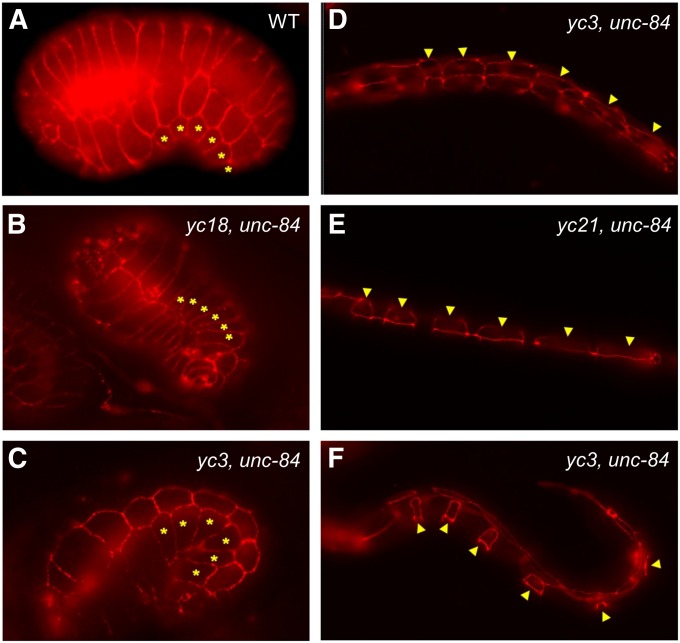
Figure 3 .
emu mutations do not disrupt P-cell specification. The morphology of P cells is shown in (A) a wild-type embryo, (B) a yc18; unc-84(n369) embryo, (C) a yc3; unc-84(n369) embryo, (D) a yc3; unc-84(n369) early-L1 larva, (E) a yc21; unc-84(n369) mid-L1 larva, and (F) a yc3; unc-84(n369) mid-L1 larva prior to the onset of nuclear migration. P-cell boundaries were marked using MH27 immunostaining to mark adherens junctions. Asterisks or arrowheads mark six P cells on one ventral–lateral side of the embryo or L1 larvae. Sample size of each mutant strain is between 18 and 50. A variety of stages were observed for each of the eight emu mutants; all worms had normal P-cell shapes.