Abstract
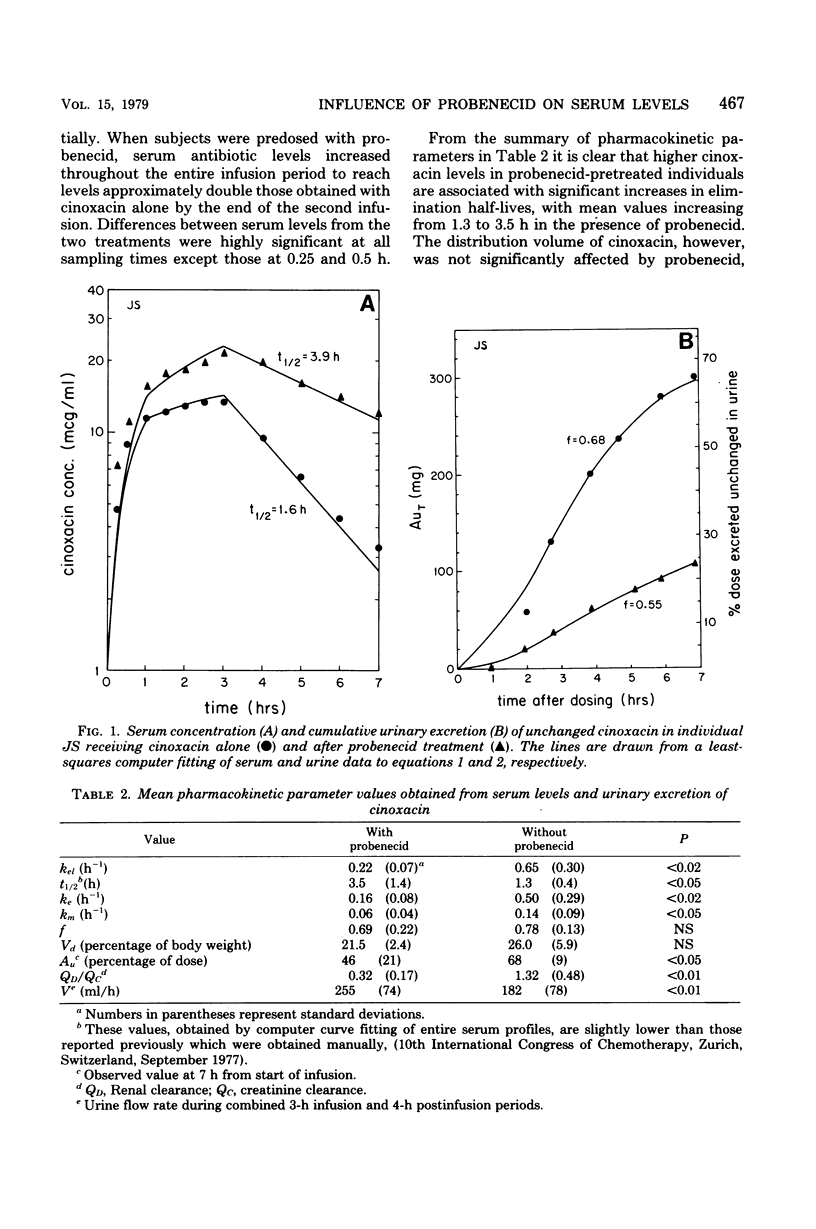
Serum levels and urinary excretion of cinoxacin were examined in healthy individuals after a two-step intravenous infusion in the presence and absence of probenecid. After dosing cinoxacin alone, steady-state serum levels were approached in 1 h and were maintained for an additional 2 h with a reduced infusion rate. After probenecid pretreatment, serum levels of cinoxacin continued to increase during 3 h of infusion, reaching levels approximately double those obtained with cinoxacin alone. The mean elimination half-life of cinoxacin from serum was increased from 1.3 to 3.5 h in the presence of probenecid, and renal clearance was significantly reduced, with 46% of dosed drug appearing in 7-h urines of probenecid-treated subjects compared with 68% in subjects receiving cinoxacin alone. Probenecid had no apparent influence on cinoxacin distribution in the body but caused a significant decrease in the rate of cinoxacin extrarenal elimination, possibly due to competition for a common metabolic pathway.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEYER K. H., RUSSO H. F., TILLSON E. K., MILLER A. K., VERWEY W. F., GASS S. R. 'Benemid,' p-(di-n-propylsulfamyl)-benzoic acid; its renal affinity and its elimination. Am J Physiol. 1951 Sep;166(3):625–640. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.166.3.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAYTON P. G., YU T. F., CHEN W., BERGER L., WEST L. A., GUTMAN A. B. The physiological disposition of probenecid, including renal clearance, in man, studied by an improved method for its estimation in biological material. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Jun;140:278–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giamarellou H., Jackson G. G. Antibacterial activity of cinoxacin in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):688–692. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibaldi M., Schwartz M. A. Apparent effect of probenecid on the distribution of penicillins in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1968 May-Jun;9(3):345–349. doi: 10.1002/cpt196893345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel K. S., Black H. R., Nelson R. L., Brunson M. K., Nash J. F., Brier G. L., Wolney J. D. Cinoxacin: pharmacokinetics and the effect of probenecid. J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;18(10):491–499. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1978.tb01577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumish R. M., Norden C. W. Cinoxacin: in vitro antibacterial studies of a new synthetic organic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):159–163. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein M. F., Westervelt F. B., Sande M. A. Pharmacodynamics of cefazolin in the presence of normal and impaired renal function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):366–371. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER I. M., BLANCHARD K. C., MUDGE G. H. FACTORS INFLUENCING RENAL EXCRETION OF FOREIGN ORGANIC ACIDS. Am J Physiol. 1964 Nov;207:953–963. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.5.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER I. M., MUDGE G. H. RENAL TUBULAR MECHANISMS FOR EXCRETION OF ORGANIC ACIDS AND BASES. Am J Med. 1964 May;36:743–762. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER I. M., WASHINGTON J. A., 2nd, MUDGE G. H. On the mechanism of action of probenecid on renal tubular secretion. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1960 Jun;106:333–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick W. E., Preston D. A., White W. A., Gordee R. S. Compound 64716, a new synthetic antibacterial agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):415–420. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



