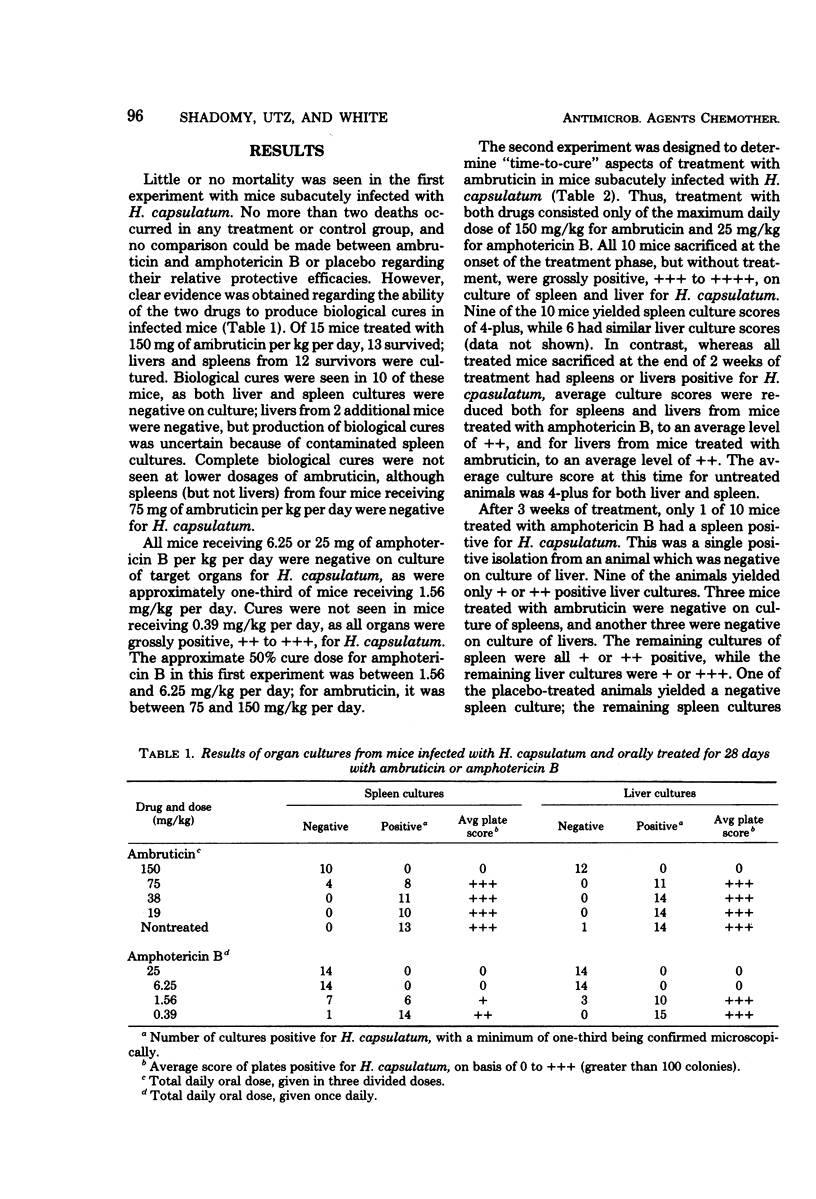
Abstract
Ambruticin (W7783) was evaluated in vivo in mice subacutely or nonlethally infected with Histoplasma capsulatum. Results were compared with those obtained with amphotericin B, the drug of choice in human histoplasmosis. In one experiment, ambruticin was shown to be capable of curing infected animals as evidenced by totally negative liver and spleen cultures obtained when mice were sacrificed after 4 weeks of oral treatment with 150 mg of drug per kg per day. The 50% cure dose for ambruticin was between 75 and 150 mg/kg per day; the 50% cure dose for oral amphotericin B in this experiment was between 1.56 and 6.25 mg/kg per day. In a second experiment, both oral ambruticin (150 mg/kg per day) and oral amphotericin B (25 mg/kg per day) were again curative, but to a lesser degree than in the first experiment. Biological cures were obtained with both drugs after 3 and 4 weeks of treatment but not after 2 weeks.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Levine H. B., Ringel S. M., Cobb J. M. Therapeutic properties of oral ambruticin (W7783) in experimental pulmonary coccidioidomycosis of mice. Chest. 1978 Feb;73(2):202–206. doi: 10.1378/chest.73.2.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringel S. M., Greenough R. C., Roemer S., Connor D., Gutt A. L., Blair B., Kanter G., von Strandtmann Ambruticin (W7783), a new antifungal antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 May;30(5):371–375. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadomy S., Dixon D. M., Espinel-Ingroff A., Wagner G. E., Yu H. P., Shadomy H. J. In vitro studies with ambruticin, a new antifungal antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jul;14(1):99–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


