Abstract
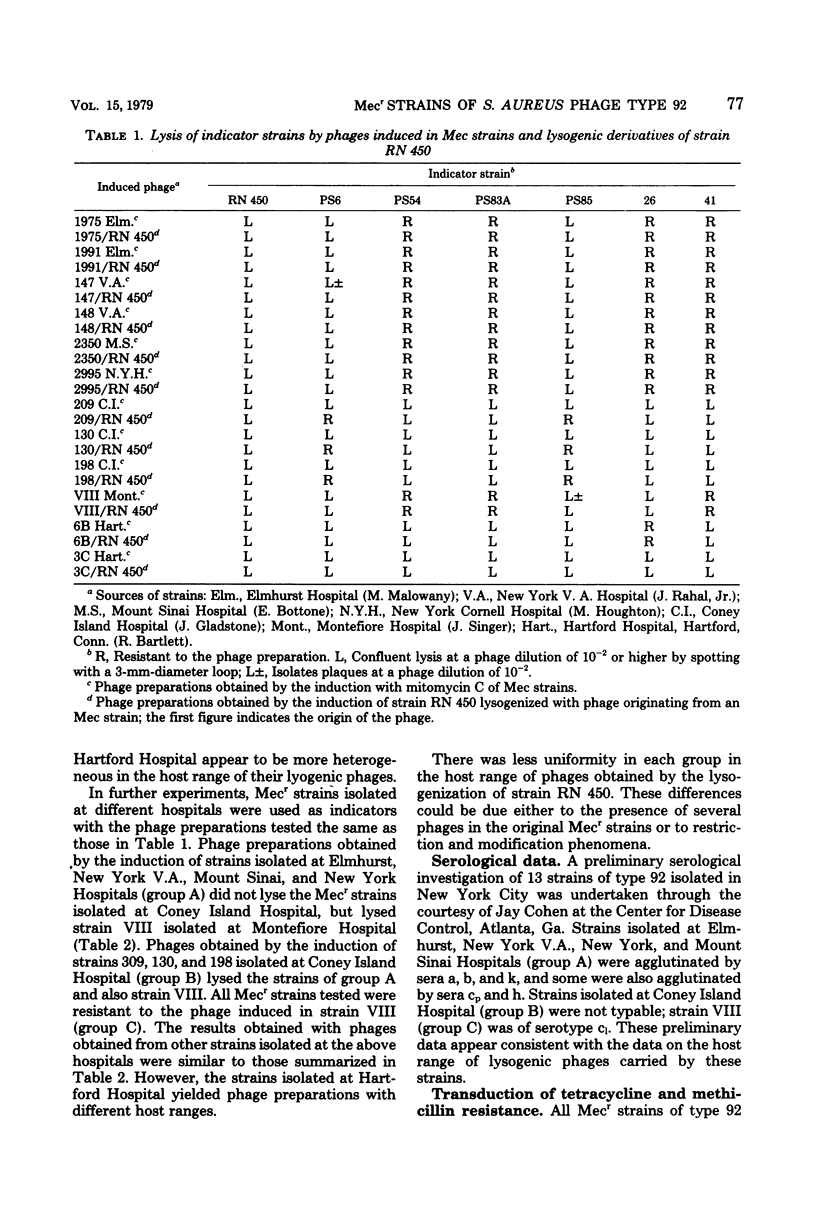
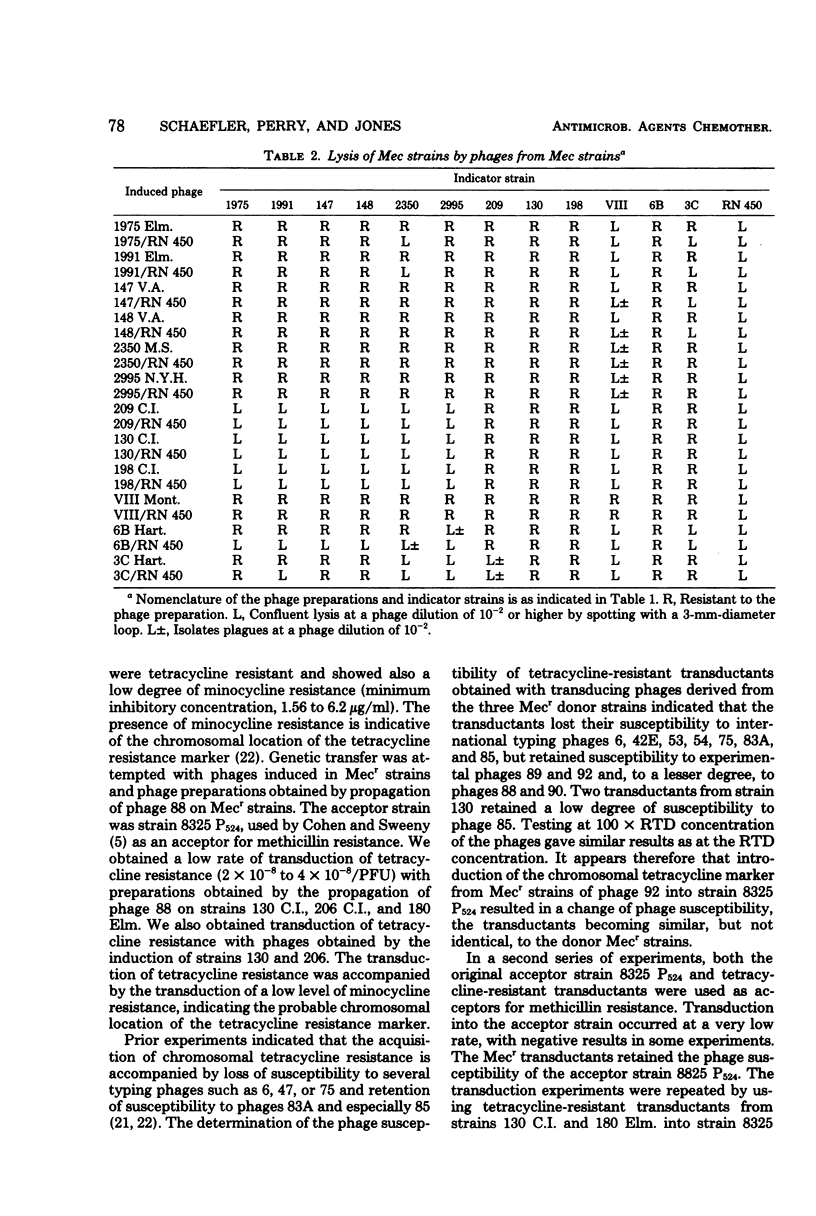
Methicillin-resistant (Mecr) strains of Staphylococcus aureus received for phage typing from several hospitals in New York City were resistant to the international set of typing phages but susceptible to experimental phage 92. Subsequently, strains of type 92 were detected in two outbreaks with Mecr strains in two other locations in the United States. In all instances, type 92 was predominant among the Mecr strains isolated in each hospital. With the exception of one strain, the methicillin resistance of the Mecr strains investigated was homogeneous. In most instances, isolates from the same hospital were closely similar in their antibiotic resistance patterns. The strains isolated in New York City could be divided into three groups by the host range of their lysogenic phages and by antigenic structure. Transduction experiments indicated that the transfer of chromosomal tetracycline resistance from Mecr strains into a strain susceptible to several international typing phages renders the latter nontypable. However, the acceptor strain remains susceptible to experimental phages 92 and 88. Transduction of methicillin resistance had no effect on the phage susceptibility of the acceptor strain. It is possible that the presence of chromosomal tetracycline resistance is a determining factor in the phage susceptibility of Mecr strains isolated in New York City.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annear D. I. The effect of temperature on resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to methicillin and some other antibioics. Med J Aust. 1968 Mar 16;1(11):444–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow P. Prevalence of extrachromosomal drug resistance. Staphylococci in Danish hospitals during the last decade: factors influencing some properties of predominant epidemic strains. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:21–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Sweeney H. M. Transduction of Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus Dependent on an Unusual Specificity of the Recipient Strain. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1158–1167. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1158-1167.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayser F. H., Wüst J., Santanam P. Genetic and molecular characterisation of resistance determinants in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus-aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1976 May;9(2):137–148. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-2-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimek J. J., Marsik F. J., Bartlett R. C., Weir B., Shea P., Quintiliani R. Clinical, epidemiologic and bacteriologic observations of an outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at a large community hospital. Am J Med. 1976 Sep;61(3):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90370-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W., Chopra I. Effect of plasmid carriage on the virulence of staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):137–147. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W., Grinsted J. Genetic analysis of methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus; evidence for their evolution from a single clone. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Nov;6(4):511–526. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-4-511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. ANALYSIS BY TRANSDUCTION OF MUTATIONS AFFECTING PENICILLINASE FORMATION IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Oct;33:121–136. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. Properties of a cryptic high-frequency transducing phage in Staphylococcus aureus. Virology. 1967 Sep;33(1):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. T., Asheshov E. H., Hewitt J. H., Nakhla L. S., Brock B. M. Endemic staphylococcal infections in hospitals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):466–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plorde J. J., Sherris J. C. Staphylococcal resistance to antibiotics: origin, measurement, and epidemiology. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):413–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer G., Pillich J. Typisierung Methicillin-resistenter Staphylokokken mit Hilfe der Lysogenie. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1970;215(4):429–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond A. S., Simberkoff M. S., Schaefler S., Rahal J. J., Jr Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to semisynthetic penicillins and cephalothin. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jan;135(1):108–112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal K., Bülow P., Bentzon M. W., Eriksen K. R. Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated in Danish hospitals from January 1st, 1966, to December 31st, 1974. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Dec;84B(6):359–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01953.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND R., ROLINSON G. N. CHARACTERISTICS OF METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:887–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.4.887-899.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S., Francois W., Ruby C. L. Minocycline resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: effect on phage susceptibility. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):600–613. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



