Abstract
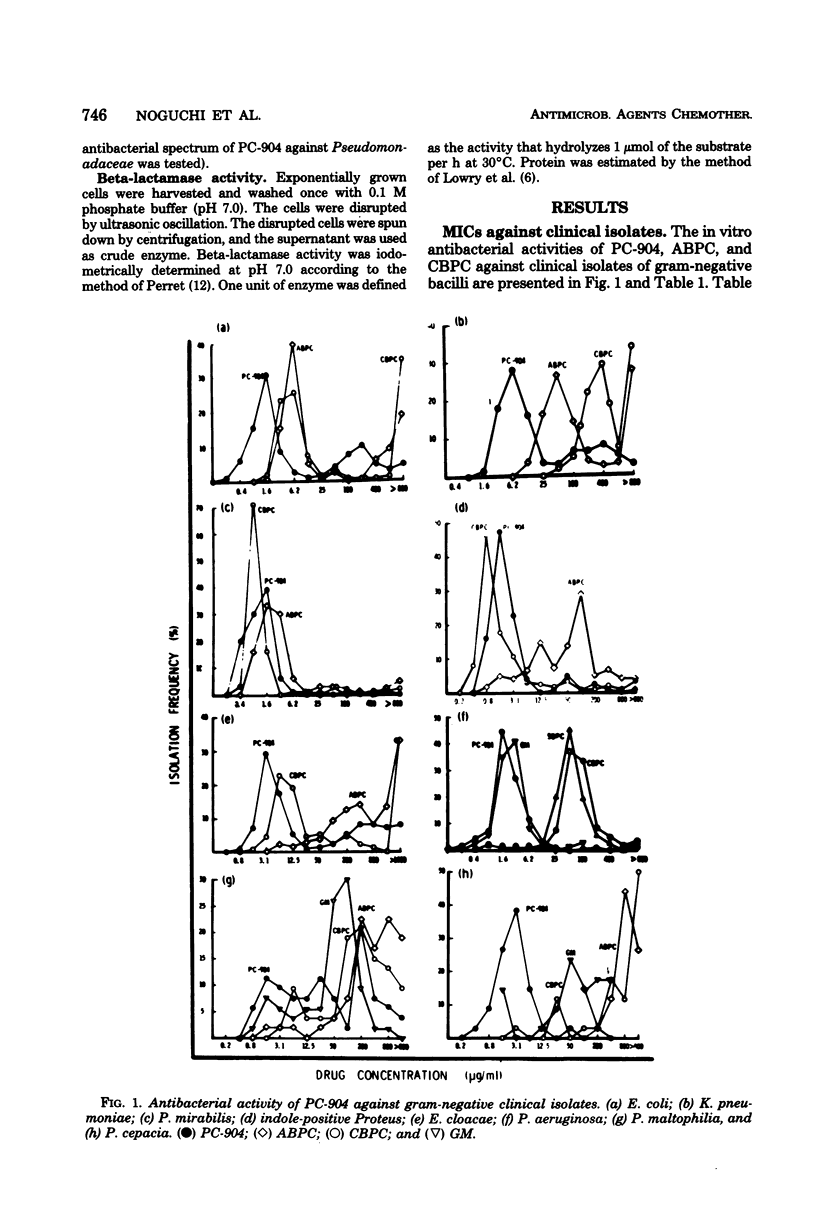
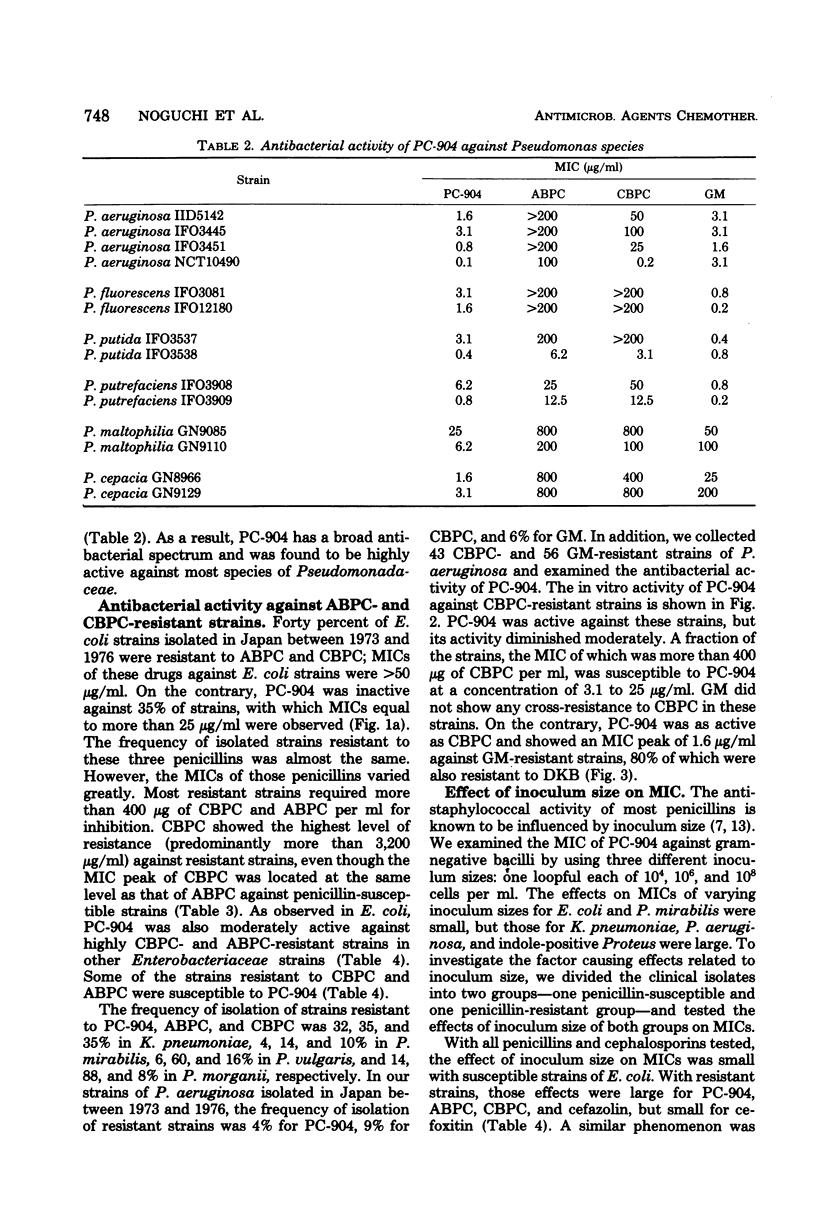
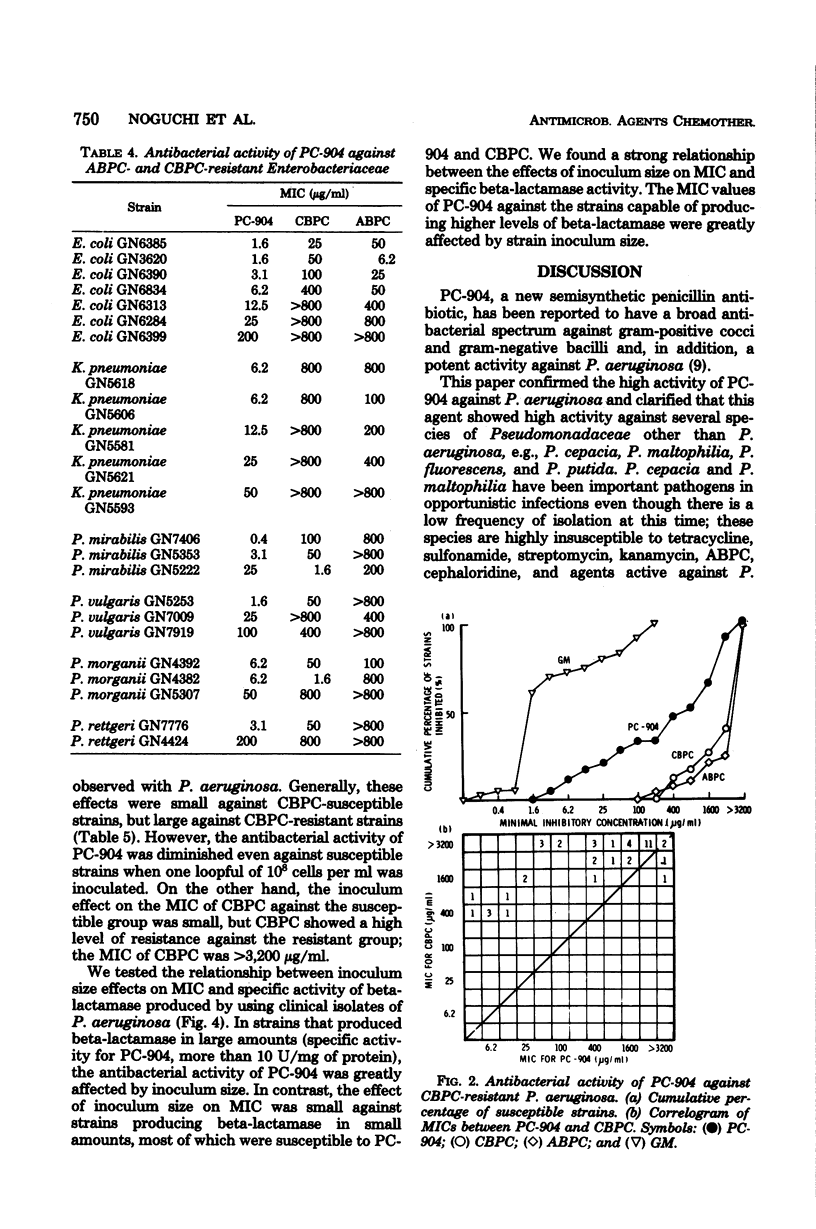
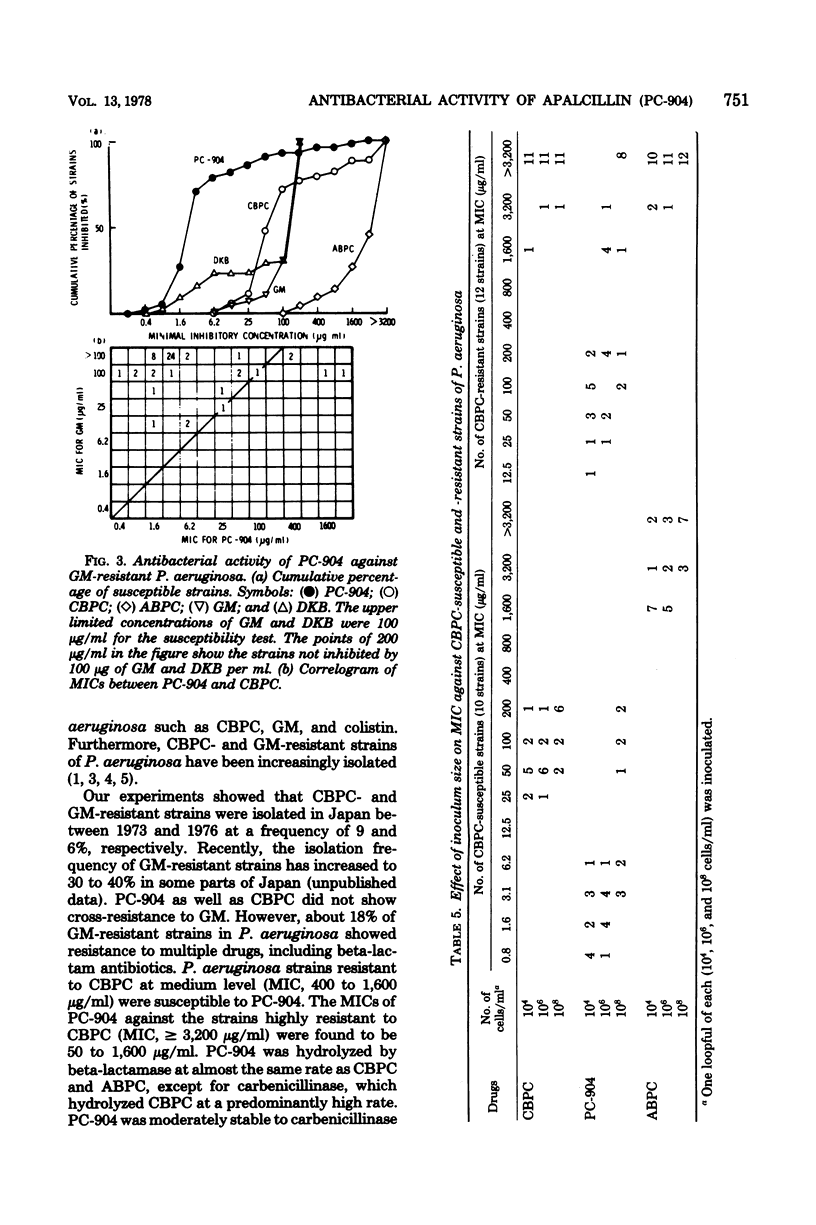
Apalcillin (PC-904) is active against carbenicillin- and ampicillin-resistant strains of gram-negative bacilli. Among Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains highly resistant to carbenicillin (≥3,200 μg/ml), half of them were susceptible to PC-904 at a concentration of 50 to 1,600 μg/ml. The minimal inhibitory concentration of PC-904 against P. aeruginosa strains resistant to carbenicillin (400 to 1,600 μg/ml) ranged from 3.1 to 25 μg/ml. Ampicillin- and carbenicillin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae strains were similarly susceptible to PC-904. However, drug resistance to PC-904 was already apparent among some strains of P. aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, P. vulgaris, and P. morganii, recently isolated in Japan; i.e., 4, 35, 32, 4, 6, and 14% of strains isolated were resistant. PC-904 was more active, on the other hand, than ampicillin and carbenicillin against antibiotic-susceptible Enterobacteriaceae and also showed high activity against most species of Pseudomonadaceae, especially P. cepacia and P. aeruginosa. The minimum inhibitory concentrations of PC-904 were greatly affected by inoculum size when the organisms tested were strains producing large amounts of beta-lactamase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird I. M., Slepack J. M., Kauffman C. A., Phair J. P. Nosocomial infection with gentamicin-carbenicillin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):626–629. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ederer G. M., Matsen J. M. Colonization and infection with Pseudomonas cepacia. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):613–618. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Minshew B. H., Gould I. K., Sanford J. P. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to gentamicin and related aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):253–262. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontomichalou P., Papachristou E., Angelatou F. Multiresistant plasmids from Pseudomonas aeruginosa highly resistant to either or both gentamicin and carbenicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):866–873. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Lilly H. A., Kidson A., Ayliffe G. A., Jones R. J. Sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antibiotics: emergence of strains highly resistant to carbenicillin. Lancet. 1969 Aug 30;2(7618):448–452. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Eda Y., Tobiki H., Nakagome T., Komatsu T. PC-904, a novel broad-spectrum semisynthetic penicillin with marked antipseudomonal activity: microbiological evaluation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Feb;9(2):262–273. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi H. R., Daoust D. R., Zimmerman S. B., Hendlin D., Stapley E. O. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: resistance to beta-lactamase inactivation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):38–48. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooka T., Hashimoto H., Mitsuhashi S. Comparison of penicillinases produced by R factors isolated from ampicillin-resistant gram-negative bacteria. Jpn J Microbiol. 1970 Mar;14(2):123–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1970.tb00499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRET C. J. Iodometric assay of penicillinase. Nature. 1954 Nov 27;174(4439):1012–1013. doi: 10.1038/1741012a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Garner C., Wilcox C., Finland M. Effect of inoculum and of beta-lactamase on the anti-staphylococcal activity of thirteen penicillins and cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Sep;8(3):344–349. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.3.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Pardee A. B. Penicillin-binding proteins and cell shape in E. coli. Nature. 1975 Apr 10;254(5500):516–517. doi: 10.1038/254516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Beta-lactamase-directed barrier for penicillins of Escherichia coli carrying R plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):936–940. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



