Abstract
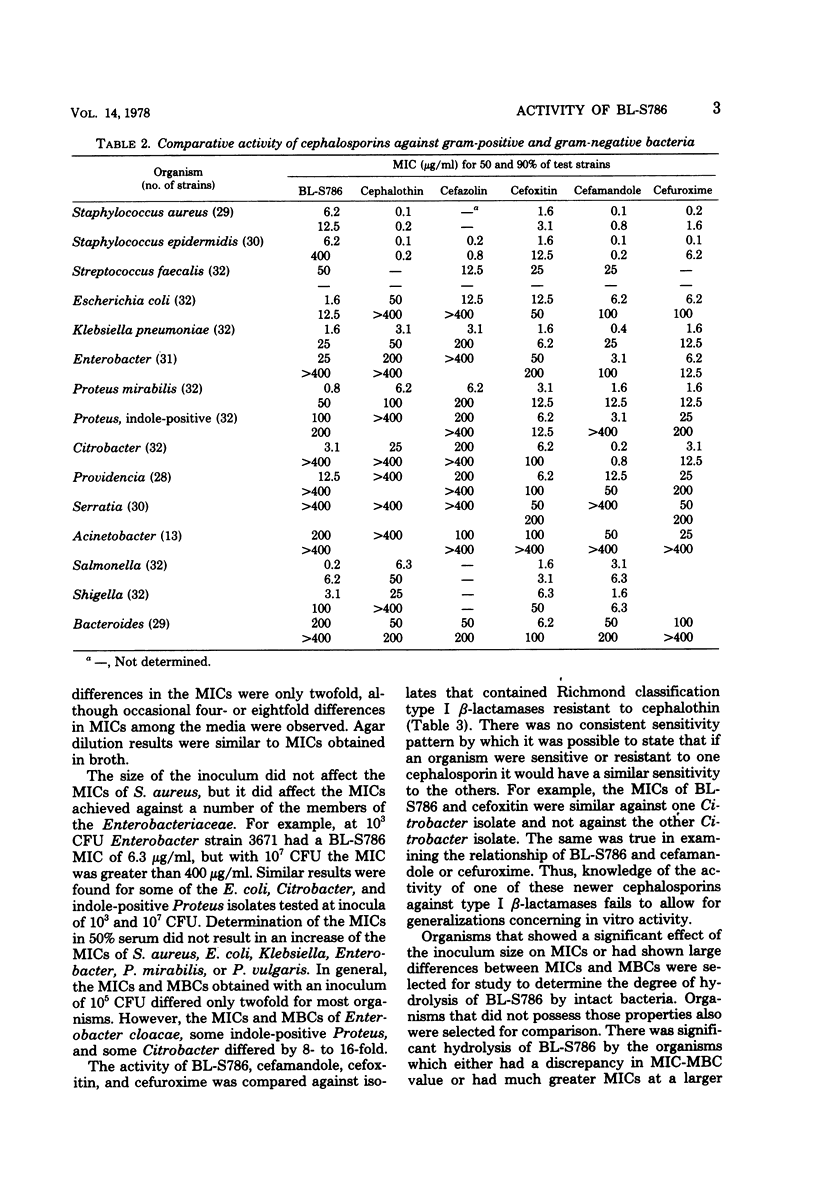
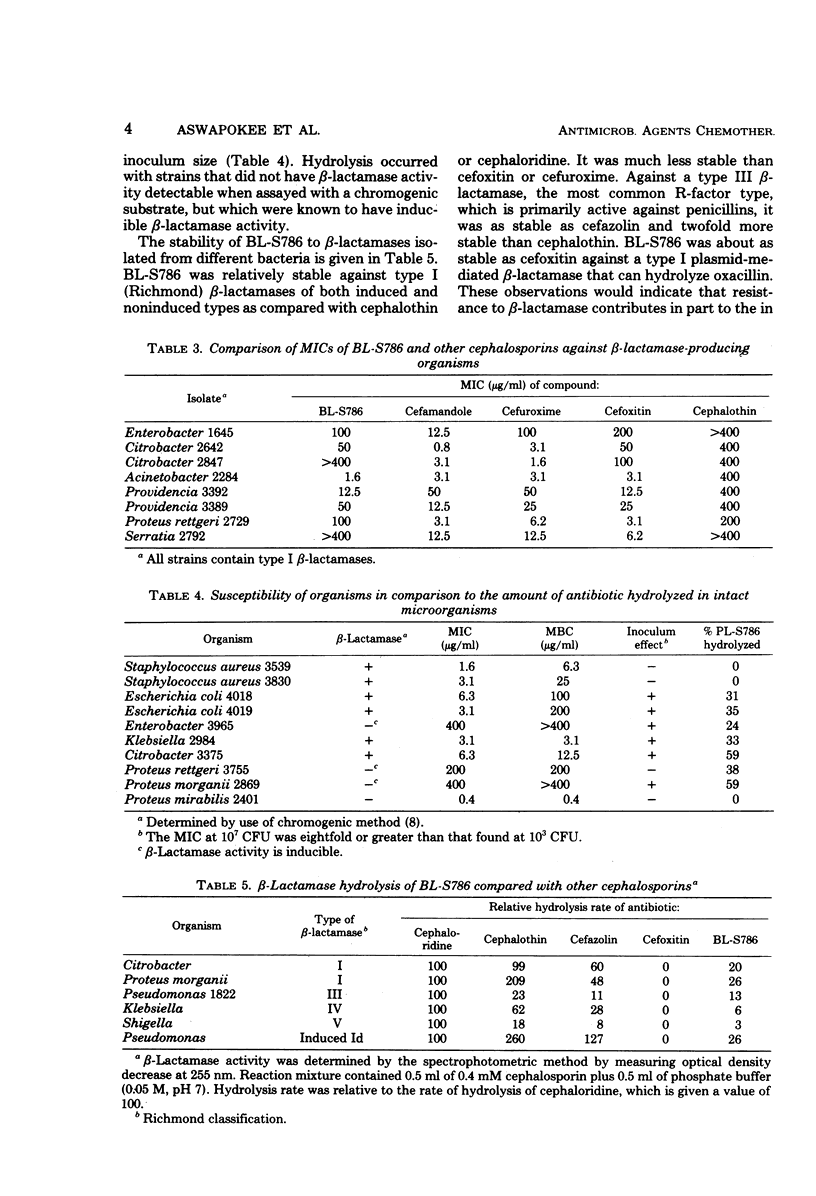
In vitro activity of BL-S786, a new parenterally semisynthetic cephalosporin, was investigated against 570 bacterial isolates. BL-S786 inhibited most Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, and Salmonella. It inhibited some Enterobacter and indole-positive Proteus, but it was less active against these later species than was cefamandole, cefuroxime, or cefoxitin. It was not active against Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, or Bacteroides fragilis. BL-S786 was the least active new cephalosporin tested against staphylococci and was less active than cephalothin against streptococcal species. The activity of BL-S786 was not altered by the type of assay medium nor by 50% serum. The size of the test inoculum altered the minimal inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations for inhibition of some organisms, particularly those with Richmond type I β-lactamases. BL-S786 was not hydrolyzed by the R-factor-mediated, Richmond type III β-lactamase, but it was hydrolyzed by type I β-lactamases.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jones R. N., Fuchs P. C., Gavan T. L., Gerlach E. H., Barry A., Thornsberry C. BL-S786, a new parenteral cephalosporin. I. A collaborative in vitro susceptibility comparison to cephalothin against 5,762 clinical bacterial isolates. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Jul;30(7):576–582. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Thornsberry C., Barry A. L., Fuchs P. C., Gavin T. L., Gerlach E. H. BL-S786, a new parenteral cephalosporin. II. In vitro antimicrobial activity comparison with six related cephalosporins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Jul;30(7):583–592. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitner F., Misiek M., Pursiano T. A., Buck R. E., Chisholm D. R., DeRegis R. G., Tsai Y. H., Price K. E. Laboratory evaluation of BL-S786, a cephalosporin with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Sep;10(3):426–435. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.3.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cefamandole, a cephalosporin antibiotic with an unusually wide spectrum of activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):177–182. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: antibacterial spectrum and resistance to hydrolysis by gram-negative beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):170–176. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Sykes R. B., Griffiths A., Thornton J. E. Cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic: activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):511–519. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


