Abstract
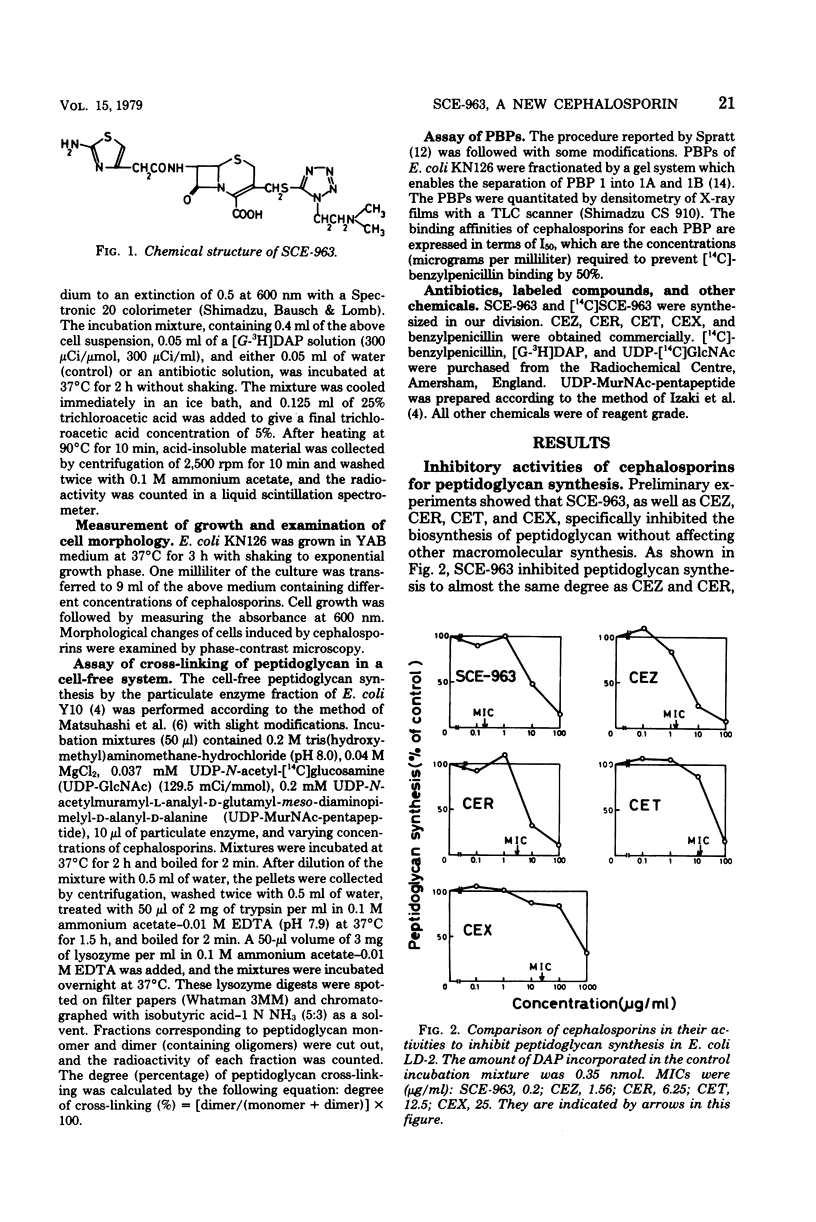
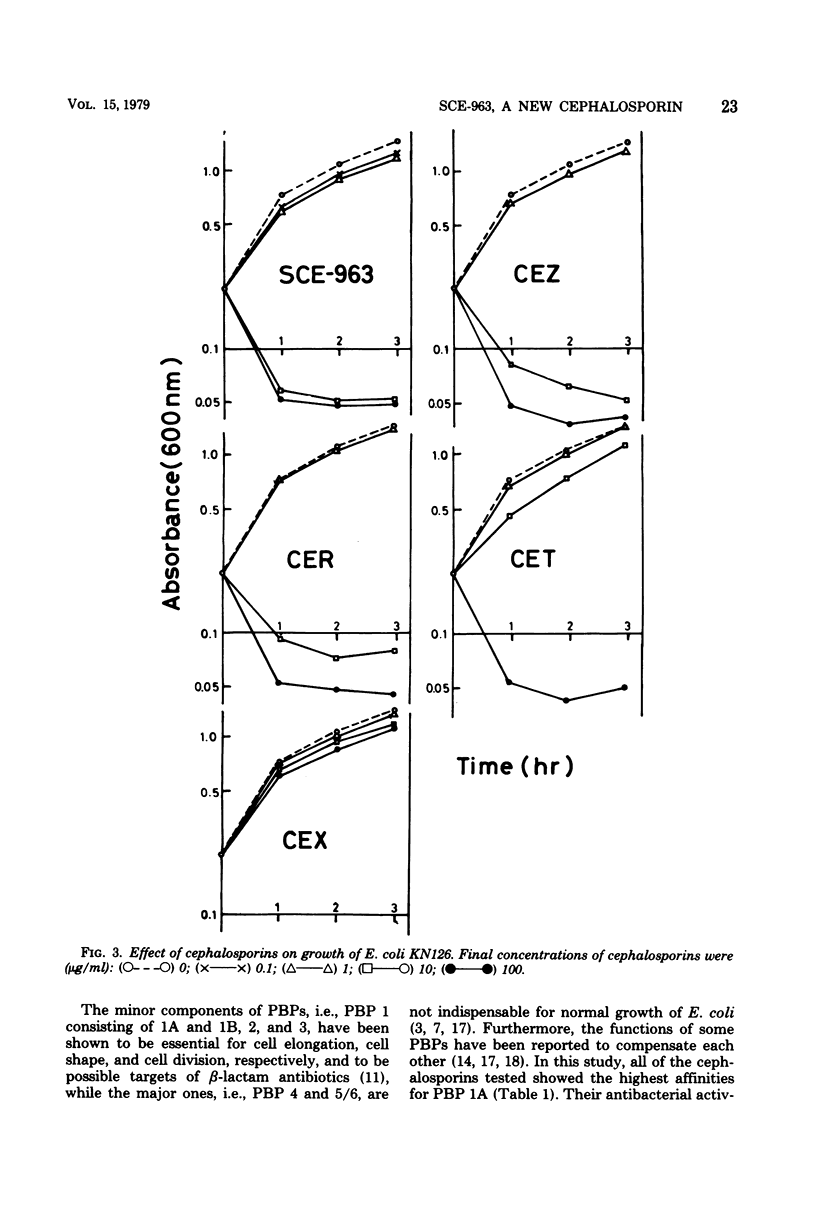
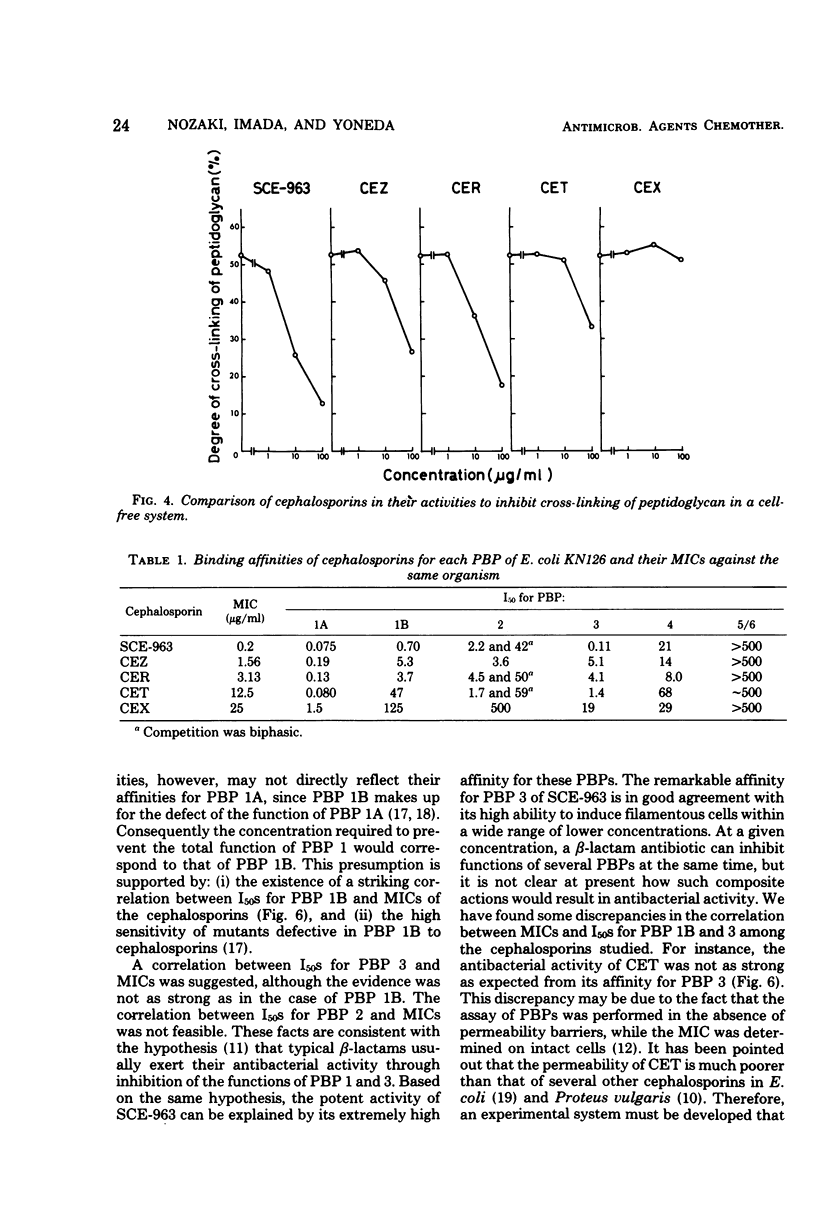
A few biochemical activities of SCE-963, a new cephalosporin with potent antibacterial activities against gram-negative bacteria, were compared with those of several currently available cephalosporins against strains of Escherichia coli K-12. The minimum inhibitory concentrations of SCE-963, cefazolin, cephaloridine, cephalothin, and cephalexin were 0.2, 1.56, 3.13, 12.5, and 25 μg/ml, respectively. Affinities of these cephalosporins for the penicillin-binding protein (PBP) 1B of E. coli correlated well with their antibacterial activities; among tested cephalosporins, SCE-963 showed the highest affinity for PBP 1B. SCE-963 inhibited cross-linking of peptidoglycan in a cell-free system the most strongly suggesting that this inhibition results from its high affinity for PBP 1B. SCE-963 also showed the highest affinity for PBP 3; it caused filamentation of cells over a wide range of relatively lower concentrations. Thus its superior antibacterial activity is believed to be manifested through its high affinity for the PBPs.
Full text
PDF

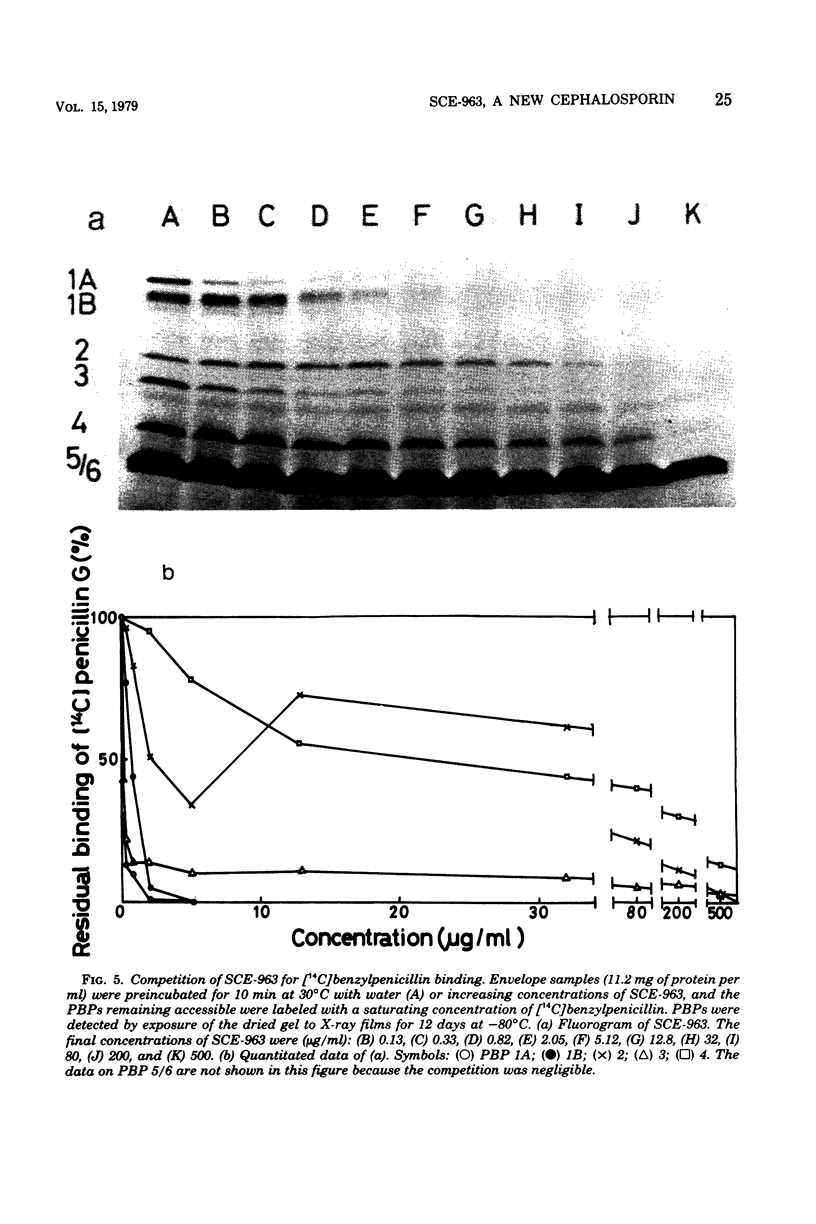
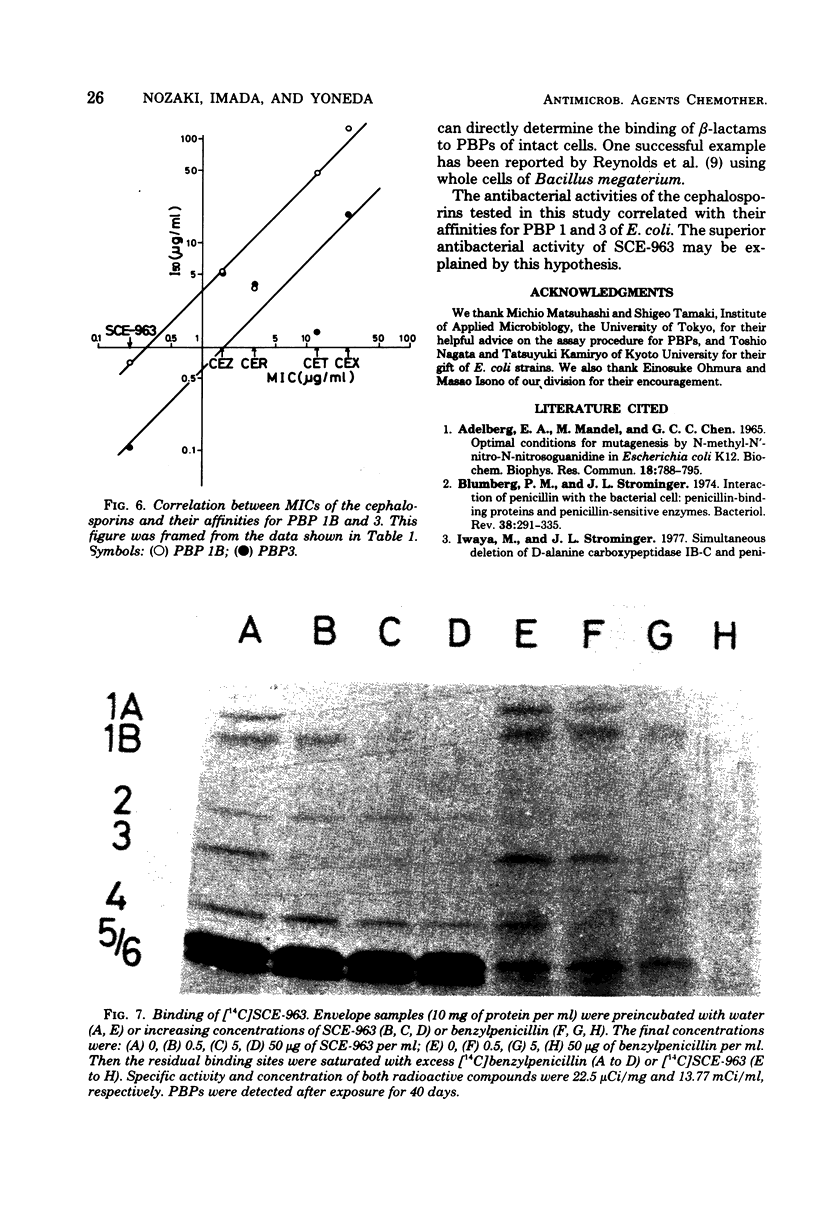

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. Interaction of penicillin with the bacterial cell: penicillin-binding proteins and penicillin-sensitive enzymes. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Sep;38(3):291–335. doi: 10.1128/br.38.3.291-335.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaki K., Matsuhashi M., Strominger J. L. Biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. 8. Peptidoglycan transpeptidase and D-alanine carboxypeptidase: penicillin-sensitive enzymatic reaction in strains of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):3180–3192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiryo T., Strominger J. L. Penicillin-resistant temperature-sensitive mutants of Escherichia coli which synthesize hypo- or hyper-cross-linked peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):568–577. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.568-577.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuhashi M., Takagaki Y., Maruyama I. N., Tamaki S., Nishimura Y., Suzuki H., Ogino U., Hirota Y. Mutants of Escherichia coli lacking in highly penicillin-sensitive D-alanine carboxypeptidase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2976–2979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuhashi S., Kamiryo T., Blumberg P. M., Linnett P., Willoughby E., Strominger J. L. Mechanism of action and development of resistance to a new amidino penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):578–587. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.578-587.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T., Horiuchi T. Isolation and characterization of a temperature-sensitive amber suppressor mutant of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1973;123(1):77–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00282991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. E., Shepherd S. T., Chase H. A. Identification of the binding protein which may be the target of penicillin action in Bacillus megaterium. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):568–570. doi: 10.1038/271568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai T., Matsuba K., Yamagishi S. A method for measuring the outer membrane-permeability of beta-lactam antibiotics in gram-negative bacteria. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Dec;30(12):1134–1136. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Jobanputra V. Mutants of Escherichia coli which lack a component of penicillin-binding protein 1 are viable. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 15;79(2):374–378. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80824-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Pardee A. B. Penicillin-binding proteins and cell shape in E. coli. Nature. 1975 Apr 10;254(5500):516–517. doi: 10.1038/254516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Temperature-sensitive cell division mutants of Escherichia coli with thermolabile penicillin-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):293–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.293-305.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: a series of mutants of E. coli altered in the penicillin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki S., Nakajima S., Matsuhashi M. Thermosensitive mutation in Escherichia coli simultaneously causing defects in penicillin-binding protein-1Bs and in enzyme activity for peptidoglycan synthesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5472–5476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W., Rosselet A. Function of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli as a permeability barrier to beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):368–372. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]