Abstract
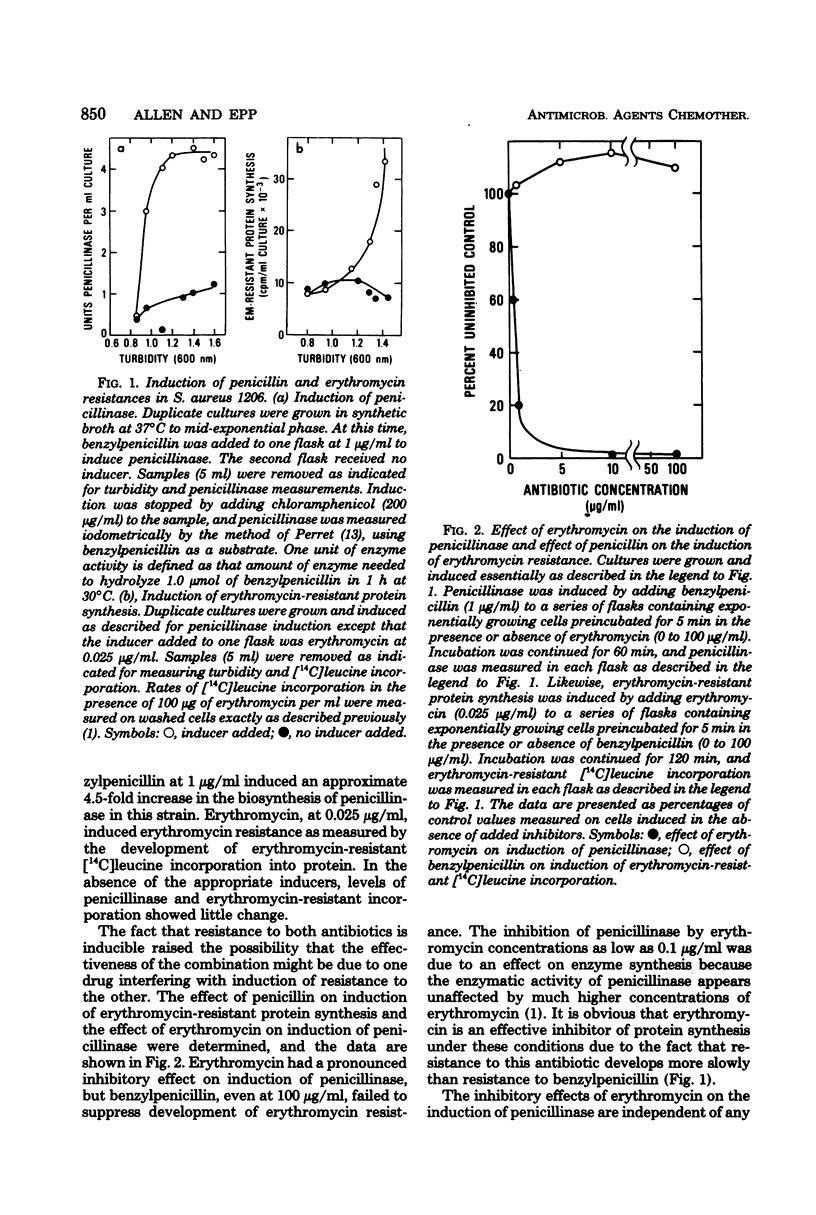
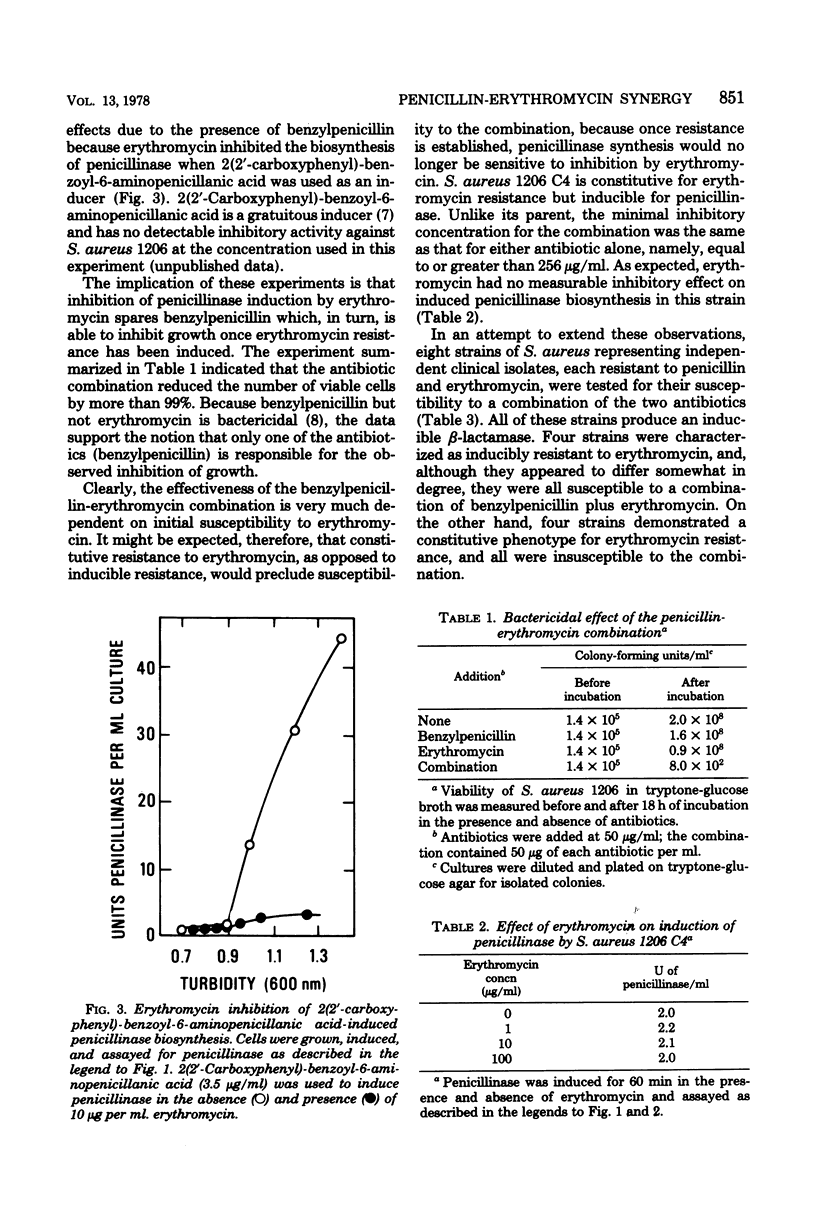
Clinically isolated strains of Staphylococcus aureus that are inducibly resistant to both erythromycin and penicillin were susceptible to a combination of the two antibiotics. The synergistic effect of the combination results from an inhibition of penicillinase induction by erythromycin, sparing penicillin and allowing this drug to inhibit growth. When resistance to erythromycin is constitutive rather than inducible, the combination is no longer synergistic.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen N. E. Macrolide resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: inducers of macrolide resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):669–674. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen N. E. Macrolide resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: induction of macrolide-resistant protein synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):661–668. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duma R. J., Kinz L. J. Simple test for identifying penicillinase-producing staphylococci. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Aug;16(8):1261–1262. doi: 10.1128/am.16.8.1261-1262.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRELL W. E., BALOWS A., BECKER J. Erythrocillin: a new approach to the problem of antibiotic-resistant staphylococci. Antibiotic Med Clin Ther (New York) 1960 Oct;7:637–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Weisblum B. Altered methylation of ribosomal RNA in an erythromycin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):856–860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggate J., Holms W. H. Gratuitous synthesis of beta-lactamase in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2110–2117. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2110-2117.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTEN A., WISSE M. J. Antagonism between antibacterial drugs. Nature. 1961 Nov 18;192:671–672. doi: 10.1038/192671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael T. M., Michael J. G., Massell B. F. Preferential inhibition of penicillinase induction by oxytetracycline and its effect on the penicillin susceptibility of staphylococci. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1749–1752. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1749-1752.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J., Bornstein H., Luboshitzky R., Sacks T. Mechanis of chlorampenicol-cephalordine synergism on Enerobacteiaeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jun;7(6):845–849. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.6.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J., Jacobs J., Sacks T. Bactericidal synergistic effect due to chloramphenicol-induced inhibition of staphyloccal penicillinase. Chemotherapy. 1977;23(1):32–36. doi: 10.1159/000221968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRET C. J. Iodometric assay of penicillinase. Nature. 1954 Nov 27;174(4439):1012–1013. doi: 10.1038/1741012a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATERWORTH P. M. Apparent synergy between penicillin and erythromycin or fusidic acid. Clin Med (Northfield) 1963 May;70:941–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Demohn V. Erythromycin-inducible resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: survey of antibiotic classes involved. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):447–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.447-452.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Siddhikol C., Lai C. J., Demohn V. Erythromycin-inducible resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: requirements for induction. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):835–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.835-847.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



