Abstract
Propionibacterium acnes CN-8, isolated from human dental plaque, was grown in a liquid medium, and its bacteriocin-like substance (acnecin) was extracted from the cells by ultrasonic treatment. Acnecin was purified to a homogeneous state with recovery of 47%. Specific activity increased 72-fold in comparison with the crude extract. The properties of acnecin were as follows. (i) Acnecin may consist of five subunits with a molecular weight of about 12,000. (ii) Its isoelectric point was 5.5. (iii) In amino acid composition, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, glycine, and alanine were predominant, whereas cystine was not present. (iv) Acnecin contained 3.3% carbohydrate but was substantially free from lipid. (v) The activity was lost by heating at 60°C or by protease and lysozyme treatments. Acnecin acted bacteriostatically on the indicator strain without killing it. The action spectrum of acnecin was very narrow; it was effective only against strains of non-acnecin-producing P. acnes and Corynebacterium parvum, a species closely related to P. acnes.
Full text
PDF

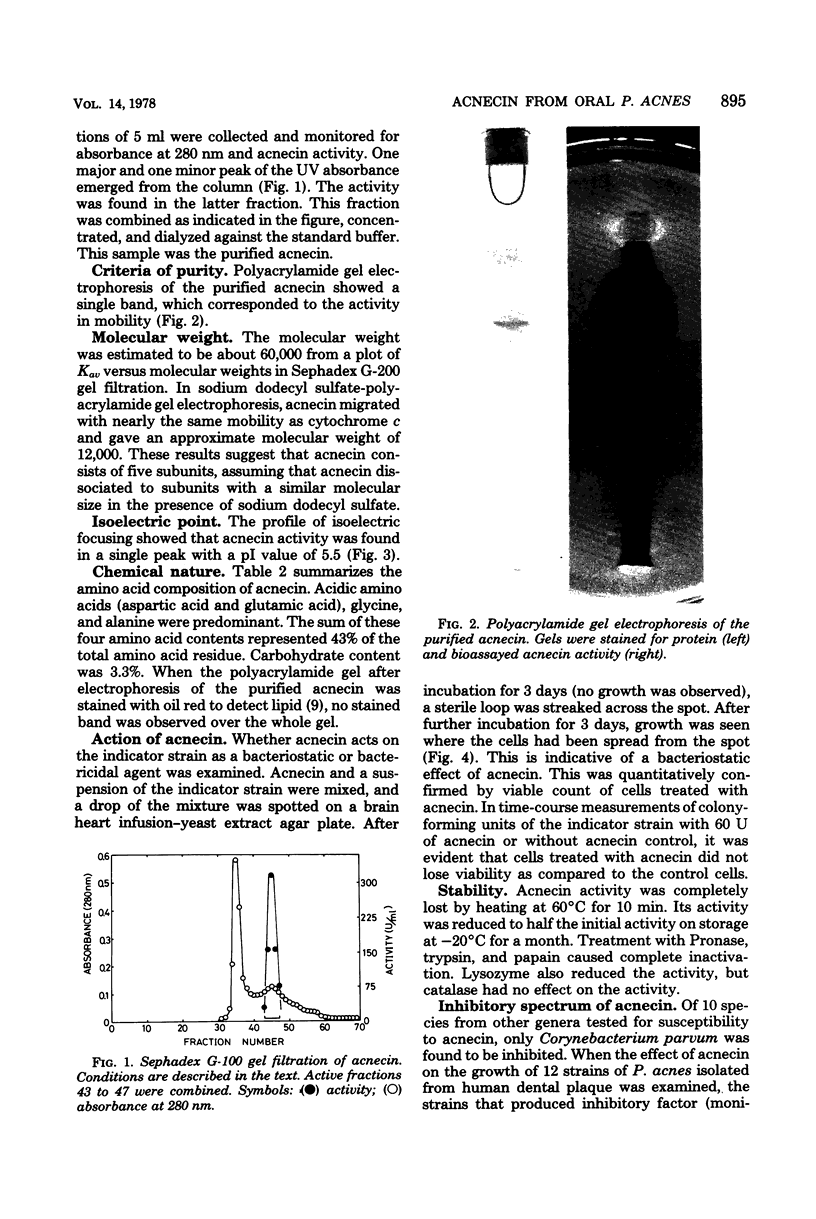
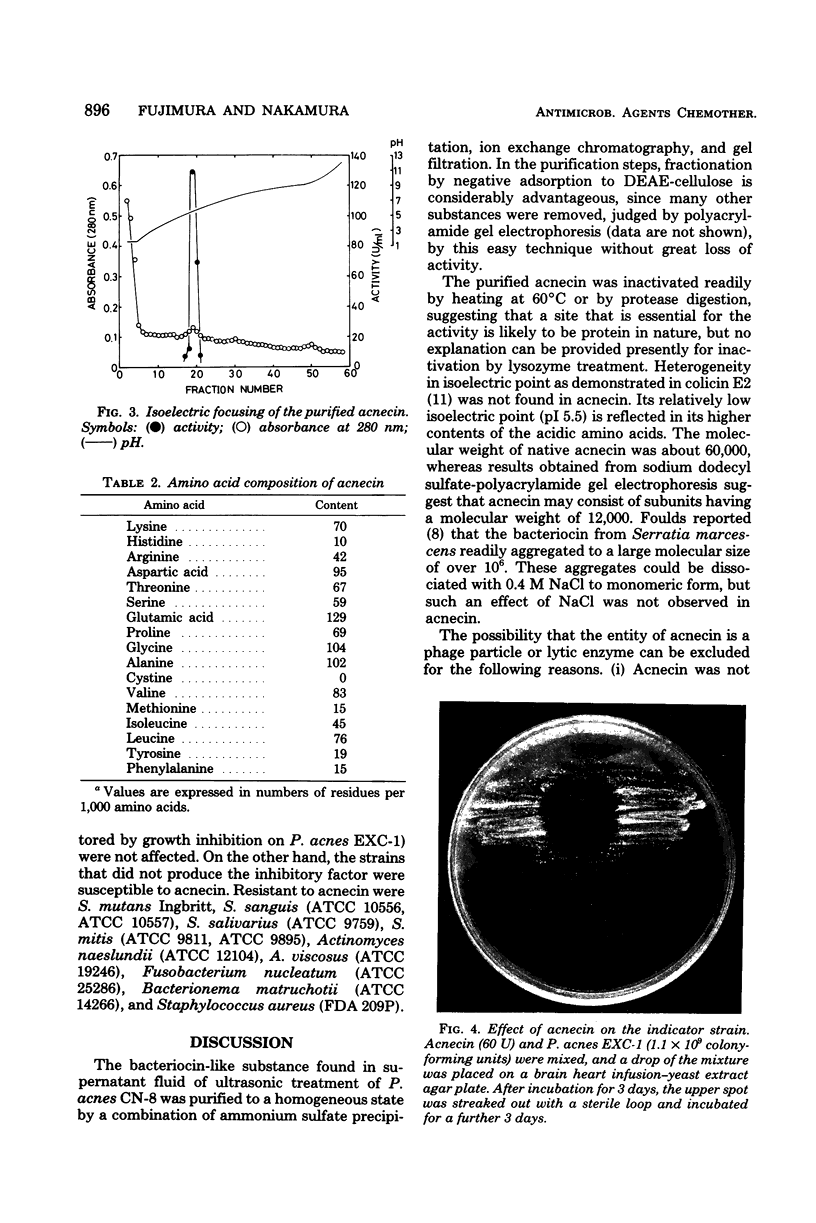


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beveridge T. J., Goldner M. Statistical relationship between the presence of human subgingival anaerobic diptheroids and periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 1973 May-Jun;52(3):451–453. doi: 10.1177/00220345730520031101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Graaf F. K., Klaasen-Boor P. Purification and characterization of a complex between cloacin and its immunity protein isolated from Enterobacter cloacae (Clo DF13). Dissociation and reconstitution of the complex. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb 15;73(1):107–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delisle A. L. Production of bacteriocins in a liquid medium by Streptococcus mutans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Dec;8(6):707–712. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.6.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulds J. Purification and partial characterization of a bacteriocin from Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1001–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1001-1009.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Ooshima T. Inhibitory spectrum of a bacteriocinlike substance (mutacin) produced by some strains of Streptococcus mutans. J Dent Res. 1975 Jan-Feb;54(1):140–145. doi: 10.1177/00220345750540010801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R., Helinski D. R. Purification and characterization of colicin E2 and colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5360–5368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg K., Hallander H. O. Production of bactericidal concentrations of hydrogen peroxide by Streptococcus sanguis. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Mar;18(3):423–434. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakes K., Zinder N. D., Boon T. Purification and properties of colicin E3 immunity protein. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):438–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelstrup J., Gibbons R. J. Bacteriocins from human and rodent streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1969 Mar;14(3):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(69)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelstrup J., Richmond S., West C., Gibbons R. J. Fingerprinting human oral streptococci by bacteriocin production and sensitivity. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Dec;15(12):1109–1116. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Suginaka Y., Obata T., Obata N., Yamazaki N. Bacteriocin-like activities of human dental plaque flora against oral anaerobic microorganisms. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 1977 Nov;18(4):217–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., Klaasen-Boor P., Sneeuwloper G., De Graaf F. K. Interaction of the complex between cloacin and its immunity protein and of cloacin with the outer and cytoplasmic membranes of sensitive cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):445–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D., Slade H. D. Production and properties of an extracellular bacteriocin from Streptococcus mutans bacteriocidal for group A and other streptococci. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1375–1385. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1375-1385.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers A. H. Bacteriocin types of Streptococcus mutans in human mouths. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Dec;20(12):853–858. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers A. H. Bacteriocinogeny and the properties of some bacteriocins of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1976;21(2):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(76)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabiston C. B., Jr, Grigsby W. R. Anaerobic bacteria from the advanced periodontal lesion. J Periodontol. 1972 Apr;43(4):199–201. doi: 10.1902/jop.1972.43.4.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Slade H. D. Alteration of macromolecular synthesis and membrane permeability by a Streptococcus sanguis bacteriocin. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Mar;81(1):275–277. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-1-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Slade H. D. Bacteriocin production by transformable group H streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):824–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.824-829.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Slade H. D. Properties of a Streptococcus sanguis (group H) bacteriocin and its separation from the competence factor of transformation. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):655–661. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.655-661.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidikaro J., Nomura M. E3 immunity substance. A protein from e3-colicinogenic cells that accounts for their immunity to colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):445–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J. A., de Klerk H. C., Coetzee J. N. Properties of a Proteus morganii bacteriocin. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Nov;54(1):67–75. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-1-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):722–756. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.722-756.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazoe I., Nakamura T. Experimental mixed infection by human gingival crevice material. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 1971 May;12(2):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterberg O., Wadström T., Vesterberg K., Svensson H., Malmgren B. Studies on extracellular PROTEINS FROM Staphylococcus aureus. I. Separation and characterization of enzymes and toxins by isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 11;133(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Imai S., Nisizawa T., Araya S. Production of, and susceptibility to, bacteriocin-like substances in oral streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 May-Jun;20(5-6):389–391. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Klerk H. C., Smit J. A. Properties of a Lactobacillus fermenti bacteriocin. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):309–316. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]