Abstract
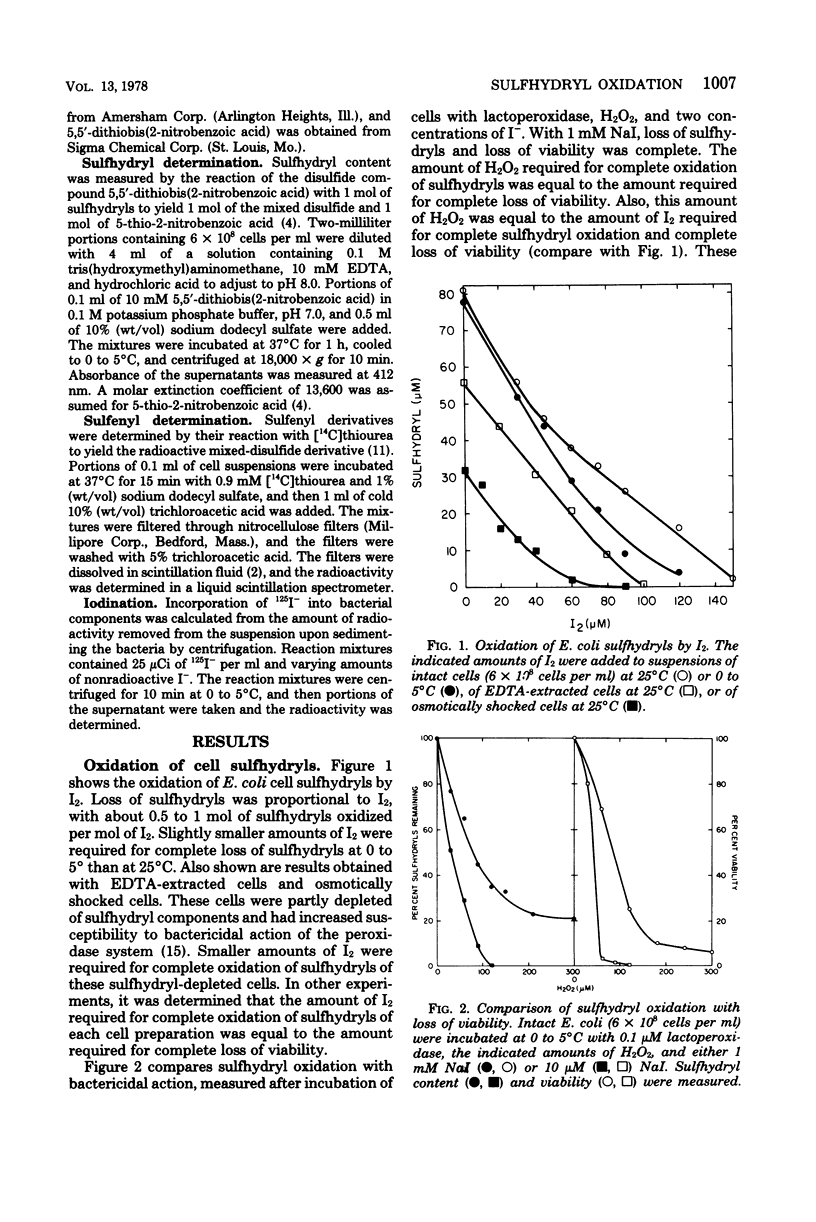
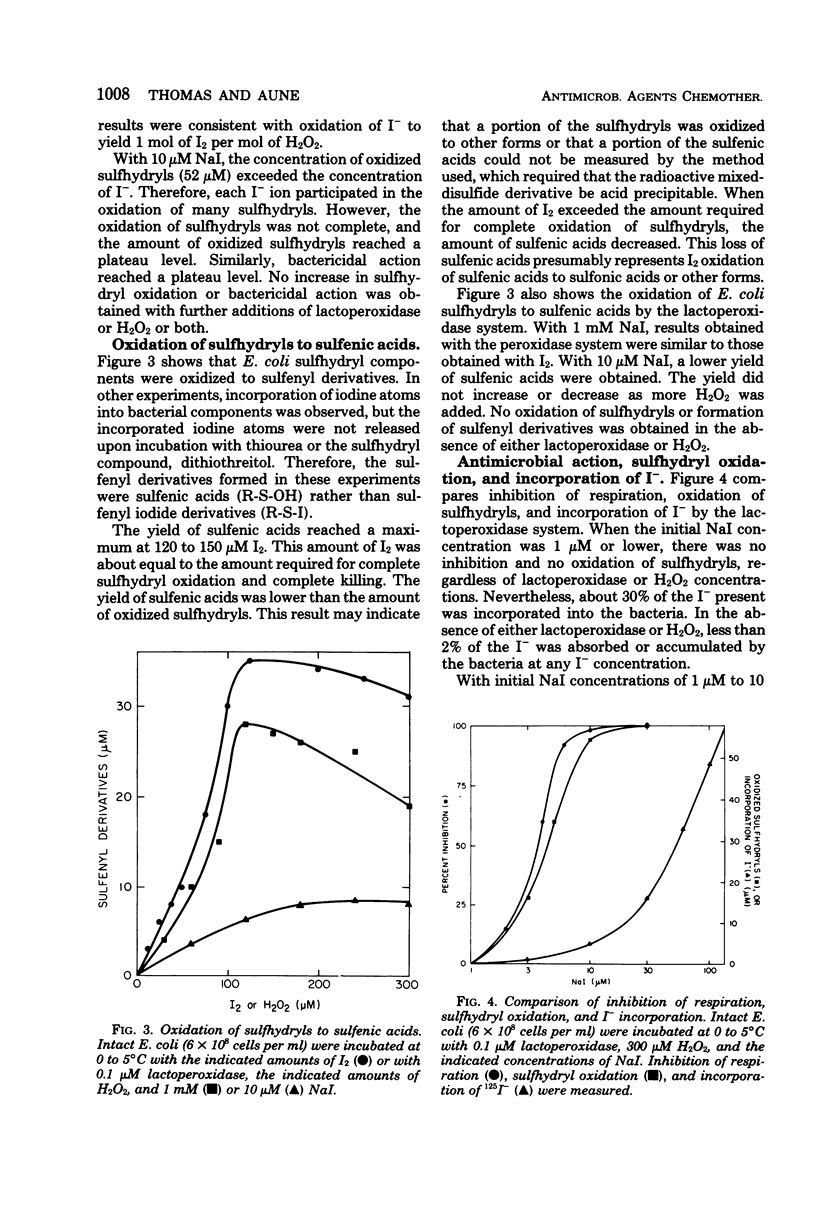
The chemical modification of bacterial components was studied following incubation of Escherichia coli with the peroxidase-hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-iodide (I−) antimicrobial system or with iodine (I2). The oxidation of cell sulfhydryls and the iodination of cell components were measured. Both the peroxidase system and I2 oxidized sulfhydryls. When the I− concentration in the peroxidase system was greater than 100 μM, the peroxidase system and I2 were equivalent. That is, sulfhydryl oxidation or killing per mole of H2O2 equaled that per mole of I2. These results were consistent with peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of I− to yield 1 mol of I2 per mol of H2O2. Sulfhydryls were oxidized to yield sulfenic acids and free I−. With I− concentrations in the range of 10 to 100 μM, the amount of sulfhydryls oxidized by the peroxidase system could exceed the amount of I−. Because the oxidation of sulfhydryls to sulfenic acids did not consume I−, one I− ion could participate in the oxidation of many sulfhydryls. With I− concentrations lower than 10 μM, complete oxidation of sulfhydryls was not obtained. Incorporation of I− into iodinated derivatives of bacterial components partly depleted the system of I− and limited the formation of I2. These results indicated that antimicrobial activity was due to peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of I− to I2, followed by I2 oxidation of cell components. There was a direct relationship between sulfhydryl oxidation and antimicrobial action. Although iodination of bacterial components accompanied sulfhydryl oxidation, the amount of I− incorporation was not directly related to antimicrobial action. Also, incorporation of I− interfered with antimicrobial action at low I− concentrations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander N. M. Oxidative cleavage of tryptophanyl peptide bonds during chemical- and peroxidase-catalyzed iodinations. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 25;249(6):1946–1952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUNNINGHAM L. W., NUENKE B. J. Physical and chemical studies of a limited reaction of iodine with proteins. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1447–1451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakim J., Cramer E., Boivin P., Troube H., Boucherot J. Quantitative iodination of human blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun 12;5(3):215–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Antimicrobial mechanisms in neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Semin Hematol. 1975 Apr;12(2):117–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Clark R. A. Iodination by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a re-evaluation. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Mar;89(3):675–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. Release of lipopolysaccharide by EDTA treatment of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison M., Schonbaum G. R. Peroxidase-catalyzed halogenation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:861–888. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.004241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. J., Allison W. S. The mechanism of inactivation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase by tetrathionate, o-iodosobenzoate, and iodine monochloride. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):180–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Klebanoff S. J. Quantitative leukocyte iodination. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 8;284(14):744–750. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104082841402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Aune T. M. Peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of protein sulfhydryls mediated by iodine. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 9;16(16):3581–3586. doi: 10.1021/bi00635a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Aune T. M. Susceptibility of Escherichia coli to bactericidal action of lactoperoxidase, peroxide, and iodide or thiocyanate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):261–265. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


