Abstract
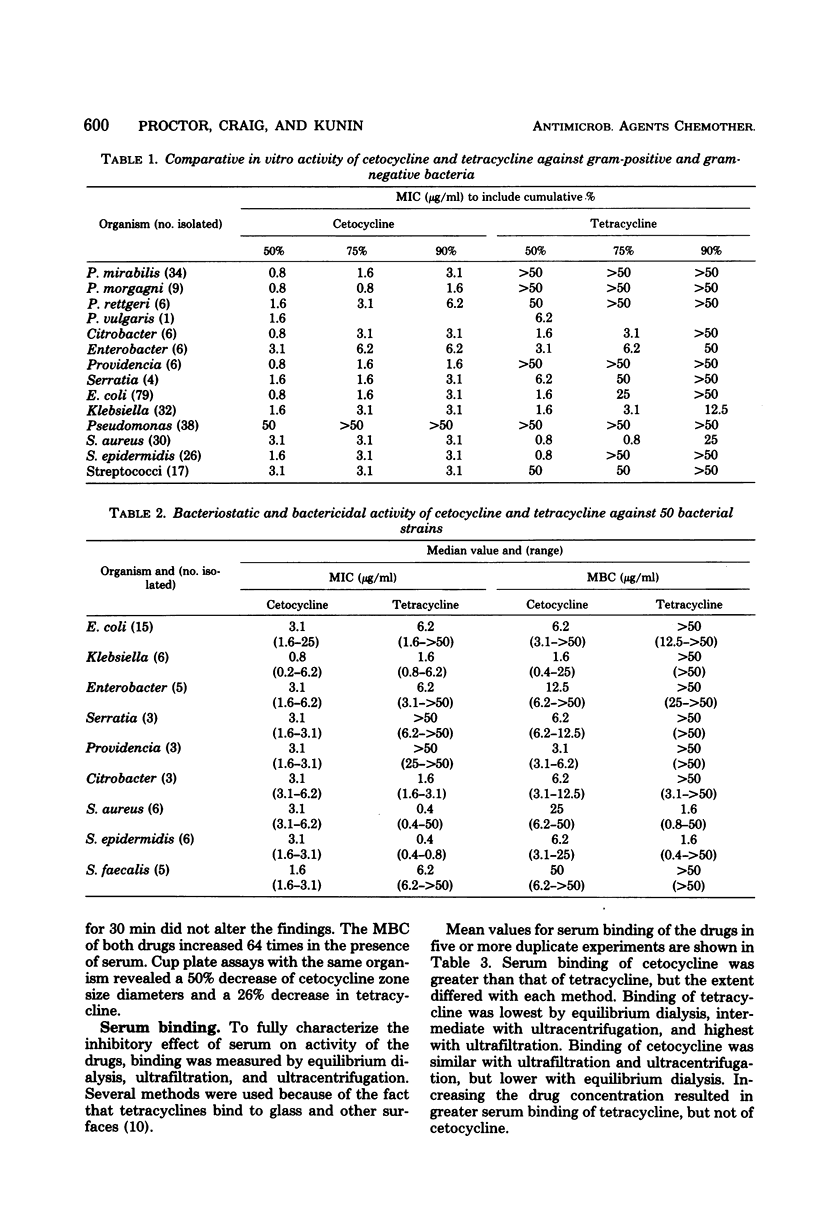
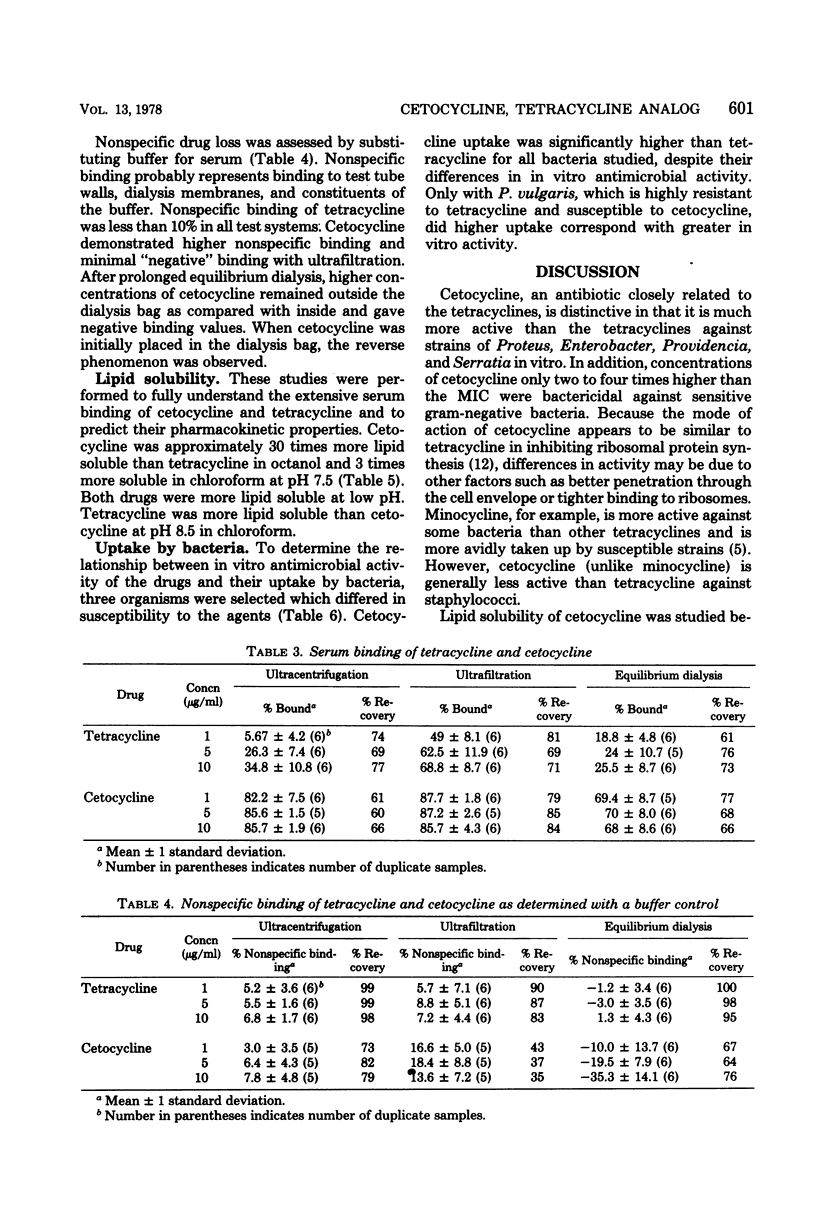
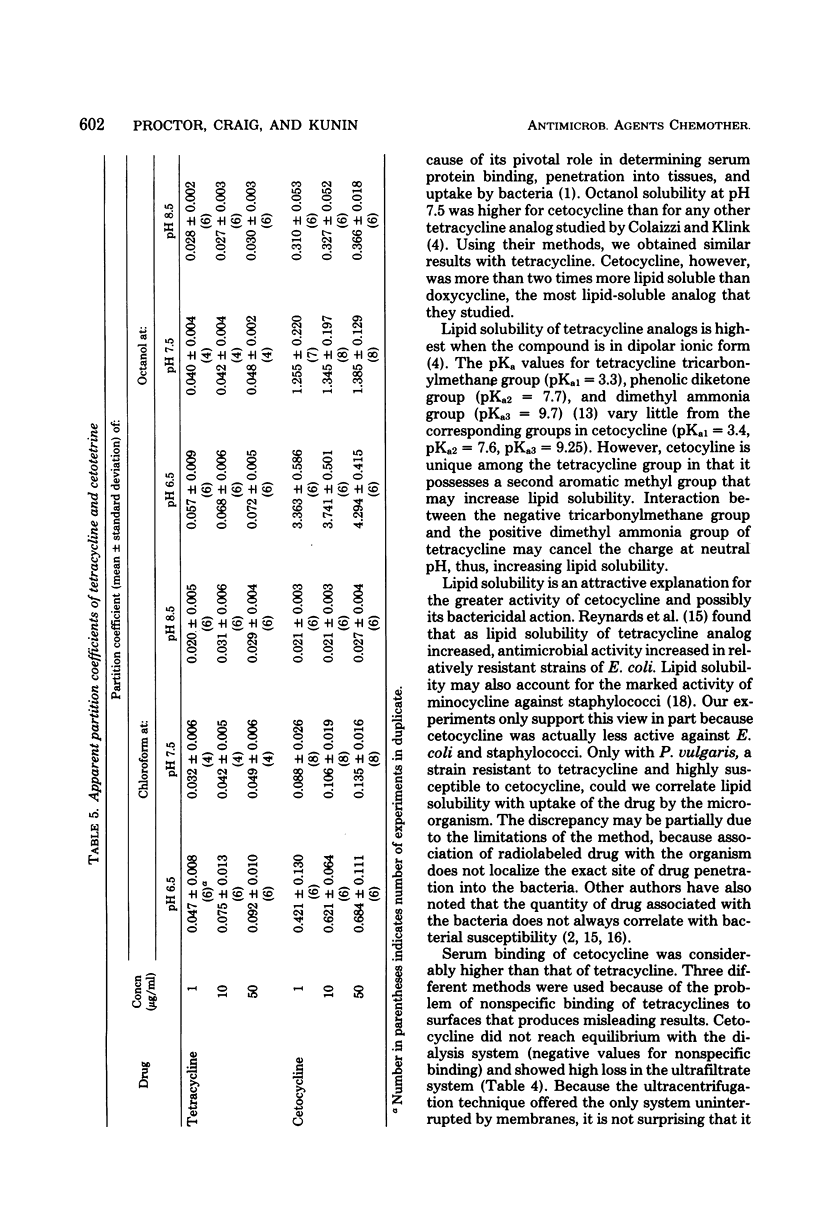
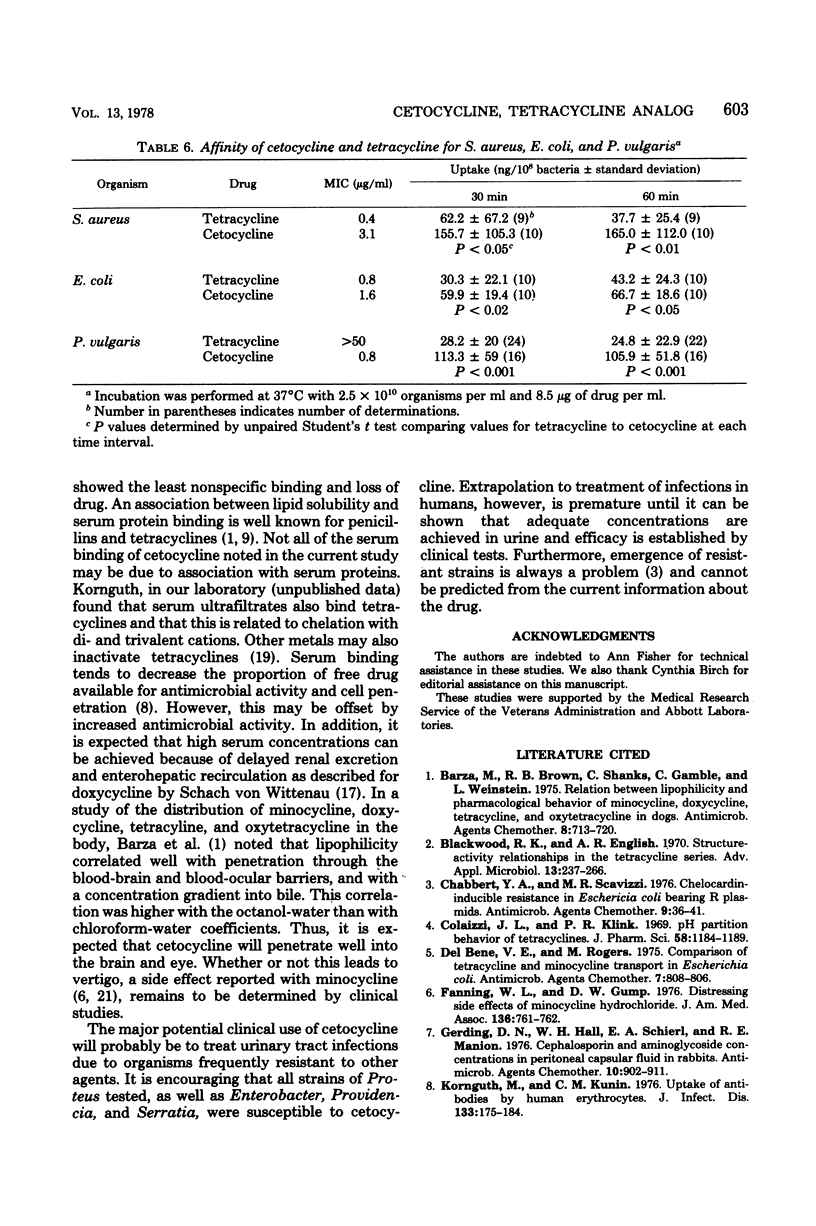
Cetocycline (formerly chelocardin or cetotetrine) is structurally related to the tetracyclines. It was found to be more active than tetracycline against many clinical isolates of aerobic gram-negative bacilli, but is less active against staphylococci, and has no activity against Pseudomonas. It is bactericidal against susceptible enteric gram-negative bacteria at concentrations two to four times higher than the minimal inhibiting concentrations. The drug is highly lipid soluble; more than 80% is bound to serum, and it is more avidly taken up by susceptible bacteria than tetracycline. A direct correlation between drug uptake and susceptibility of bacteria was not noted, except with a strain of Proteus vulgaris.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barza M., Brown R. B., Shanks C., Gamble C., Weinstein L. Relation between lipophilicity and pharmacological behavior of minocycline, doxycycline, tetracycline, and oxytetracycline in dogs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Dec;8(6):713–720. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.6.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert Y. A., Scavizzi M. R. Chelocardin-inducible resistance in Escherichia coli bearing R plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colaizzi J. L., Klink P. R. pH-Partition behavior of tetracyclines. J Pharm Sci. 1969 Oct;58(10):1184–1189. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600581003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Bene V. E., Rogers M. Comparison of tetracycline and minocyclie transport in Escherichia Coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jun;7(6):801–806. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.6.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning W. L., Gump D. W. Distressing side-effects of minocycline hydrochloride. Arch Intern Med. 1976 Jul;136(7):761–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerding D. N., Hall W. H., Schierl E. A., Manion R. E. Cephalosporin and aminoglycoside concentrations in peritoneal capsular fluid in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Dec;10(6):902–911. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.6.902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M., FINLAND M. Clinical pharmacology of the tetracycline antibiotics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1961 Jan-Feb;2:51–69. doi: 10.1002/cpt19612151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M. INHIBITORS OF PENICILLIN BINDING TO SERUM PROTEINS. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Mar;65:416–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornguth M. L., Kunin C. M. Uptake of antibiotics by human erythrocytes. J Infect Dis. 1976 Feb;133(2):175–184. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.2.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E. Mode of action of beta-chelocardin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 29;238(1):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitscher L. A., Juvarkar J. V., Rosenbrook W., Jr, Andres W. W., Schenk J., Egan R. S. Structure of chelocardin, a novel tetracycline antibiotic. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Oct 7;92(20):6070–6071. doi: 10.1021/ja00723a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynard A. M., Nellis L. F., Beck M. E. Uptake of 3H-Tetracycline by resistant and sensitive Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jan;21(1):71–75. doi: 10.1128/am.21.1.71-75.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schach von Wittenau M., Twomey T. M. The disposition of doxycyline by man and dog. Chemotherapy. 1971;16(4):217–228. doi: 10.1159/000220730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Krausz J. Action of 12 tetracyclines on susceptible and resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):237–247. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Samra Z. Influence of magnesium and manganese on some biological and physical properties of tetracycline. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):468–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.468-476.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. N., Laughlin L. W., Lee Y. H. Minocycline: Possible vestibular side-effects. Lancet. 1974 Sep 28;2(7883):744–746. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90941-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


