Abstract
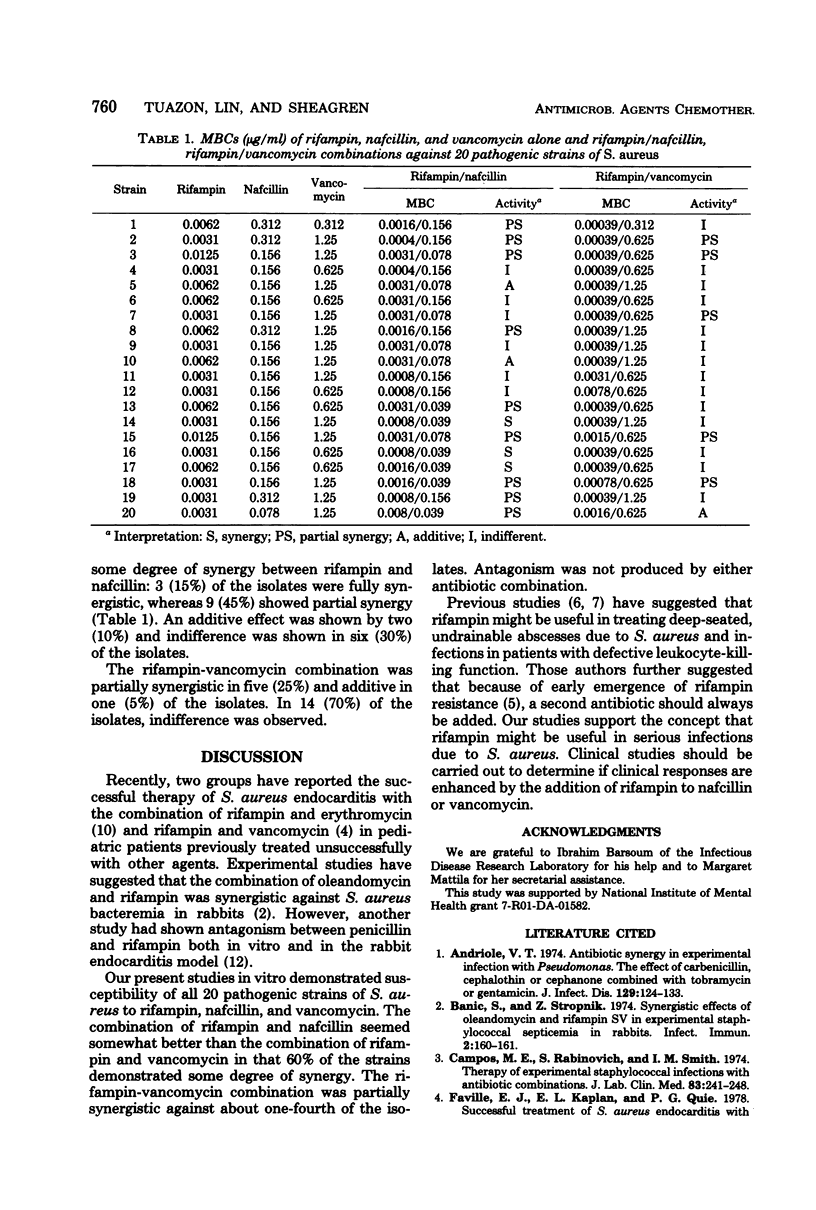
Twenty strains of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from patients with endocarditis were examined in vitro for susceptibility to rifampin, nafcillin, and vancomycin and to combinations of rifampin with nafcillin or vancomycin. Minimum bactericidal concentrations of rifampin ranged from 0.0031 to 0.0125 μg/ml, of nafcillin ranged from 0.078 to 0.312 μg/ml, and of vancomycin ranged from 0.312 to 1.25 μg/ml. The combination of rifampin with nafcillin was synergistic for 12 strains; the combination of rifampin plus vancomycin was synergistic for 5 of the isolates.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andriole V. T. Antibiotic synergy in experimental infection with Pseudomonas. II. The effect of carbenicillin, cephalothin, or cephanone combined with tobramycin or gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):124–133. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banic S., Stropnik Z. Synergistic effects of oleandomycin and rifamycin SV in experimental staphylococcal septicaemia in rabbits. Infection. 1974;2(3):160–161. doi: 10.1007/BF01642237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos M. E., Rabinovich S., Smith I. M. Therapy of experimental staphylococcal infection with antibiotic combinations. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Feb;83(2):241–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M., Brandt D., Wood H. Bacteriologic studies of rifampin, a new semisynthetic antibiotic. J Infect Dis. 1969 Feb;119(2):132–137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.2.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo M. C., Mandell G. L. Treatment of experimental staphylococcal infection with rifampin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Sep;2(3):195–200. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.3.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L., Vest T. K. Killing of intraleukocytic Staphylococcus aureus by rifampin: in-vitro and in-vivo studies. J Infect Dis. 1972 May;125(5):486–490. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.5.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marymont J. H., Jr, Wentz R. M. Serial dilution antibiotic sensitivity testing with the microtitrator system. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 May;45(5):548–551. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/45.5.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Wigley F. M., Mann J. J., Arthur R. R. Combination antibiotic therapy in staphylococcal endocarditis. The use of methicillin sodium-gentamicin sulfate therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1976 Apr;136(4):480–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peard M. C., Fleck D. G., Garrod L. P., Waterworth P. M. Combined rifampicin and erythromycin for bacterial endocarditis. Br Med J. 1970 Nov 14;4(5732):410–411. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5732.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Courtney K. B. Nafcillin-gentamicin synergism in experimental staphylococcal endocarditis. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jul;88(1):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Johnson M. L. Antimicrobial therapy of experimental endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):367–375. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steigbigel R. T., Greenman R. L., Remington J. S. Antibiotic combinations in the treatment of experimental Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Infect Dis. 1975 Mar;131(3):245–251. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorm C., Glotzbecker C. Enhancement of the effects of anti-staphylococcal antibiotics by aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):802–806. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



