Abstract
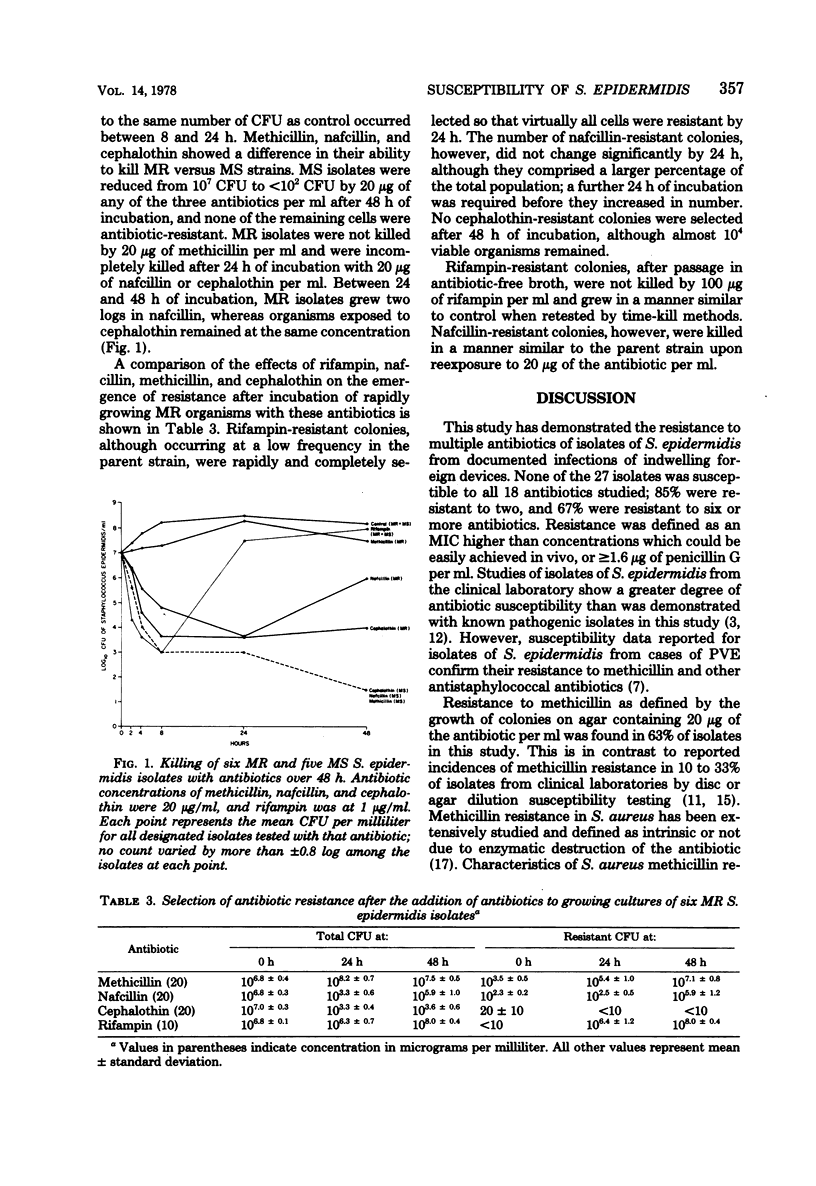
Twenty-seven isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis from patients with prosthetic valve endocarditis or infected cerebrospinal fluid shunts were examined for susceptibility to antimicrobial agents. Subpopulations resistant to 20 and 100 μg of methicillin per ml were present in 63% of the isolates (methicillin-resistant isolates). Subpopulations resistant to 20 μg of nafcillin and cephalothin per ml were found in every methicillin-resistant isolate but with frequencies (10−5.0 ± 0.5 and 10−6.4 ± 0.9, respectively) which were not always detectable by susceptibility testing. Resistance to ≥1.6 μg of penicillin per ml was found in 80% of isolates. Cephalothin, cefazolin, and cefamandole were more active than cefoxitin or cephradine, and gentamicin was more active than tobramycin or amikacin; rifampin was the single most active agent against all isolates. There was no difference in susceptibility between prosthetic valve endocarditis and cerebrospinal fluid shunt infection isolates. Among methicillin-resistant isolates, the phenotypic expression of resistance to methicillin or nafcillin but not to cephalothin could be enhanced by 48 h of incubation with each drug. Isolates containing no methicillin-resistant subpopulations were killed by incubation with methicillin, nafcillin, or cephalothin. High-level resistance to rifampin emerged in both methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive isolates after 8 to 24 h of incubation with this drug. The presence or absence of antibiotic-resistant subpopulations among S. epidermidis isolates and their selection during treatment should be considered when therapy is devised.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arioli V., Berti M., Carniti G., Rossi E. Interaction between rifampicin and trimethoprim in vitro and in experimental infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Jan;3(1):87–94. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Badal R. E. Reliability of the microdilution technic for detection of methicillin-resistant strains of staphylococcus aureus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 May;67(5):489–495. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/67.5.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corse J., Williams R. E. Antibiotic resistance of coagulase-negative staphylococci and micrococci. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Nov;21(6):722–728. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.6.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dismukes W. E., Karchmer A. W., Buckley M. J., Austen W. G., Swartz M. N. Prosthetic valve endocarditis. Analysis of 38 cases. Circulation. 1973 Aug;48(2):365–377. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.48.2.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito A. L., Gleckman R. A. Vancomycin. A second look. JAMA. 1977 Oct 17;238(16):1756–1757. doi: 10.1001/jama.238.16.1756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Lancet. 1968 Nov 16;2(7577):1078–1078. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91549-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keys T. F., Hewitt W. L. Endocarditis due to Micrococci and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Arch Intern Med. 1973 Aug;132(2):216–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverdiere M., Peterson P., Verhoef J., Williams D. N., Sabath L. D. In vitro activity of cephalosporins against methicillin-resistant, coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1978 Mar;137(3):245–250. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND R., ROLINSON G. N. CHARACTERISTICS OF METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:887–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.4.887-899.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Garner C., Wilcox C., Finland M. Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis to 65 antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):962–969. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Wheeler N., Laverdiere M., Blazevic D., Wilkinson B. J. A new type of penicillin resistance of Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1977 Feb 26;1(8009):443–447. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91941-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbaum S. C., Gardner P., Shillito J. Infections of cerebrospinal fluid shunts: epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and therapy. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):543–552. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter L., Morris J. E., Starr A. Prosthetic valvular endocarditis. A 12-year review. Circulation. 1973 Jun;47(6):1319–1326. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.47.6.1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. B., Farkas-Himsley H. The relationship of pathogenic coagulase-negative staphylococci to Staphylococcus aureus. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Aug;15(8):879–890. doi: 10.1139/m69-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. O., Carter M. J., Best G. K. Plasmid-mediated resistance to gentamicin in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Oct;12(4):513–517. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.4.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Mauro E., Synder L., Marino P., Lamberti A., Coppo A., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Rifampicin sensitivity of the components of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 May 10;222(5193):533–537. doi: 10.1038/222533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



