Abstract
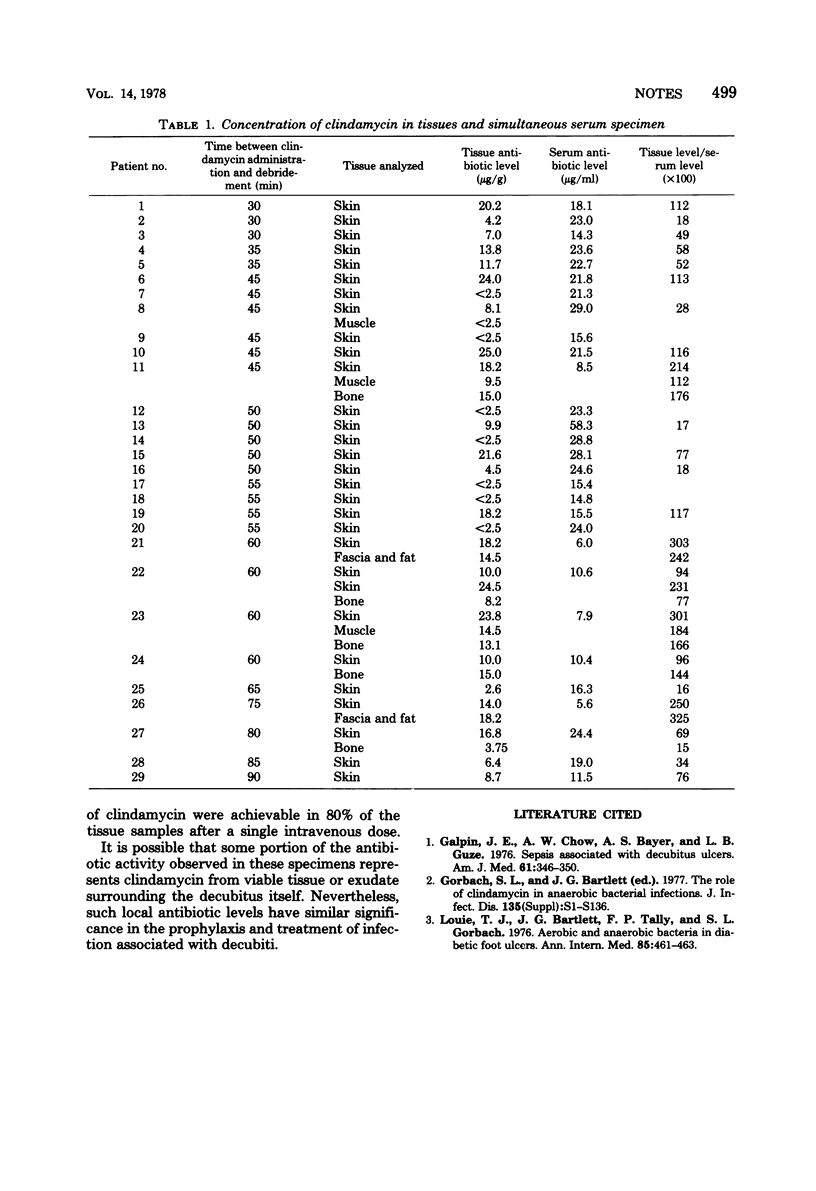
Forty tissue samples, primarily of skin and bone, were obtained from 29 patients undergoing excision of decubitus ulcers after intravenous injection of 600 mg of clindamycin. Antibiotic concentrations exceeded 2.5 μg/g in 80% of the samples. In 50% of the instances, tissue levels were greater than those simultaneously present in the serum.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Galpin J. E., Chow A. W., Bayer A. S., Guze L. B. Sepsis associated with decubitus ulcers. Am J Med. 1976 Sep;61(3):346–350. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90371-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie T. J., Bartlett J. G., Tally F. P., Gorbach S. L. Aerobic and anaerobic bacteria in diabetic foot ulcers. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Oct;85(4):461–463. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-4-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



