Abstract
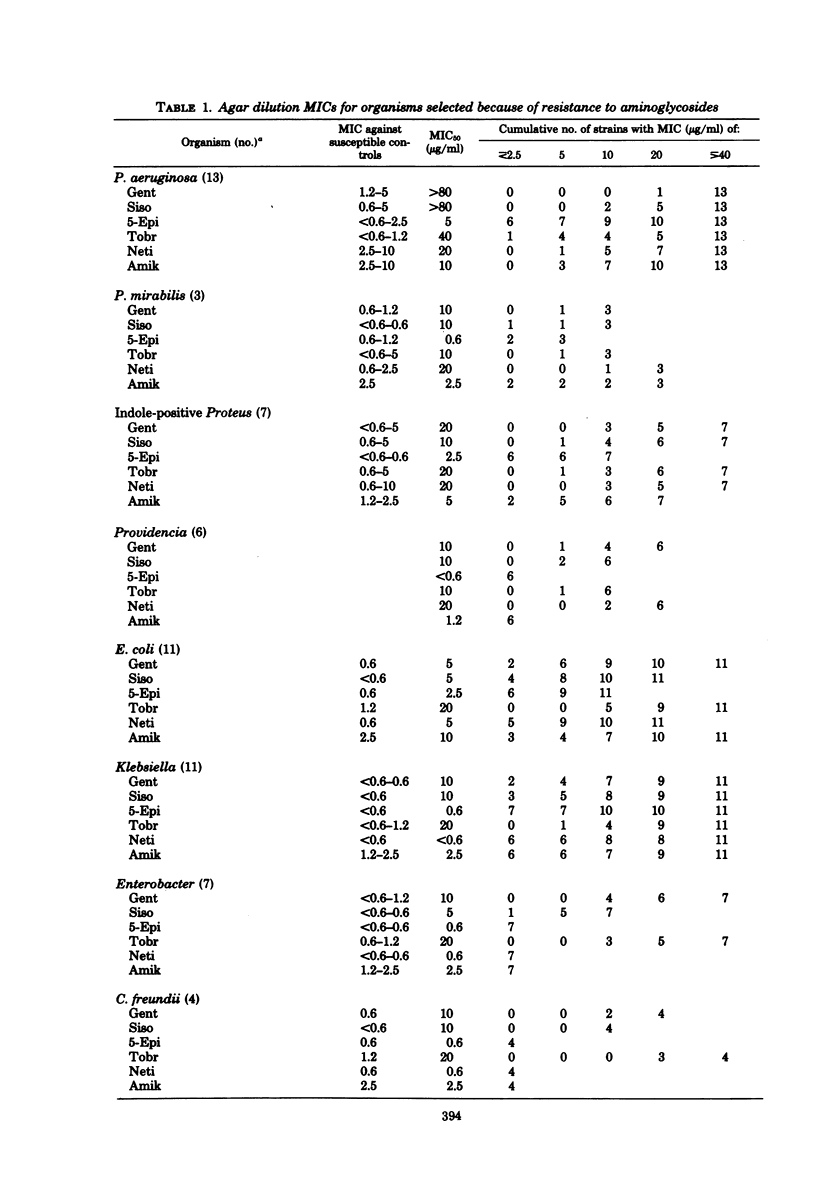
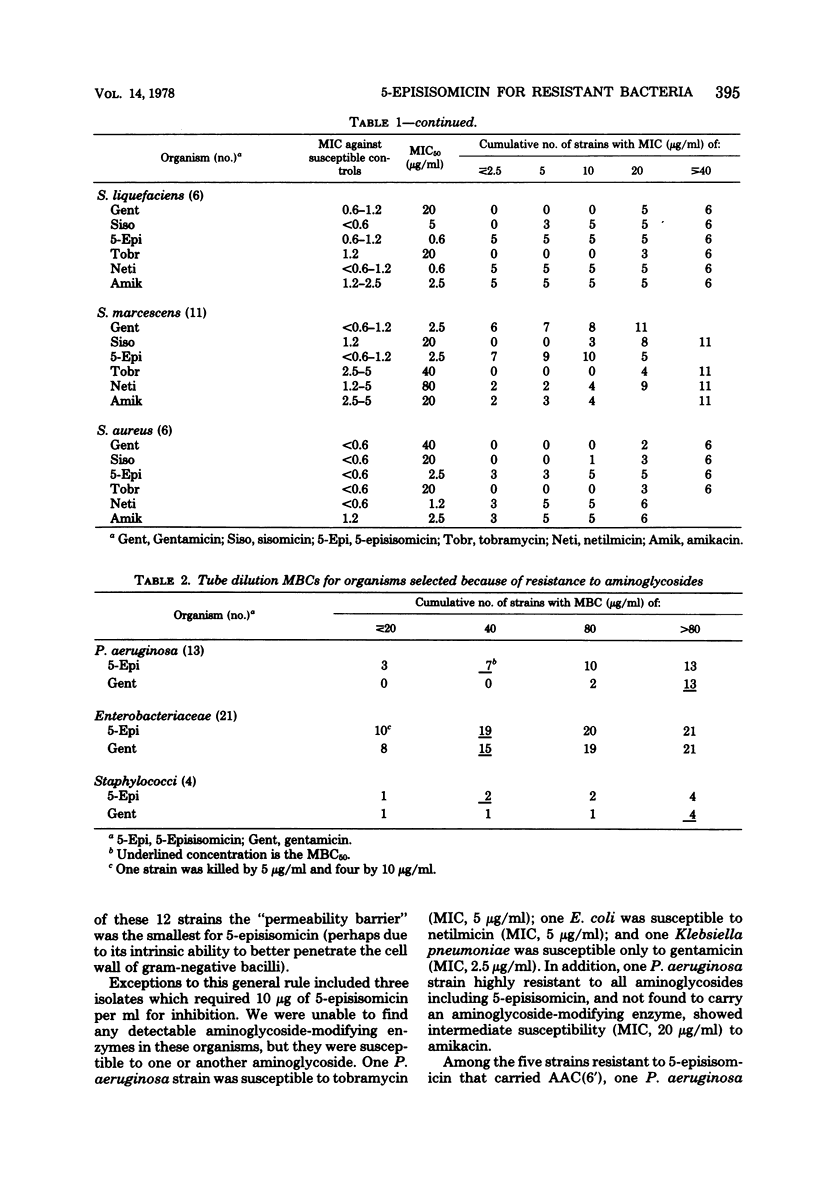
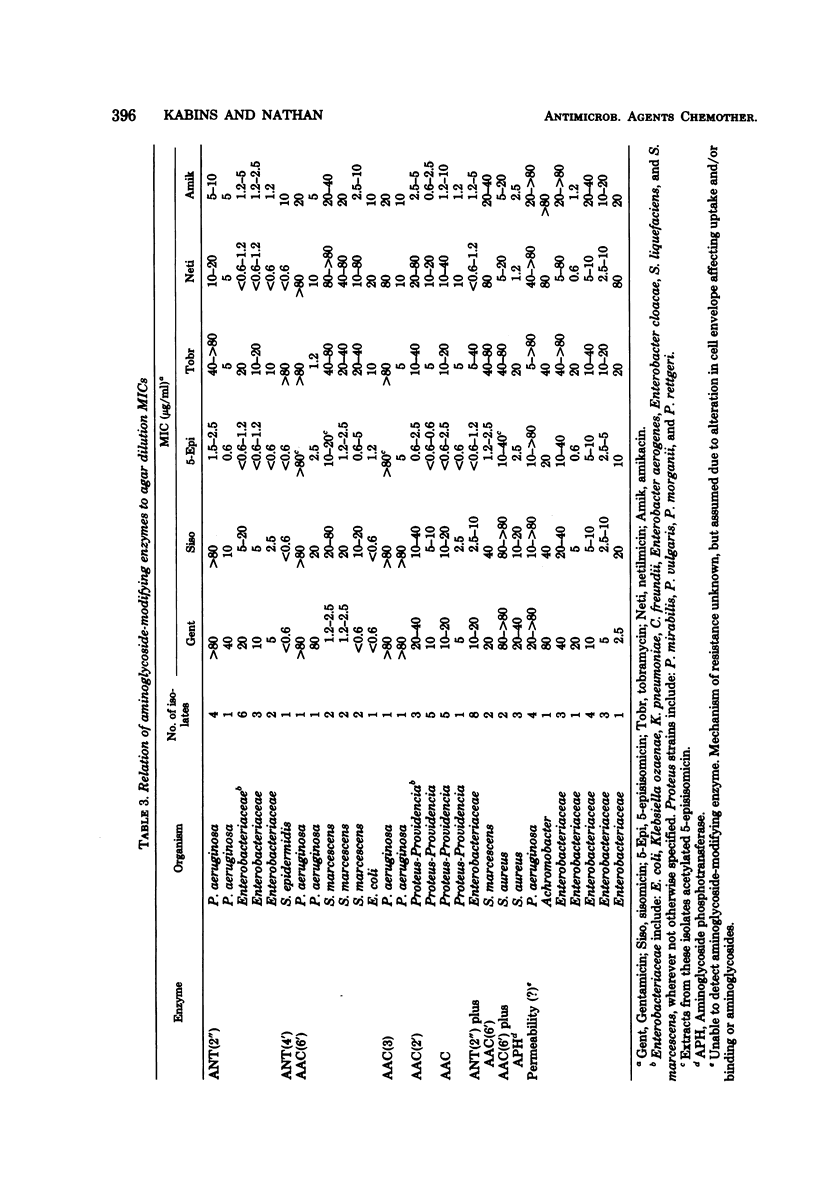
Eighty-seven isolates of Pseudomonas, Enterobacteriaceae, and Staphylococcus, chosen because of their resistance to other aminoglycosides, were tested for susceptibility to 5-episisomicin. Tests were performed in Mueller-Hinton agar and also, with 38 of these isolates, in Mueller-Hinton broth. Of Enterobacteriaceae, 85 and 95.5% were inhibited by 5 and 10 μg of 5-episisomicin per ml, respectively. Amikacin inhibited 74 and 91% of the strains at 10 and 20 μg/ml, respectively. Fifty-four percent of P. aeruginosa were inhibited by 5-episisomicin and amikacin. Eighty-three percent of S. aureus were inhibited by netilmicin and amikacin, whereas only 50% were inhibited by 5-episisomicin. Isolates resistant to 5-episisomicin were most often resistant to the other aminoglycosides and occurred in gram-negative bacilli that did not carry aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Five of 23 isolates that carried a 6′-N-acetyltransferase (AAC-6′) and one of two that carried an aminoglycoside 3-acetyltransferase were resistant to and acetylate 5-episisomicin. Strains carrying other aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes were inhibited by 5-episisomicin. Thus, 5-episisomicin is a promising aminoglycoside not attacked by most aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Resistance will probably most often be based upon nonenzymatic mechanisms which will also affect other aminoglycosides.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davies J., Courvalin P. Mechanisms of resistance to aminoglycosides. Am J Med. 1977 Jun;62(6):868–872. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90654-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. J., Dowding J. E. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:611–628. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabins S. A., Nathan C., Cohen S. In vitro comparison of netilmicin, a semisynthetic derivative of sisomicin, and four other aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):139–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabins S., Nathan C., Cohen S. Gentamicin-adenylyltransferase activity as a cause of gentamicin resistance in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jun;5(6):565–570. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.6.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel L., Nathan C., Sweeney H. M., Kabins S. A., Cohen S. Infections due to gentamicin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain in a nursery for neonatal infants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):466–472. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz J. A., Miller G. H., Moss E., Jr, Chiu P. J. Chemotherapeutic evaluation of 5-episisomicin (Sch 22591), a new semisynthetic aminoglycoside. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):41–48. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


