Abstract
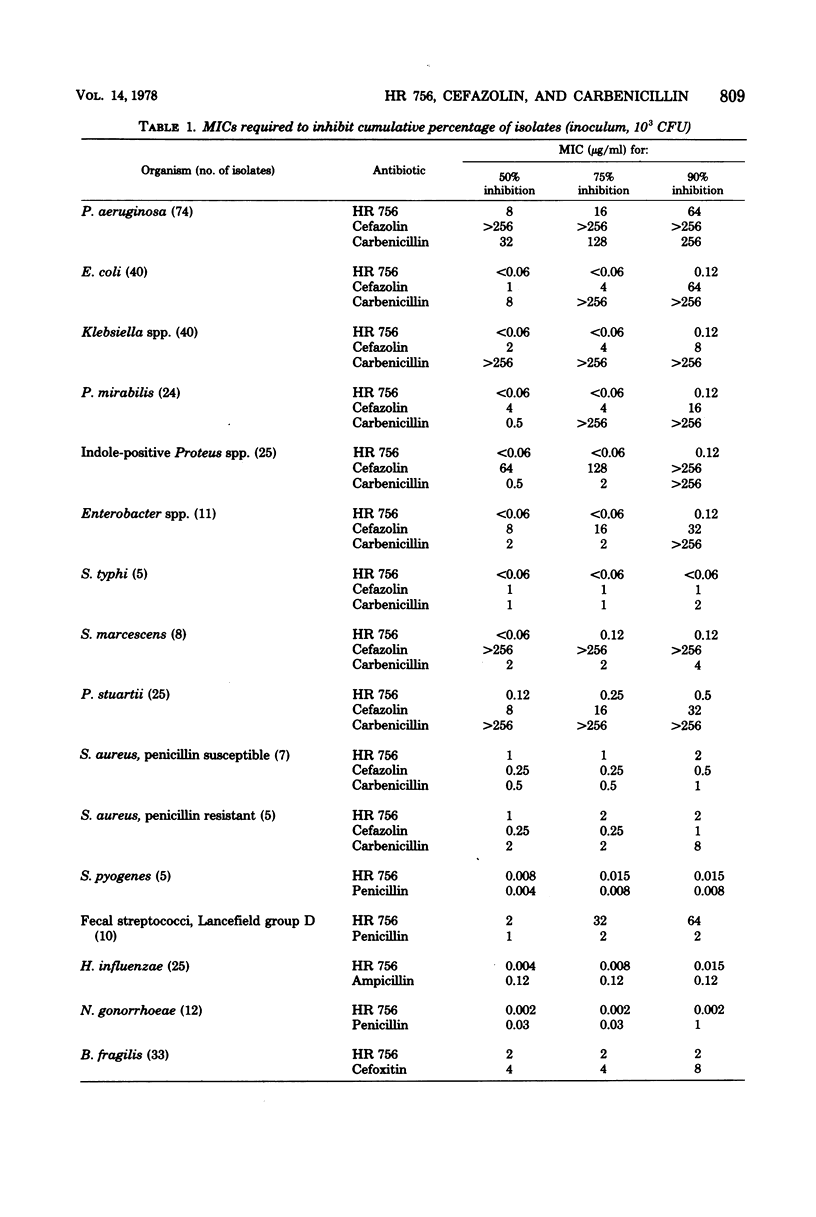
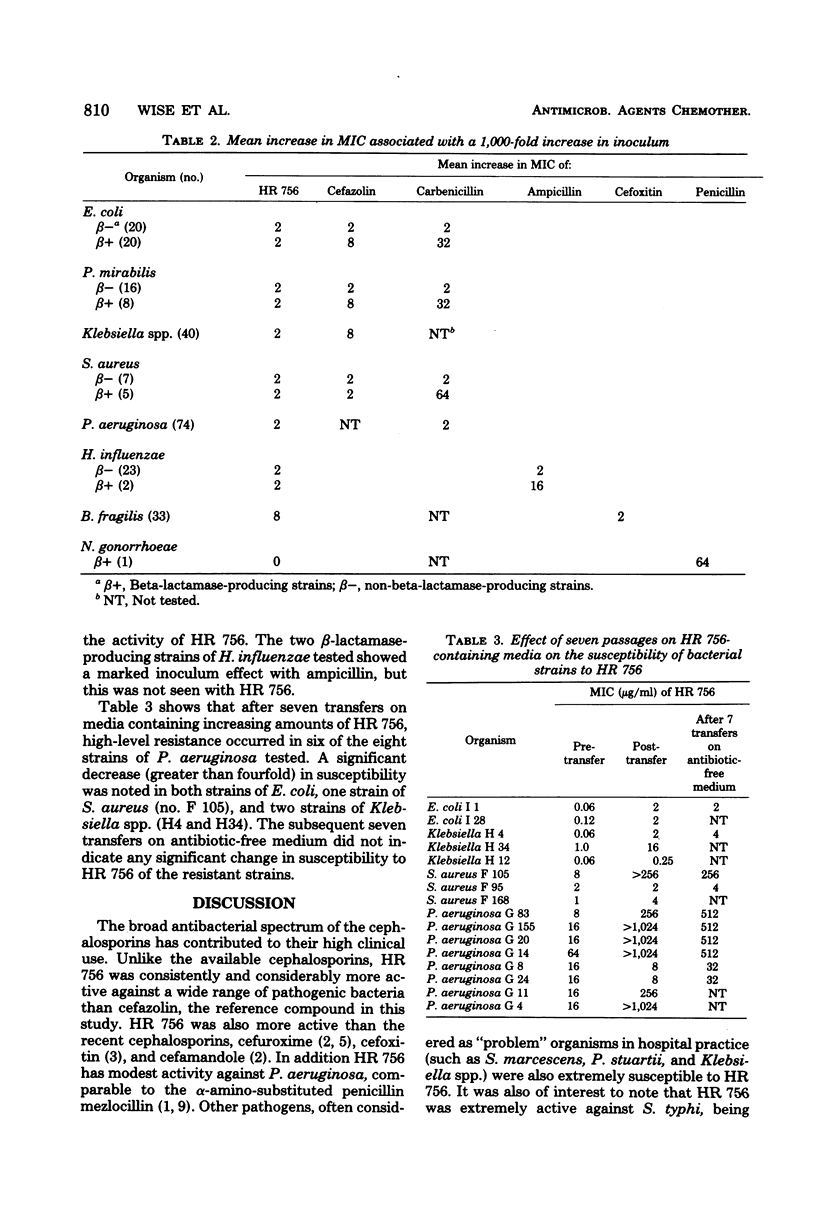
HR 756, a new parenteral cephalosporin, was compared with cefazolin and carbenicillin for activity against a total of 264 strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp., Proteus mirabilis, Proteus spp. (indole positive), Enterobacter spp., Salmonella typhi, Serratia marcescens, Providencia stuartii, and Staphylococcus aureus. In every comparison, except that with the last organism, HR 756 was clearly more active than cefazolin and carbenicillin. All three compounds had similar activity against penicillin-susceptible staphylococci; against penicillin-resistant strains, HR 756 and cefazolin were equally active and superior to carbenicillin. HR 756 was compared with penicillin for activity against strains of Streptococcus pyogenes, Lancefield group D streptococci, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae; with ampicillin against Haemophilus influenzae; and with cefoxitin against Bacteriodes fragilis. HR 756 was clearly more active than the respective reference compounds in all of these comparisons, except those involving the streptococci. HR 756 and penicillin were essentially equally active against S. pyogenes; against Lancefield group D, penicillin was 32 times as active as HR 756. HR 756 not only compared favorably with the reference compounds with respect to relative activity, but also effected growth inhibition of essentially all test organisms (P. aeruginosa and group D streptococci excepted) at remarkably low concentrations ranging from 0.015 to 2.0 μg/ml. A series of seven transfers of selected strains of E. coli, Klebsiella spp., S. aureus, and P. aeruginosa through medium containing HR 756 led to emergence of strains with significant levels of resistance to the agent. Resistance to HR 756 was retained for at least seven transfers through plain medium.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P., Pan T. Mezlocillin: in vitro studies of a new broad-spectrum penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):74–79. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eykyn S., Jenkins C., King A., Phillips I. Antibacterial activity of cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic, compared with that of cephaloridine, cephalothin, and cefamandole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):690–695. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: antibacterial spectrum and resistance to hydrolysis by gram-negative beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):170–176. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Sykes R. B., Griffiths A., Thornton J. E. Cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic: activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):511–519. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Sykes R. B., Ryan D. M., Foord R. D., Muggleton P. W. Cefuroxime - a new cephalosporin antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Jan;29(1):29–37. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson B., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Formation of beta-lactamase in Bacteroides fragilis: cell-bound and extracellular activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):727–735. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S. Antibacterial activity of mecillinam. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Jul;3 (Suppl B):5–11. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.suppl_b.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Gillett A. P., Andrews J. M., Bedford K. A. Activity of azlocillin and mezlocillin against gram-negative organisms: comparison with other penicillins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):559–565. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


