Abstract
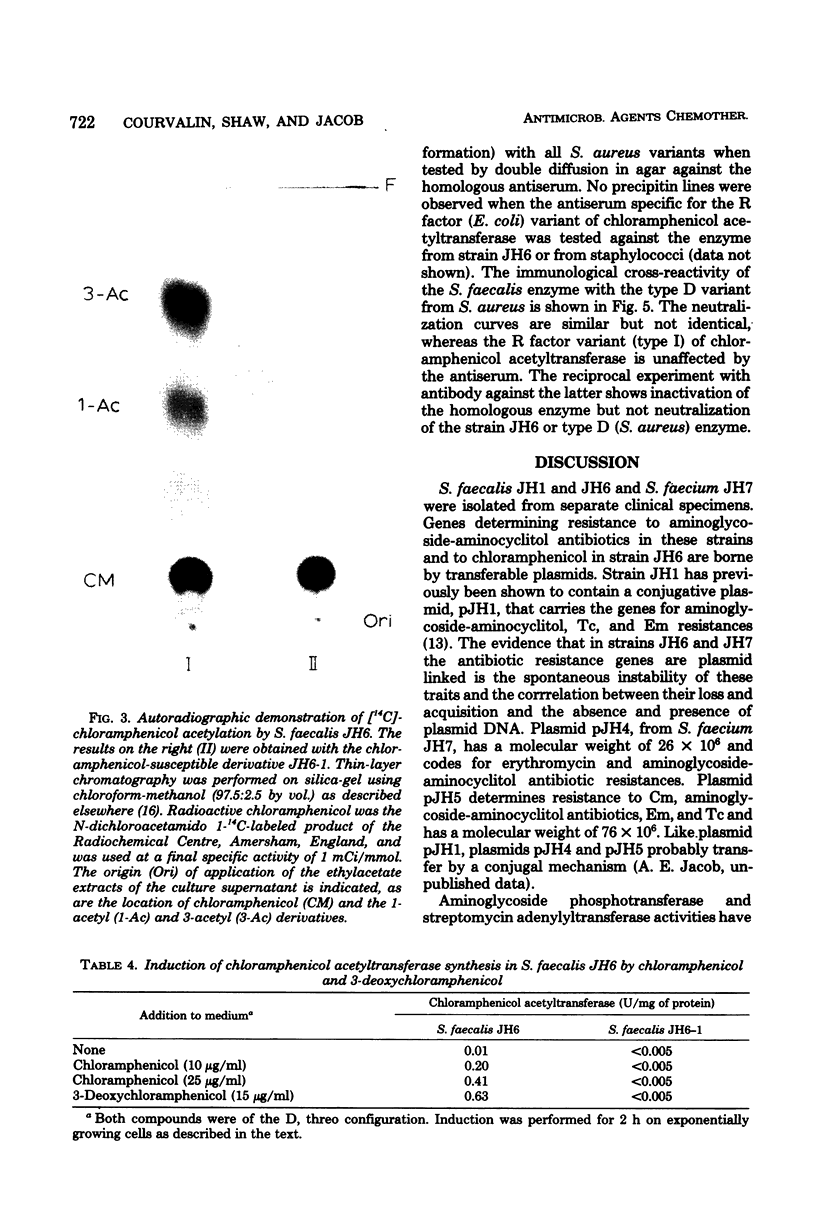
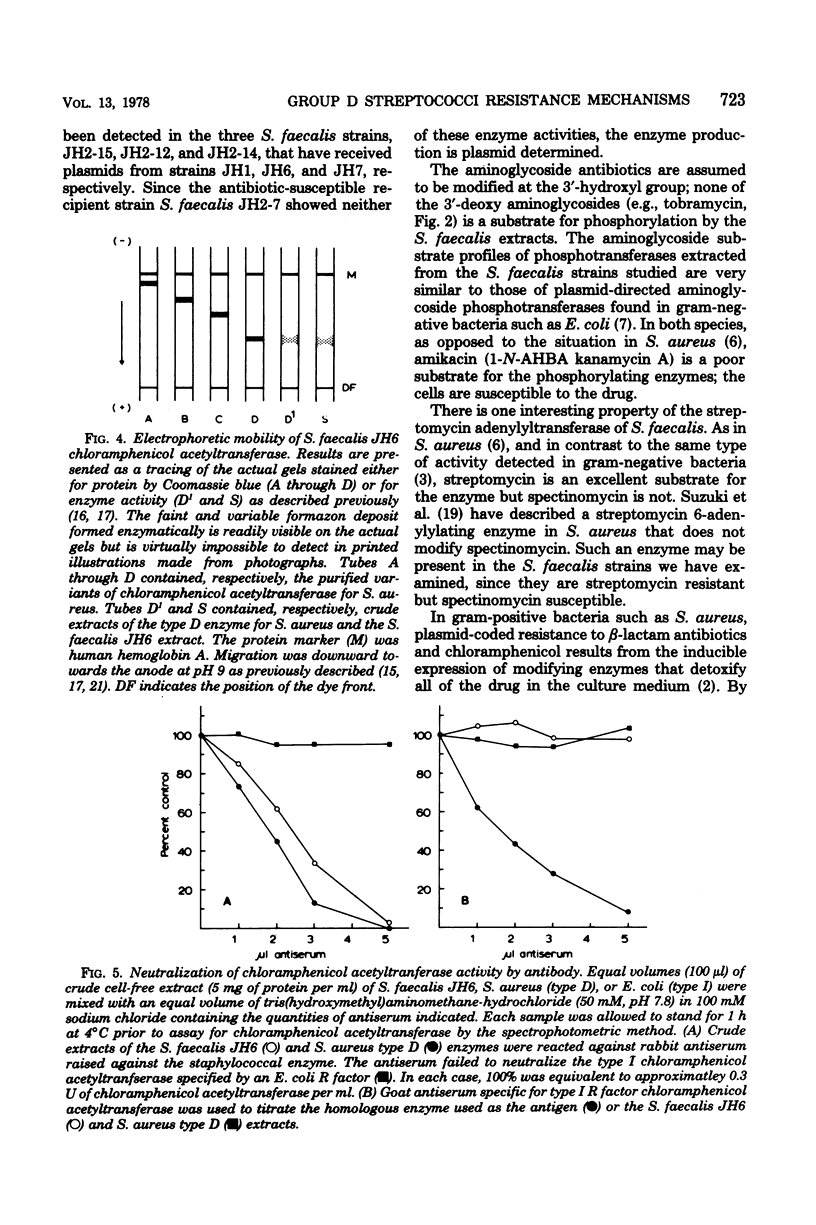
Genes conferring resistance to aminoglycoside-aminocyclitol antibiotics in three group D streptococcal strains, Streptococcus faecalis JH1 and JH6 and S. faecium JH7, and to chloramphenicol in JH6 are carried by plasmids that can transfer to other S. faecalis cells. The aminoglycoside resistance is mediated by constitutively synthesized phosphotransferase enzymes that have substrate profiles very similar to those of aminoglycoside phosphotransferases found in gram-negative bacteria. Phosphorylation probably occurs at the aminoglycoside 3′-hydroxyl group. Plasmid-borne streptomycin resistance is due to production of the enzyme streptomycin adenylyltransferase, which, as in staphylococci and in contrast to that detected in gram-negative bacteria, is less effective against spectinomycin as substrate. Resistance to chloramphenicol is by enzymatic acetylation. The chloramphenicol acetyltransferase is inducible and bears a close resemblance to the type D chloramphenicol acetyltransferase variant from staphylococci.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barth P. T., Grinter N. J. Comparison of the deoxyribonucleic acid molecular weights and homologies of plasmids conferring linked resistance to streptomycin and sulfonamides. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):618–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.618-630.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:471–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Yamada T., Davies J. Enzymatic Adenylylation of Streptomycin and Spectinomycin by R-Factor-Resistant Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1970 Jan;1(1):109–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.1.109-119.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Yagi Y., Dunny G. M., Schultz S. K. Characterization of three plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid molecules in a strain of Streptococcus faecalis: identification of a plasmid determining erythromycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):283–289. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.283-289.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin P. M., Carlier C., Chabbert Y. A. Plasmid-linked tetracycline and erythromycin resistance in group D "streptococcus". Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Dec;123(6):755–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin P., Davies J. Plasmid-medicated aminoglycoside phosphotransferase of broad substrate range that phosphorylates amikacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):619–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. E., Benveniste R. E. Enzymes that inactivate antibiotics in transit to their targets. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):130–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Clewell D. B. Transmissible toxin (hemolysin) plasmid in Streptococcus faecalis and its mobilization of a noninfectious drug resistance plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):784–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.784-790.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J., Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferases specified by fi minus R factors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jan;3(1):99–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. J., Dowding J. E. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:611–628. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob A. E., Douglas G. J., Hobbs S. J. Self-transferable plasmids determining the hemolysin and bacteriocin of Streptococcus faecalis var. zymogenes. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):863–872. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.863-872.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob A. E., Hobbs S. J. Conjugal transfer of plasmid-borne multiple antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus faecalis var. zymogenes. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):360–372. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.360-372.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamura S., Ochiai H., Nitahara Y., Nakagawa Y., Terao M. Resistance mechanism of chloramphenicol in Streptococcus haemolyticus, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus faecalis. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(2):69–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb02809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands L. C., Shaw W. V. Mechanism of chloramphenicol resistance in staphylococci: characterization and hybridization of variants of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):299–305. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V., Brodsky R. F. Characterization of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):28–36. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.28-36.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa Y., Yagisawa M., Sawa T., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase III, a new phosphotransferase. Resistance mechanism. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1975 Nov;28(11):845–853. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.28.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winshell E., Shaw W. V. Kinetics of induction and purification of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1248–1257. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1248-1257.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]