Abstract
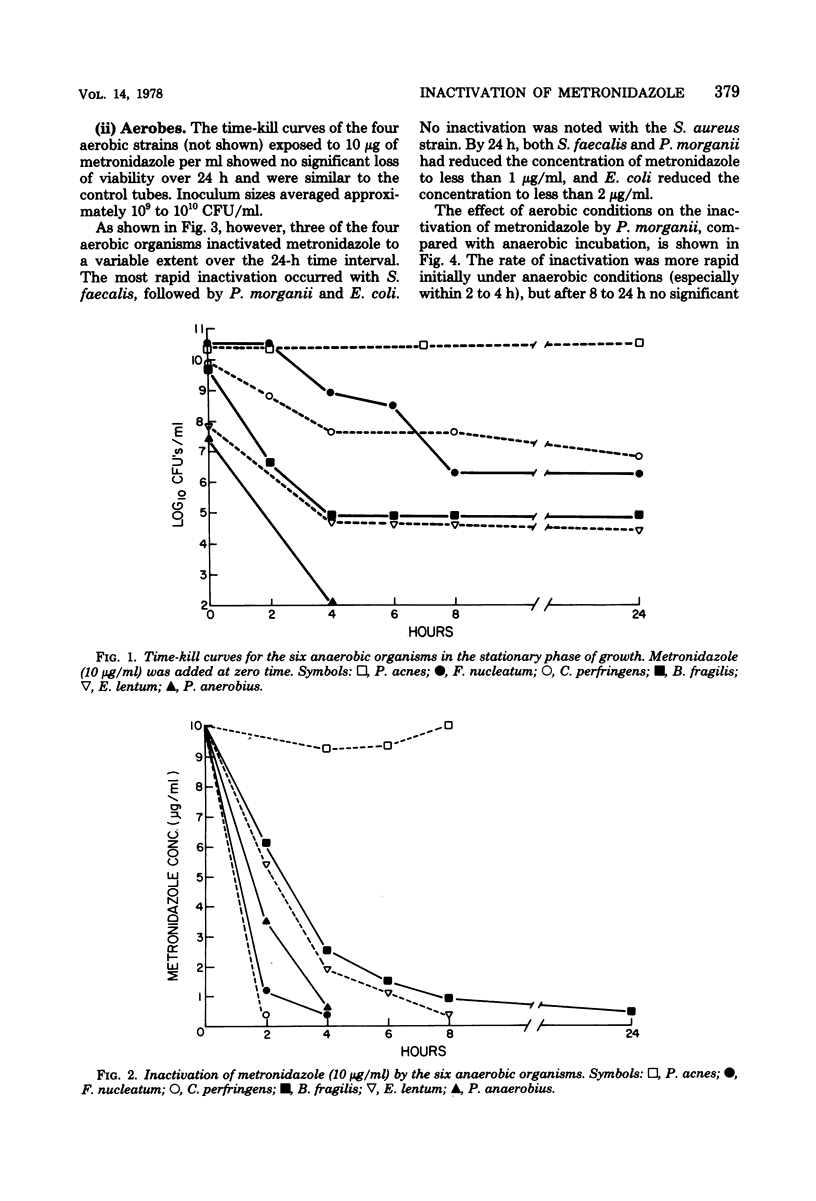
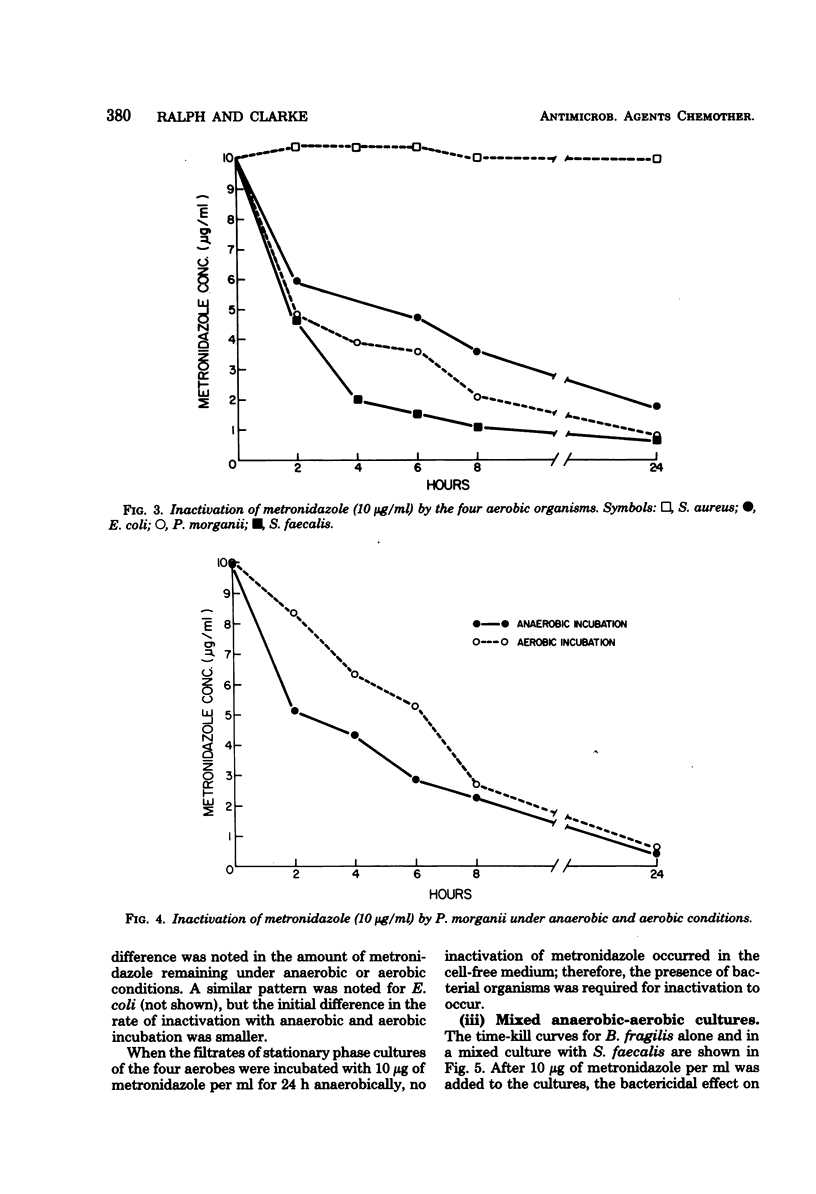
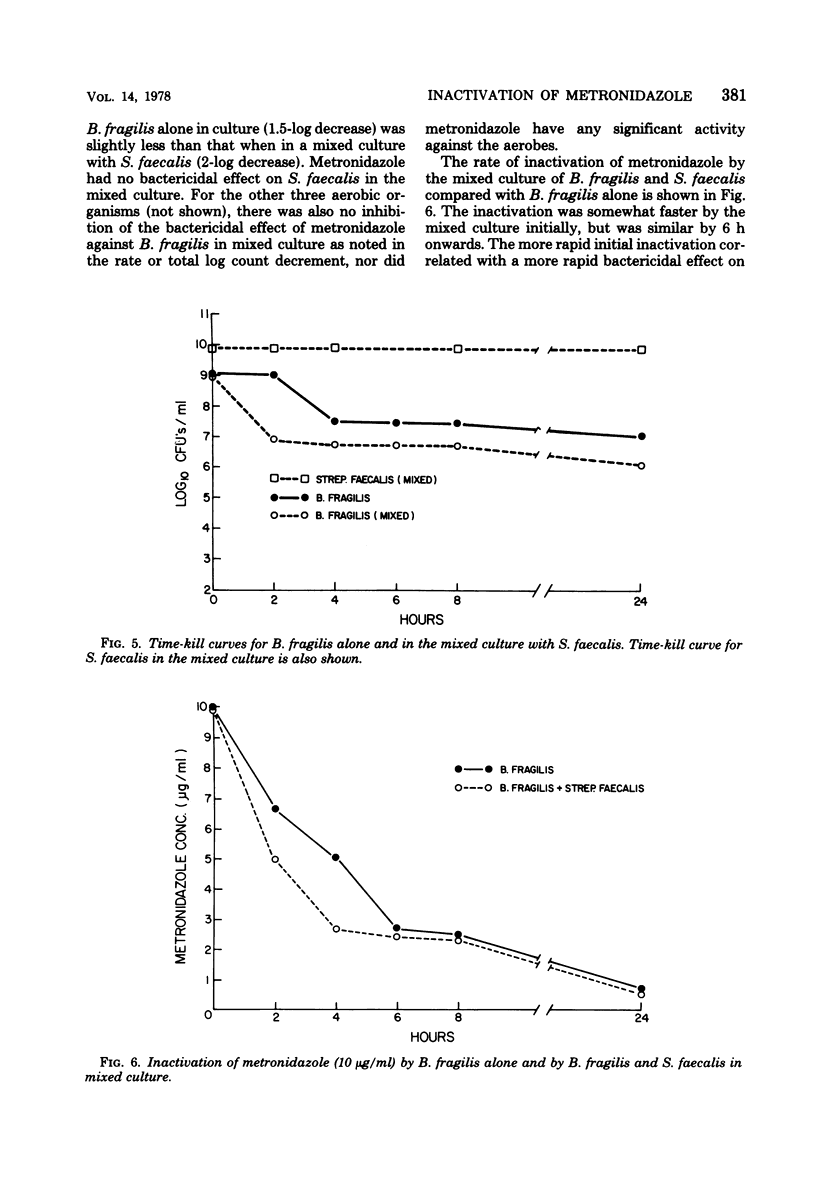
The rate of inactivation of metronidazole in vitro was determined during the course of time-kill curves against anaerobic and aerobic bacteria in the stationary phase of growth. Metronidazole at a concentration of 10 μg/ml, as measured by bioassay, was rapidly inactivated in broth culture by susceptible anaerobic bacteria (minimum bactericidal concentration ≤ 3 μg/ml), and this correlated closely with its bactericidal activity. In contrast, the drug was neither inactivated nor had any bactericidal activity against a resistant strain of Propionibacteriumacnes (minimum bactericidal concentration > 1,500 μg/ml). Three of four aerobic bacteria also inactivated metronidazole, although at generally slower rates than the anaerobes, but this was not associated with a bactericidal effect against these organisms. The presence of aerobic bacteria in mixed cultures with Bacteroides fragilis did not, moreover, inhibit the bactericidal activity of metronidazole against the latter organism. However, the possibility still remains that, in vivo, aerobic bacteria capable of inactivating metronidazole could inhibit the action of the drug against anaerobes in mixed infections.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Giamarellou H., Kanellakopoulou K., Pragastis D., Tagaris N., Daikos G. K. Treatment with metronidazole of 48 patients with serious anaerobic infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Jul;3(4):347–353. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.4.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham H. R., Selkon J. B., Hale J. H. The antibacterial activity of netronidazole. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1975 Dec;1(4):355–361. doi: 10.1093/jac/1.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ings R. M., McFadzean J. A., Ormerod W. E. The mode of action of metronidazole in Trichomonas vaginalis and other micro-organisms. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 May 1;23(9):1421–1429. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Tomasz M., Müller M., Lipman R. Interaction of metronidazole with nucleic acids in vitro. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;13(5):872–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindmark D. G., Müller M. Antitrichomonad action, mutagenicity, and reduction of metronidazole and other nitroimidazoles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Sep;10(3):476–482. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.3.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadzean J. A., Pugh I. M., Squires S. L., Whelan J. P. Further observations on strain sensitivity of Trichomonas vaginalis to metronidazole. Br J Vener Dis. 1969 Jun;45(2):161–162. doi: 10.1136/sti.45.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Lindmark D. G. Uptake of metronidazole and its effect on viability in trichomonads and Entamoeba invadens under anaerobic and aerobic conditions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):696–700. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph E. D., Clarke J. T., Libke R. D., Luthy R. P., Kirby W. M. Pharmacokinetics of metronidazole as determined by bioassay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):691–696. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph E. D., Kirby W. M. Bioassay of metronidazole with either anaerobic or aerobic incubation. J Infect Dis. 1975 Nov;132(5):587–591. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.5.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph E. D., Kirby W. M. Unique bactericidal action of metronidazole against Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium perfringens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Oct;8(4):409–414. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Goldin B. R., Sullivan N., Johnston J., Gorbach S. L. Antimicrobial activity of metronidazole in anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):460–465. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Metronidazole versus anaerobes. In vitro data and initial clinical observations. Calif Med. 1972 Dec;117(6):22–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Treatment of anaerobic infections with metronidazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):672–675. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



