Abstract
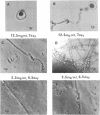
The antifungal activity of a lyophilized powder containing aloe leaf homogenate (whole-leaf powder) against Trichophyton mentagrophytes was investigated. The minimal inhibitory concentration was 25 mg/ml by the agar dilution method, using Sabouraud glucose agar medium. At subinhibitory concentrations, the powder exerted its main effect on colony growth by prolongation of the lag phase and inhibition of growth rate. Homogenates of fresh whole leaf were filtered through Whatman GF/A paper, and the filtrate was dialyzed and concentrated by molecular filtration using an Amicon hollow-fiber dialyzer concentrator DC-2, and a powder containing components with molecular weights higher than 10,000 (high-molecular-weight component powder) was prepared by lyophilization. The minimal inhibitory concentrations against three strains of T. mentagrophytes were all 10 mg/ml. The inhibitory activity was fungicidal and was lost by heating at 100°C for 30 min. Both the whole-leaf powder and the high-molecular-weight component powder induced various morphological abnormalities in spores and hyphae by the inhibition of spore germination and development of hyphae.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fujita K., Suzuki I., Ochiai J., Shinpo K., Inoue S., Saito H. Specific reaction of aloe extract with serum proteins of various animals. Experientia. 1978 Apr 15;34(4):523–524. doi: 10.1007/BF01935968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita K., Teradaira R., Nagatsu T. Bradykinase activity of aloe extract. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Jan 15;25(2):205–205. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90292-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley V. C., English M. P. Some effects of nystatin on the growth of four Aspergillus species. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jul;40(1):107–118. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Azuma K. Evaluation of the in vitro antifungal activity of allicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):743–749. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]