Abstract
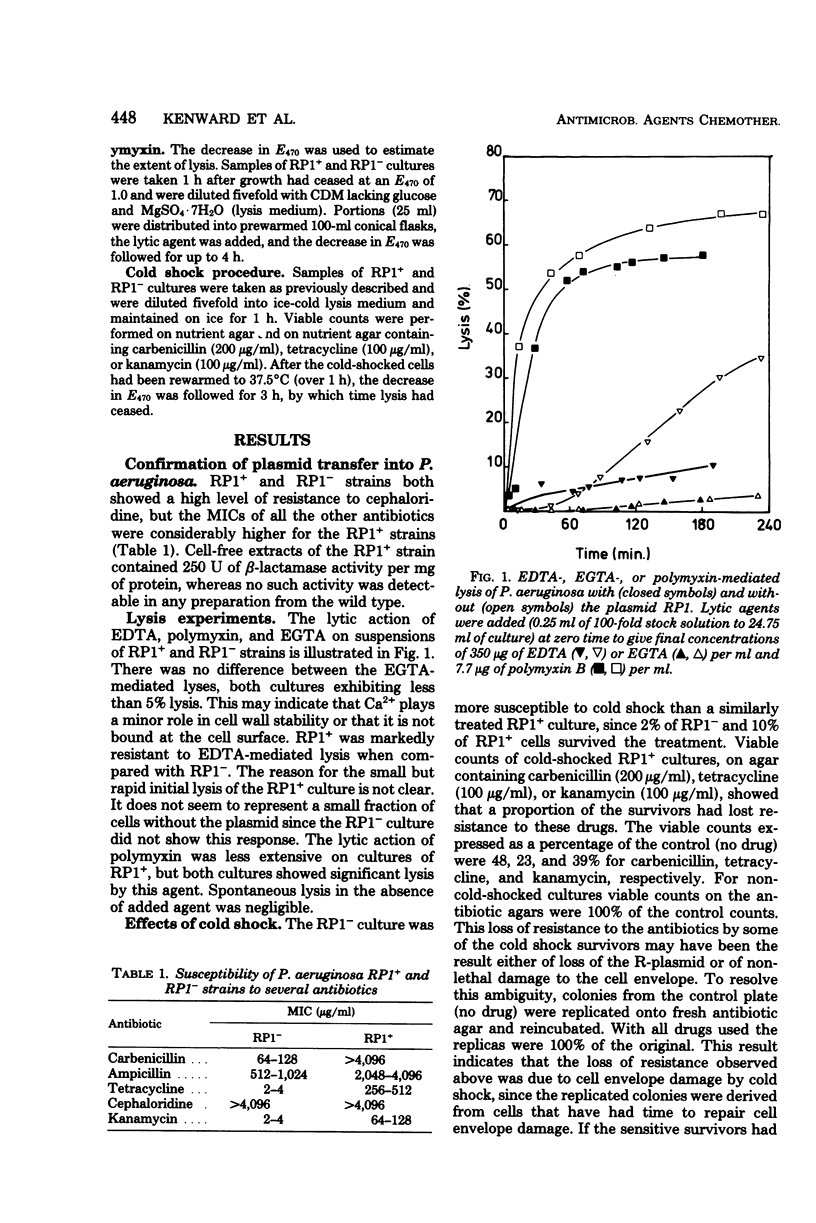
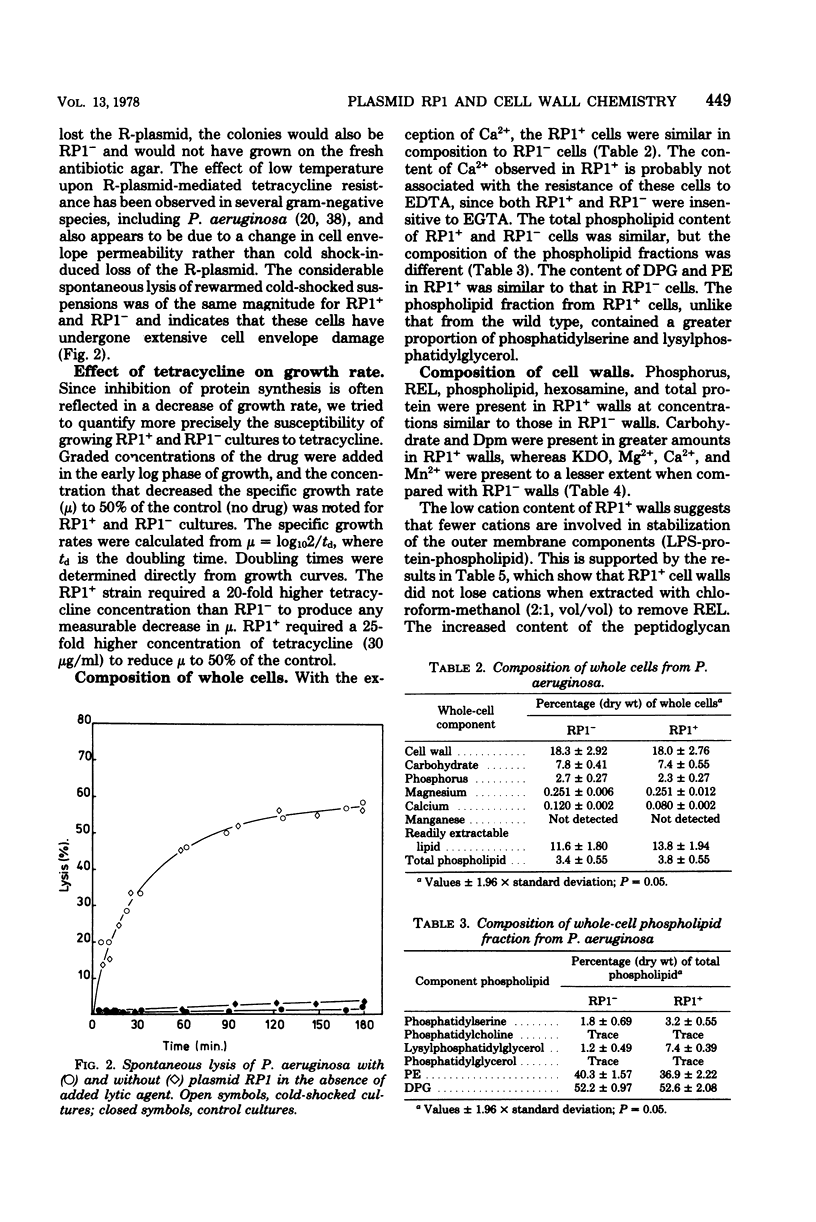
R-plasmid RP1 was transferred to Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells, as indicated by their resistance to carbenicillin, ampicillin, cephaloridine, kanamycin, and tetracycline, and by the presence of a periplasmic beta-lactamase. The wild-type cells (RP1-) were lysed by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid but not by ethylene-glycol-bis(2-aminoethyl ether)-N,N-tetraacetic acid, whereas cells carrying the plasmid (RP1+) were resistant to both these chelating agents. RP1+ and RP1- strains were both sensitive to the lytic action of polymyxin B and the lethal action of cold shock, but the effect was less marked in the RP1+ cultures. A proportion of the RP1+ cells surviving cold shock lost resistance to carbenicillin, tetracycline, and kanamycin. The chemical composition of whole cells and cell walls of RP1+ differed from that RP1- in the content of cation, phospholipid, and markers for lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan. Differences in cell wall composition, response to ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and polymyxin B, and the effects of cold shock are all compatible with the hypothesis that RP1 confers changes in the cell envelope, probably in the outer membrane, of P. aeruginosa.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baginski E. S., Foà P. P., Zak B. Microdetermination of inorganic phosphate, phospholipids, and total phosphate in biologic materials. Clin Chem. 1967 Apr;13(4):326–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E., Asscher A. W. Action of ethylenediaminetetra-acetic acid (EDTA) on carbenicillin-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Aug;5(3):355–359. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:471–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobrowski M., Borowski E. Interaction between carbenicillin and beta-lactamases from Gram-negative bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Nov;68(3):263–272. doi: 10.1099/00221287-68-3-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Nordström K., Normark S. Penicillin resistance in Escherichia coli K12: synergism between penicillinases and a barrier in the outer part of the envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):569–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Watkins W. M. Low magnesium and phospholipid content of cell wals of Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistant to polymyxin. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1360–1361. doi: 10.1038/2271360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Ingram J. M., Cheng K. J. Structure and function of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):87–110. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.87-110.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis N. A., Richmond M. H., Stanisich V. R-factor mediated resistance to penicillins which does not involve a beta-lactamase. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Nov;79(1):163–166. doi: 10.1099/00221287-79-1-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale J. W., Smith J. T. The purification and properties of the -lactamase specified by the resistance factor R-1818 in Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(4):493–500. doi: 10.1042/bj1230493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W., Shaw E. J., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Properties of an R factor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1244–1249. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1244-1249.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derylo M., Glowacka M., Lorkiewicz Z., Russa R. Plasmid-determined alterations of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Sep 29;140(2):175–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00329785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derylo M., Glowacka M., Lorkiewicz Z., Russa R., Zajaczkowska K. Cell wall lipopolysaccharide response to the ColIb plasmid mutants. Acta Microbiol Pol. 1976;25(2):109–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C. The distribution of 2-keto-3-deoxy-octonic acid in bacterial walls. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):373–380. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell J., Rose A. H. Cold shock in a mesophilic and a psychrophilic pseudomonad. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Mar;50(3):429–439. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-3-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., HsuChen C. C., Sud I. J. Basis for the selectivity of action of the polymyxin antibiotics on cell membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):480–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J. R factor tetracycline and chloramphenicol resistance in Escherichia coli K12 cmlB mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Oct;90(2):303–310. doi: 10.1099/00221287-90-2-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin T. J., Foster S. J. Effect of osmotic shock on tetracycline resistance in Escherichia coli bearing an R-factor. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(2):287–292. doi: 10.1042/bj1210287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILVARG C. The enzymatic synthesis of diaminopimelic acid. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1501–1504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOOD T. A., BESSMAN S. P. DETERMINATION OF GLUCOSAMINE AND GALACTOSAMINE USING BORATE BUFFERS FOR MODIFICATION OF THE ELSON-MORGAN AND MORGAN-ELSON REACTIONS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Nov;9:253–262. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Stinnett J. D., Roth I. L., Eagon R. G. Freeze-etch study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: localization within the cell wall of an ethylenediaminetetraacetate-extractable. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):417–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.417-432.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesslewood S. R., Smith J. T. Envelope alterations produced by R factors in Proteus mirabilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Nov;85(1):146–152. doi: 10.1099/00221287-85-1-146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono M., O'Hara K. Mechanism of chloramphenicol-resistance mediated by kR102 factor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Feb;29(2):176–180. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono M., O'Hara K. Mechanisms of streptomycin(SM)-resistance of highly SM-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Feb;29(2):169–175. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder I. G. Interrelated effects of cold shock and osmotic pressure on the permeability of the Escherichia coli membrane to permease accumulated substrates. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):211–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.211-219.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. B., McMurry L. Detection of an inducible membrane protein associated with R-factor-mediated tetracycline resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 27;56(4):1060–1068. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80296-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Lilly H. A., Kidson A., Ayliffe G. A., Jones R. J. Sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antibiotics: emergence of strains highly resistant to carbenicillin. Lancet. 1969 Aug 30;2(7618):448–452. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKelvie R. M., Gronlund A. F., Campbell J. J. Influence of cold-shock on the endogenous metabolism of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jun;14(6):633–638. doi: 10.1139/m68-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnikin D. E., Abdolrahimzadeh H. Thin-layer chromatography of bacterial lipids on sodium acetate-impregnated silica gel. J Chromatogr. 1971 Dec 23;63(2):452–454. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)85672-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayman M. K., MacLeod R. A. Interaction of Mg-2+ with peptidoglycan and its relation to the prevention of lysis of a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):650–659. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.650-659.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Curtis N. A. The interplay of beta-lactamases and intrinsic factors in the resistance of gram-negative bacteria to penicillins and cephalosporins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):553–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosselet A., Zimmermann W. Mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with impaired -lactamase inducibility and increased sensitivity to -lactam antibiotics. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jun;76(2):455–457. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-2-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANGE R. E., POSTGATE J. R. PENETRATION OF SUBSTANCES INTO COLD-SHOCKED BACTERIA. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Sep;36:393–403. doi: 10.1099/00221287-36-3-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley P. L., Olsen R. H. Characteristics and expression of tetracycline resistance in gram-negative bacteria carrying the Pseudomonas R factor RP1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):183–190. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuber M., Bader J. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes: phosphatidylglycerol- and cardiolipin-induced susceptibility to polymyxin B in Acholeplasma laidlawii B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):26–35. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng J. T., Bryan L. E. Mechanisms of R factor R931 and chromosomal tetracycline resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 May;3(5):638–641. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.5.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson C. A., Vande Zande H., Green D. E. Phospholipids as ionophores. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1326–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HURWITZ J. The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



