Abstract
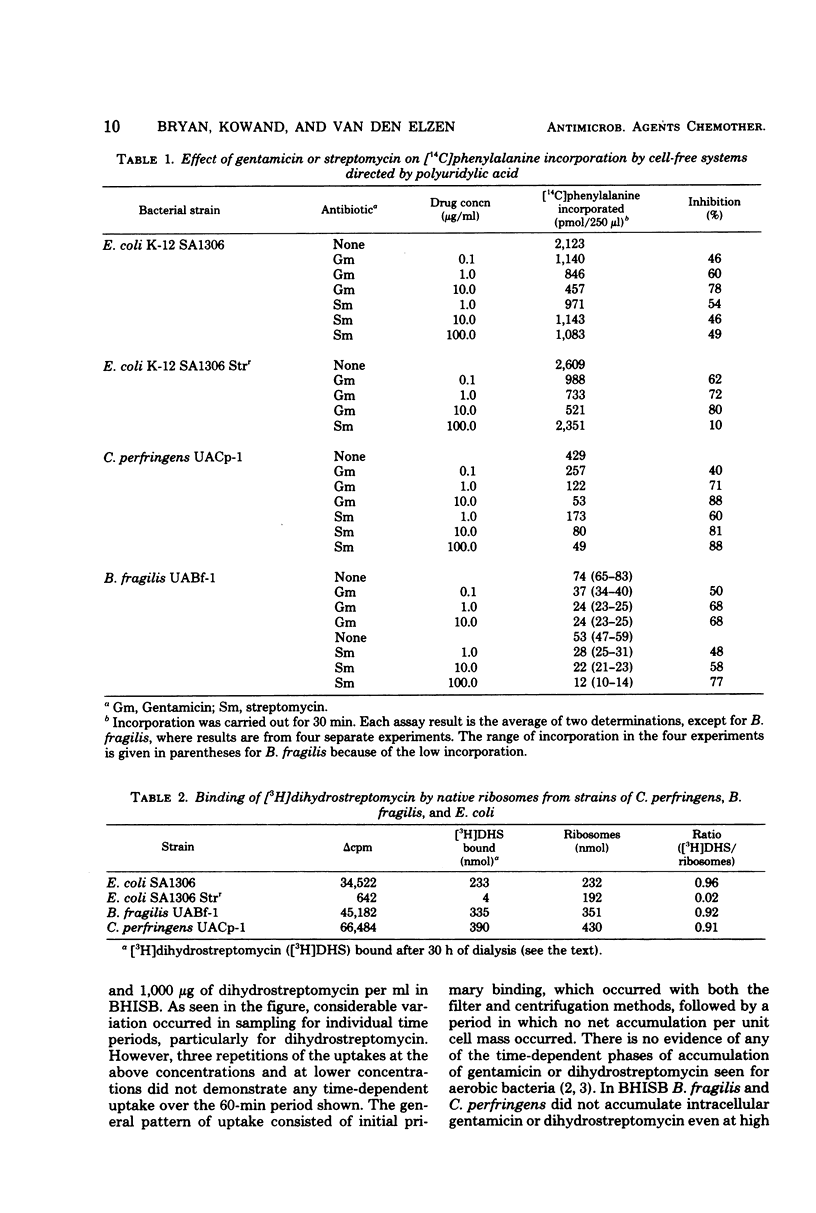
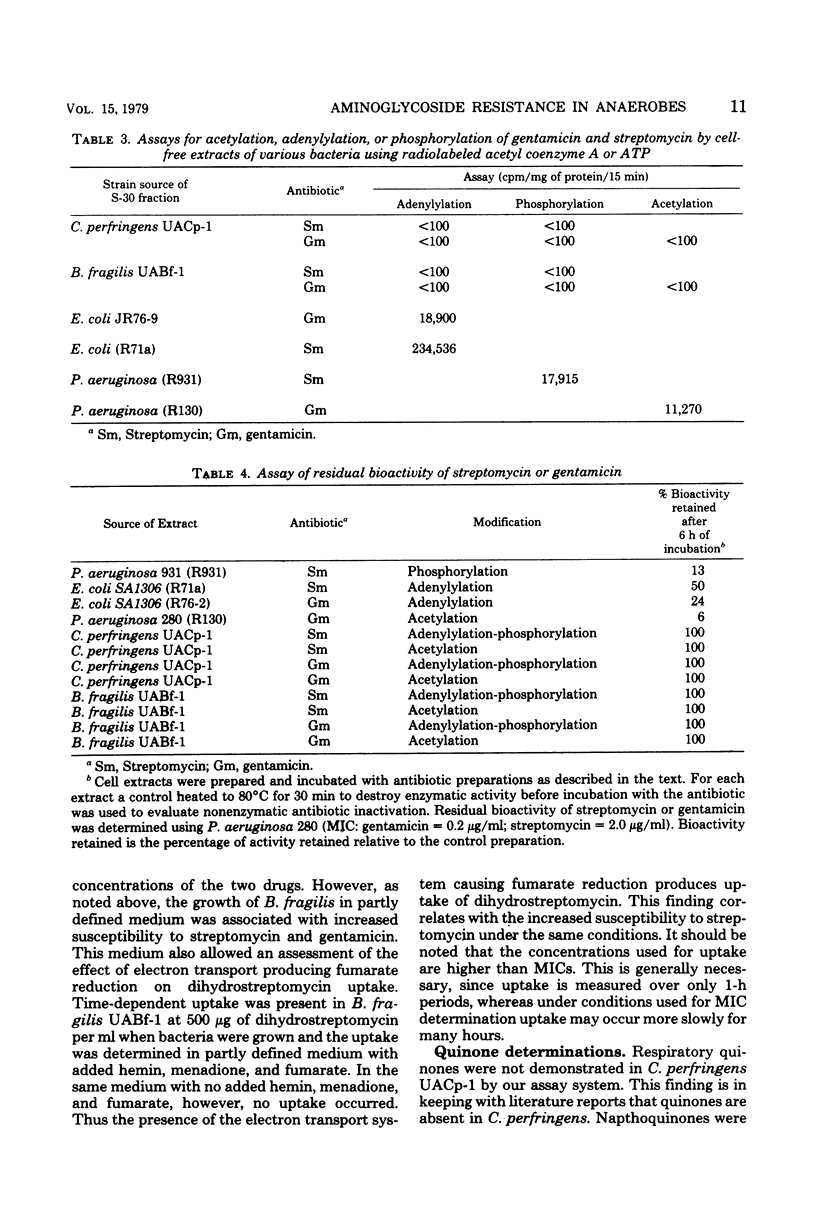
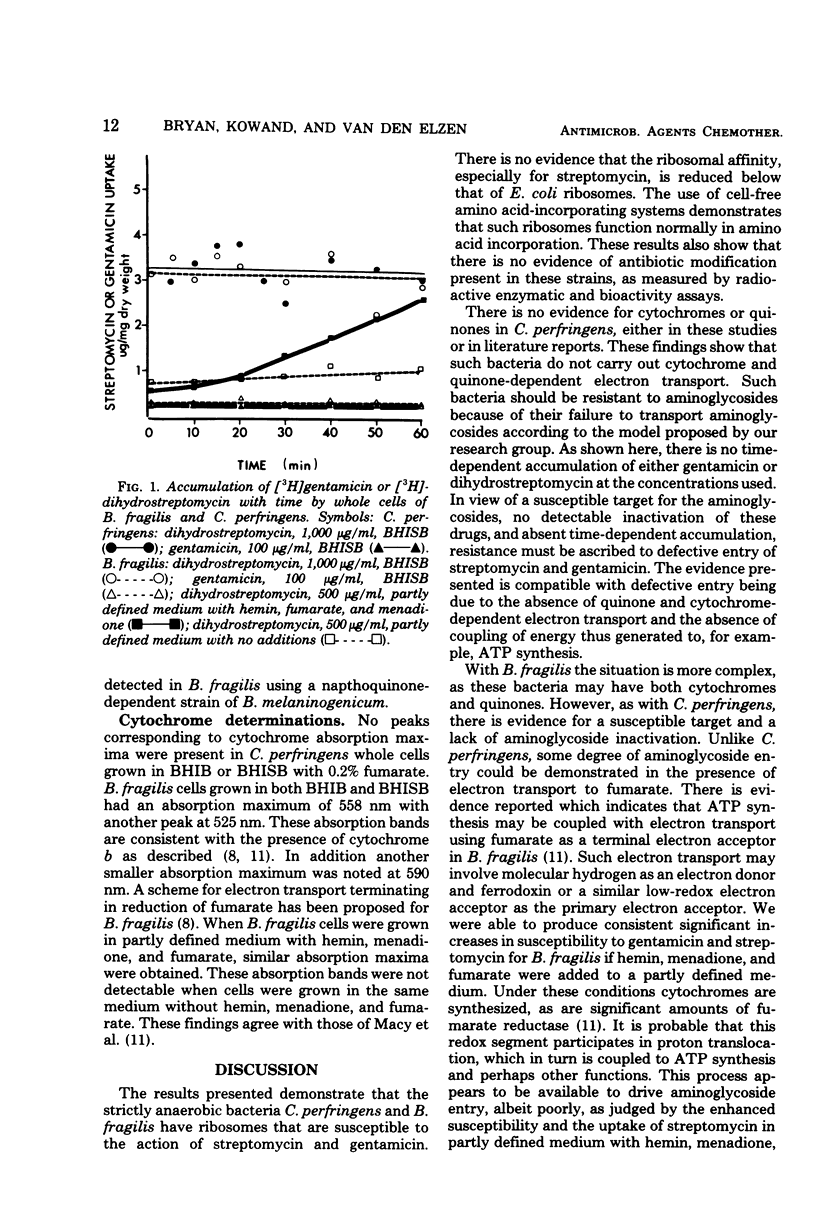
Cell-free amino acid incorporation using ribosomes from strains of either Clostridium perfringens or Bacteroides fragilis was shown to be susceptible to inhibition by streptomycin and gentamicin. Ribosomes bound dihydrostreptomycin as effectively as ribosomes from Escherichia coli. No inactivation of streptomycin or gentamicin was detected by cell extracts of either anaerobic bacterial species. B. fragilis, grown without added hemin, menadione, and fumarate, and C. perfringens did not show any time-dependent accumulation of dihydrostreptomycin or gentamicin at concentrations tested. Decreased resistance to aminoglycosides and time-dependent uptake of dihydrostreptomycin at 500 μg/ml was observed with B. fragilis grown with hemin, menadione, and fumarate. With the last additions, cytochrome b was detected by cytochrome spectra of B. fragilis. These results demonstrate that anaerobic bacteria unable to carry out oxygen- or nitrate-dependent electron transport are resistant to streptomycin and gentamicin because of failure to transport aminoglycosides. The induction of fumarate-dependent electron transport in B. fragilis is associated with some aminoglycoside transport that is of poor efficiency relative to bacteria with electron transport to oxygen or nitrate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryan L. E., Haraphongse R., Van den Elzen H. M. Gentamicin resistance in clinical-isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with diminished gentamicin accumulation and no detectable enzymatic modification. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Jul;29(7):743–753. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van Den Elzen H. M. Effects of membrane-energy mutations and cations on streptomycin and gentamicin accumulation by bacteria: a model for entry of streptomycin and gentamicin in susceptible and resistant bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):163–177. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van Den Elzen H. M. Gentamicin accumulation by sensitive strains of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1975 Sep;28(9):696–703. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.28.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van den Elzen H. M. Streptomycin accumulation in susceptible and resistant strains of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):928–938. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Flaks J. G. Binding of dihydrostreptomycin to Escherichia coli ribosomes: characteristics and equilibrium of the reaction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Oct;2(4):294–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.4.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. J., ENGLE L. P. VITAMIN K COMPOUNDS IN BACTERIA THAT ARE OBLIGATE ANAEROBES. Science. 1964 Dec 4;146(3649):1307–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3649.1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. J., Dowding J. E. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:611–628. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. A., Reddy C. A. Hydrogenase activity and the H2-fumarate electron transport system in Bacteroides fragilis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Sep;131(3):922–928. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.3.922-928.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V. Streptomycin uptake via an inducible polyamine transport system in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May 16;86(2):345–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macy J., Probst I., Gottschalk G. Evidence for cytochrome involvement in fumarate reduction and adenosine 5'-triphosphate synthesis by Bacteroides fragilis grown in the presence of hemin. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):436–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.436-442.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton N. A., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Function of ubiquinone in Escherichia coli: a mutant strain forming a low level of ubiquinone. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):69–73. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.69-73.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahrabadi M. S., Bryan L. E., Van Den Elizen H. M. Further properties of P-2 R-factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their relationship to other plasmid groups. Can J Microbiol. 1975 May;21(5):592–605. doi: 10.1139/m75-086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


