Abstract
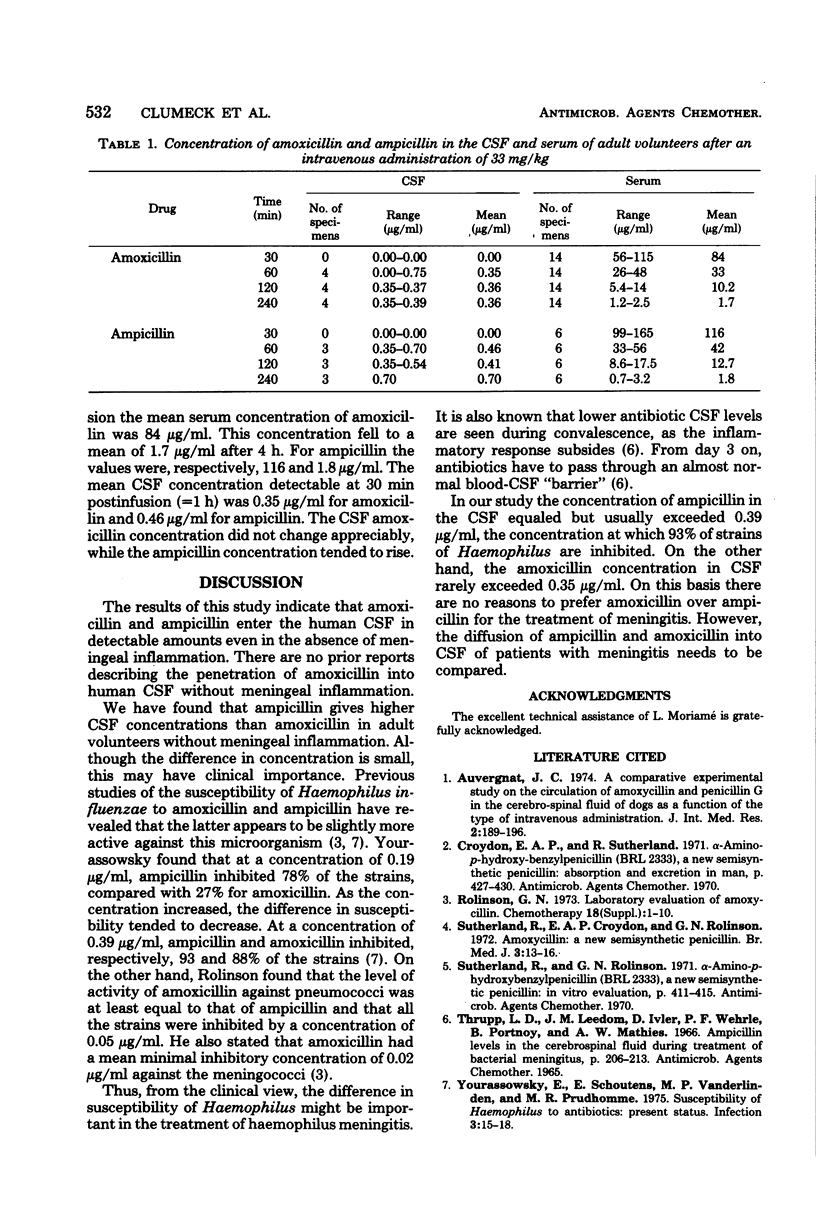
The entry of amoxicillin and ampicillin into cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of humans was studied in the absence of meningeal inflammation. Twelve volunteers received 33 mg of amoxicillin per kg intravenously over 30 min and nine volunteers received 33 mg of ampicillin per kg. The CSF specimens were sampled at 1, 2, and 4 h after the beginning of the infusion. Blood samples were obtained at the end of the infusion and at 45, 60, 90, 120, 180, and 240 min after the beginning of the infusion. Amoxicillin and ampicillin were both detected in the CSF. Ampicillin tended to give higher CSF levels than amoxicillin, although the difference was small. Serum concentrations of ampicillin equaled those of amoxicillin.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Rolinson G. N. Laboratory evaluation of amoxycillin. Chemotherapy. 1973;18(Suppl):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000221287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R., Croydon E. A., Rolinson G. N. Amoxycillin: a new semi-synthetic penicillin. Br Med J. 1972 Jul 1;3(5817):13–16. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5817.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



