Abstract
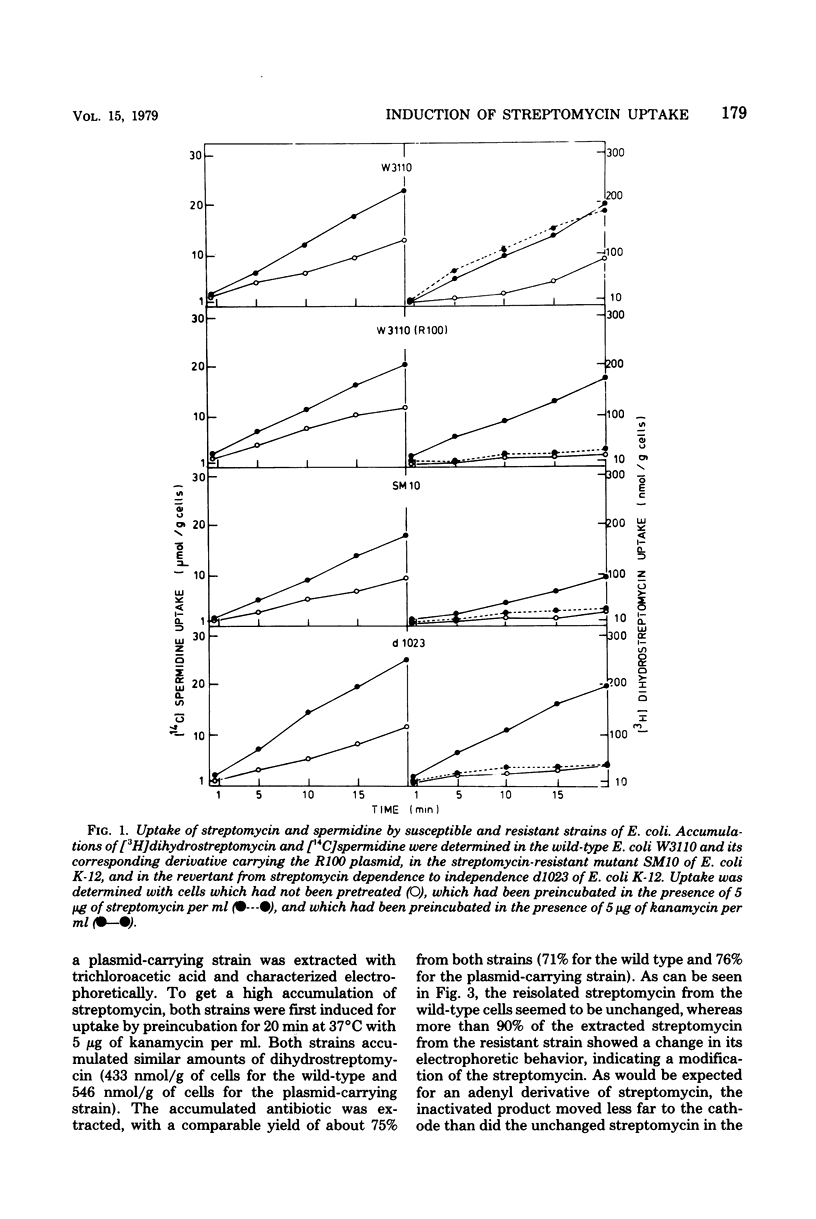
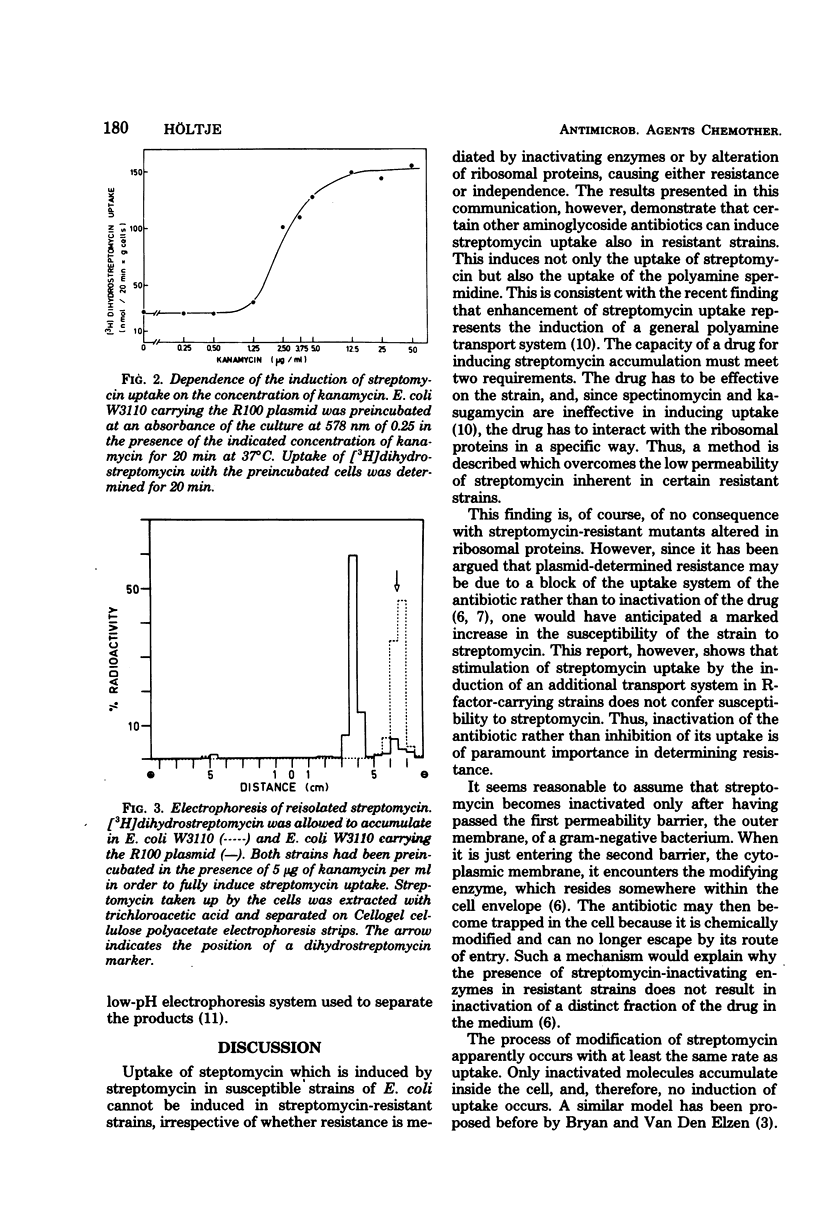
Different streptomycin-resistant strains of Escherichia coli, including an R100 plasmid-carrying strain of E. coli W3110, the ribosomally resistant mutant SM10, and the spontaneous revertant from dependence to independence d1023, exhibited poor accumulation capacity for aminoglycoside antibiotics. This was due to a failure of these mutants to induce the general polyamine transport system that is utilized by streptomycin to enter the cell. It is shown that the aminoglycoside kanamycin, which is effective on these streptomycin-resistant strains, was capable of inducing the uptake of streptomycin, thus giving rise to streptomycin accumulation up to wild-type levels. Plasmid-determined resistance, which has been speculated to be the result of a blockage of the uptake system by modified antibiotic molecules, cannot be overcome by the induction of streptomycin transport. Increase in permeability of the antibiotic does not affect the susceptibility of the bacteria. It is shown that all of the antibiotic taken up was enzymatically modified. R-plasmid-conferred resistance to aminoglycosides is therefore explained by the inactivation of the antibiotic entering the bacterial cell.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Enzymatic acetylation of aminoglycoside antibiotics by Escherichia coli carrying an R factor. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1787–1796. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van Den Elzen H. M. Effects of membrane-energy mutations and cations on streptomycin and gentamicin accumulation by bacteria: a model for entry of streptomycin and gentamicin in susceptible and resistant bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):163–177. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van den Elzen H. M. Streptomycin accumulation in susceptible and resistant strains of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):928–938. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin P., Davies J. Plasmid-medicated aminoglycoside phosphotransferase of broad substrate range that phosphorylates amikacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):619–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. E., Benveniste R. E. Enzymes that inactivate antibiotics in transit to their targets. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):130–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Courvalin P. Mechanisms of resistance to aminoglycosides. Am J Med. 1977 Jun;62(6):868–872. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90654-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu G., Nierhaus K., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. XXXVII. Determination of allelle types and amino acid exchanges in protein S12 of three streptomycin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 6;287(2):282–291. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90377-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasenbank R., Guthrie C., Stöffler G., Wittmann H. G., Rosen L., Apirion D. Electrophoretic and immunological studies on ribosomal proteins of 100 Escherichia coli revertants from streptomycin dependence. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 14;127(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00267778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V. Streptomycin uptake via an inducible polyamine transport system in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May 16;86(2):345–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Takasawa S., Okanishi M., Utahara R. Adenylylstreptomycin, a product of streptomycin inactivated by E. coli carrying R factor. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Jan;21(1):81–82. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



