola GM, Karreth FA, Humpton TJ, Gopinathan A, Wei C, Frese K, et al. Oncogene-induced Nrf2 transcription promotes ROS detoxification and tumorigenesis. Nature. 2011;475:106–109. doi: 10.1038/nature10189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.McMahon M, Thomas N, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Hayes JD. Redox-regulated turnover of Nrf2 is determined by at least two separate protein domains, the redox-sensitive Neh2 degron and the redox-insensitive Neh6 degron. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:31556–31567. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403061200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Salazar M, Rojo AI, Velasco D, de Sagarra RM, Cuadrado A. Glycogen synthase kinase-3β inhibits the xenobiotic and antioxidant cell response by direct phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of the transcription factor Nrf2. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:14841–14851. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M513737200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rojo AI, Sagarra MR, Cuadrado A. GSK-3β down-regulates the transcription factor Nrf2 after oxidant damage: relevance to exposure of neuronal cells to oxidative stress. J Neurochem. 2008a;105:192–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rojo AI, Rada P, Egea J, Rosa AO, López MG, Cuadrado A. Functional interference between glycogen synthase kinase-3β and the transcription factor Nrf2 in protection against kainate-induced hippocampal cell death. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008b;39:125–132. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2008.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rada P, Rojo AI, Chowdhry S, McMahon M, Hayes JD, Cuadrado A. SCF/β-TrCP promotes glycogen synthase kinase 3-dependent degradation of the Nrf2 transcription factor in a Keap1-independent manner. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31:1121–1133. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01204-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wu G, Xu G, Schulman BA, Jeffrey PD, Harper JW, Pavletich NP. Structure of a β-TrCP1-Skp1-β-catenin complex: destruction motif binding and lysine specificity of the SCF(β-TrCP1) ubiquitin ligase. Mol Cell. 2003;11:1445–1456. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00234-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tsuchiya Y, Morita T, Kim M, Iemura S, Natsume T, Yamamoto M, Kobayashi A. Dual regulation of the transcriptional activity of Nrf1 by β-TrCP- and Hrd1-dependent degradation mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31:4500–4512. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05663-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sutherland C, Leighton I, Cohen P. Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β by phosphorylation; new kinase connections in insulin and growth factor signalling. Biochem J. 1993;296:15–19. doi: 10.1042/bj2960015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature. 1995;378(6559):785–789. doi: 10.1038/378785a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Frescas D, Pagano M. Deregulated proteolysis by the F-box proteins SKP2 and β-TrCP: tipping the scales of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:438–449. doi: 10.1038/nrc2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Aberle H, Bauer A, Stappert J, Kispert A, Kemler R. β-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. EMBO J. 1997;16:3797–3804. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.13.3797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Winston JT, Strack P, Beer-Romero P, Chu CY, Elledge SJ, Harper JW. The SCFβ-TRCP-ubiquitin ligase complex associates specifically with phosphorylated destruction motifs in IκBα and β-catenin and stimulates IκBα ubiquitination in vitro. Genes Dev. 1999;13:270–283. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.3.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Meyer L, Deau B, Forejtníková H, Duménil D, Margottin-Goguet F, Lacombe C, Mayeux P, Verdier F. β-Trcp mediates ubiquitination and degradation of the erythropoietin receptor and controls cell proliferation. Blood. 2007;109:5215–5222. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-10-055350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhao B, Li L, Tumaneng K, Wang CY, Guan KL. A coordinated phosphorylation by Lats and CK1 regulates YAP stability through SCFβ-TRCP. Genes Dev. 2010;24:72–85. doi: 10.1101/gad.1843810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fong A, Sun SC. Genetic evidence for the essential role of β-transducin repeat-containing protein in the inducible processing of NF-κB2/p100. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:22111–22114. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C200151200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Watanabe N, Arai H, Nishihara Y, Taniguchi M, Watanabe N, Hunter T, et al. M-phase kinases induce phospho-dependent ubiquitination of somatic Wee1 by SCFβ-TrCP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:4419–24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307700101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kaidanovich-Beilin O, Woodgett JR. GSK-3: Functional Insights from Cell Biology and Animal Models. Front Mol Neurosci. 2011;4:40. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2011.00040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yu R, Lei W, Mandlekar S, Weber MJ, Der CJ, Wu J, et al. Role of a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in the induction of phase II detoxifying enzymes by chemicals. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:27545–27552. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.39.27545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Alam J, Wicks C, Stewart D, Gong P, Touchard C, Otterbein S, et al. Mechanism of heme oxygenase-1 gene activation by cadmium in MCF-7 mammary epithelial cells. Role of p38 kinase and Nrf2 transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:27694–27702. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M004729200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zipper LM, Mulcahy RT. Inhibition of ERK and p38 MAP kinases inhibits binding of Nrf2 and induction of GCS genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;278:484–492. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lee JM, Hanson JM, Chu WA, Johnson JA. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, not extracellular signal-regulated kinase, regulates activation of the antioxidant-responsive element in IMR-32 human neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:20011–20016. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100734200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Huang HC, Nguyen T, Pickett CB. Phosphorylation of Nrf2 at Ser-40 by protein kinase C regulates antioxidant response element-mediated transcription. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:42769–42774. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206911200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rushworth SA, Chen XL, Mackman N, Ogborne RM, O’Connell MA. Lipopolysaccharide-induced heme oxygenase-1 expression in human monocytic cells is mediated via Nrf2 and protein kinase C. J Immunol. 2005;175:4408–4415. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.7.4408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hwang YP, Kim HG, Han EH, Jeong HG. Metallothionein-III protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative stress by increasing expression of heme oxygenase-1 in a PI3K and ERK/Nrf2-dependent manner. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008;231:318–327. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2008.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sun Z, Huang Z, Zhang DD. Phosphorylation of Nrf2 at multiple sites by MAP kinases has a limited contribution in modulating the Nrf2-dependent antioxidant response. PLoS One. 2009;4:e6588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rojo AI, Medina-Campos ON, Rada P, Zúñiga-Toalá A, López-Gazcó A, Espada S, et al. Signaling pathways activated by the phytochemical nordihydroguaiaretic acid contribute to a Keap1-independent regulation of Nrf2 stability: role of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;52:473–487. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cohen P, Frame S. The renaissance of GSK3. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:769–76. doi: 10.1038/35096075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Watai Y, Kobayashi A, Nagase H, Mizukami M, McEvoy J, Singer JD, Itoh K, Yamamoto M. Subcellular localization and cytoplasmic complex status of endogenous Keap1. Genes Cells. 2007;12:1163–1178. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2007.01118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Seo E, Kim H, Kim R, Yun S, Kim M, Han JK, et al. Multiple isoforms of β-TrCP display differential activities in the regulation of Wnt signaling. Cell Signal. 2009;21:43–51. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.09.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Putters J, Slotman JA, Gerlach JP, Strous GJ. Specificity, location and function of βTrCP isoforms and their splice variants. Cell Signal. 2011;23:641–647. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lassot I, Ségéral E, Berlioz-Torrent C, Durand H, Groussin L, Hai T, Benarous R, Margottin-Goguet F. ATF4 degradation relies on a phosphorylation-dependent interaction with the SCFβ-TrCP ubiquitin ligase. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:2192–2202. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.6.2192-2202.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Trachootham D, Alexandre J, Huang P. Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8:579–591. doi: 10.1038/nrd2803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Finlay D, Patel S, Dickson LM, Shpiro N, Marquez R, Rhodes CJ, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 regulates IGFBP-1 gene transcription through the thymine-rich insulin response element. BMC Mol Biol. 2004;5:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-5-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhang Y, Crouch DH, Yamamoto M, Hayes JD. Negative regulation of the Nrf1 transcription factor by its N-terminal domain is independent of Keap1: Nrf1, but not Nrf2, is targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 2006;399:373–385. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Murai H, Okazaki M, Kikuchi A. Tyrosine dephosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 is involved in its extracellular signal-dependent inactivation. FEBS Lett. 1996;392:153–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00806-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ikeda S, Kishida S, Yamamoto H, Murai H, Koyama S, Kikuchi A. Axin, a negative regulator of the Wnt signaling pathway, forms a complex with GSK-3β and β-catenin and promotes GSK-3β-dependent phosphorylation of β-catenin. EMBO J. 1998;17:1371–1384. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.5.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Treier M, Staszewski LM, Bohmann D. Ubiquitin-dependent c-Jun degradation in vivo is mediated by the delta domain. Cell. 1994;78:787–798. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90502-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Higgins LG, Kelleher MO, Eggleston IM, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Hayes JD. Transcription factor Nrf2 mediates an adaptive response to sulforaphane that protects fibroblasts in vitro against the cytotoxic effects of electrophiles, peroxides and redox-cycling agents. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009;237:267–280. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.03.005. 2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Midgley CA, Desterro JM, Saville MK, Howard S, Sparks A, Hay RT, et al. An N-terminal p14ARF peptide blocks Mdm2-dependent ubiquitination in vitro and can activate p53 in vivo. Oncogene. 2000;19:2312–2323. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.MacLeod AK, McMahon M, Plummer SM, Higgins LG, Penning TM, Igarashi K, et al. Characterization of the cancer chemopreventive NRF2-dependent gene battery in human keratinocytes: demonstration that the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway, and not the BACH1-NRF2 pathway, controls cytoprotection against electrophiles as well as redox-cycling compounds. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:1571–1580. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]