Abstract
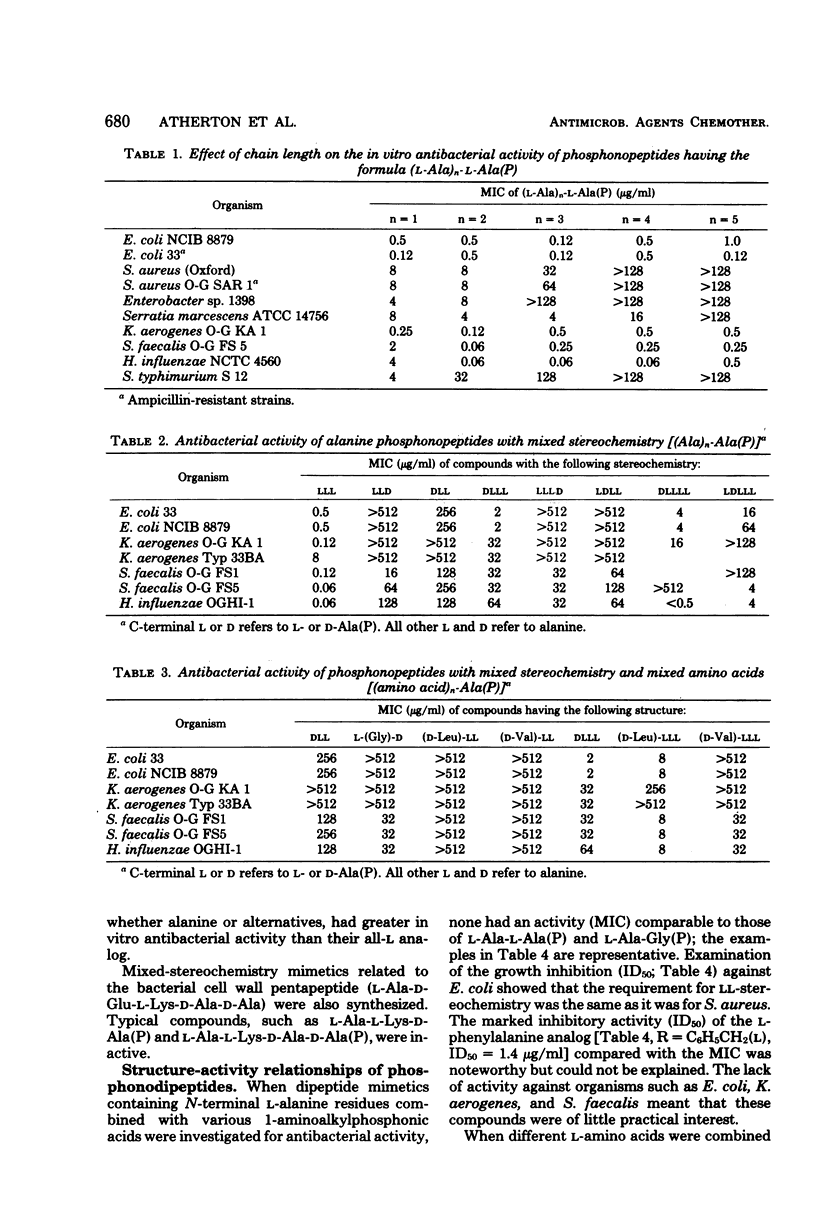
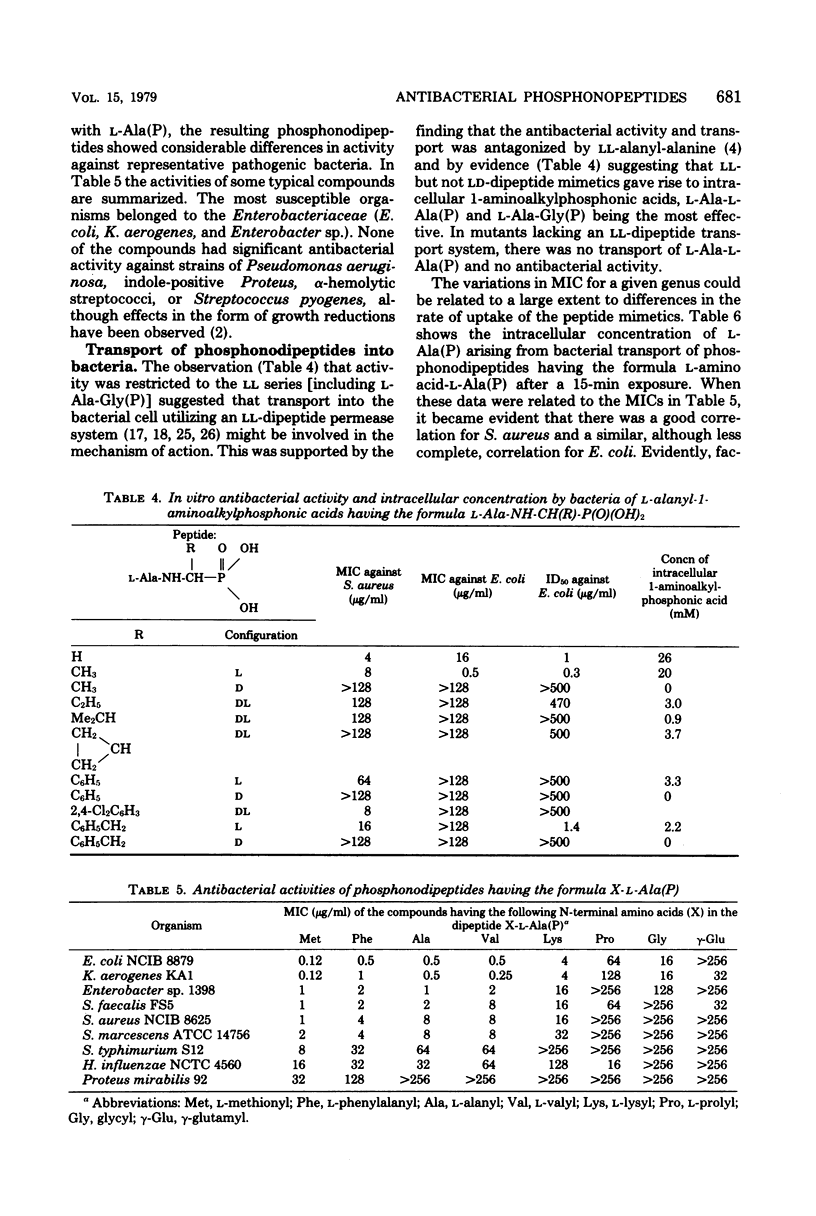
Peptide mimetics with C-terminal residues simulating natural amino acids have been designed as inhibitors of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. The phosphonopeptide series consisting of various l and d residues of natural amino acids combined with 1-aminoalkyl (and aryl-alkyl-) phosphonic acid residues had the most interesting antibacterial properties when the C-terminal residue was l-1-aminoethylphosphonic acid. The in vitro antibacterial activities of representative phosphonodi- to phosphonohexapeptides were investigated. The antibacterial action of the active compounds has been explained in terms of transport into the bacterial cell and intracellular release of the alanine mimetic, which interferes with the biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of the bacterial cell wall.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. G., Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Holmes S. W., Lambert R. W., Nisbet L. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides as antibacterial agents: alaphosphin and related phosphonopeptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):684–695. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. G., Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Holmes S. W., Lambert R. W., Nisbet L. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides, a new class of synthetic antibacterial agents. Nature. 1978 Mar 2;272(5648):56–58. doi: 10.1038/272056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Lambert R. W., Lloyd W. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides as antibacterial agents: mechanism of action of alaphosphin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):696–705. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E., Gugel K. H., Hägele K., Hagenmaier H., Jessipow S., König W. A., Zähner H. Stoffwechselprodukte von Mikroorganismen. 98. Phosphinothricin und Phosphinothricyl-Alanyl-Alanin. Helv Chim Acta. 1972 Jan 31;55(1):224–239. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19720550126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Parant F., Lefrancher P., Choay J., Lederer E. Enhancement of nonspecific immunity to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection by a synthetic immunoadjuvant (N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine) and several analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2089–2093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulaney E. L. 1-aminoethylphosphonic acid, an inhibitor of bacterial cell wall synthesis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Nov;23(11):567–568. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale G. R., Smith A. B. Insensitivity of bacteria to proposed antimetabolites of D-alanyl-D-alanine. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):460–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.460-461.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilvarg C., Levin Y. Response of Escherichia coli to ornithyl peptides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 25;247(2):543–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith R. S. Ten years of cephalosporins. Adv Clin Pharmacol. 1974;8:6–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber J. W., 3rd, Gilmore F., Robertson L. W. Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of N-D-alanyl-1-aminoethylphosphonic acid. J Med Chem. 1975 Jan;18(1):106–108. doi: 10.1021/jm00235a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIHARA H., IKAWA M., SNELL E. E. Peptides and bacterial growth. X. Relation of uptake and hydrolysis to utilization of D-alanine peptides for growth of Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jan;236:172–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenig M., Abraham E. P. Antimicrobial activities and antagonists of bacilysin and anticapsin. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):37–45. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenig M., Vandamme E., Abraham E. P. The mode of action of bacilysin and anticapsin and biochemical properties of bacilysin-resistant mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):46–54. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEACH F. R., SNELL E. E. The absorption of glycine and alanine and their peptides by Lactobacillus casei. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3523–3531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus F. C., Goyer S., Neuhaus D. W. Growth inhibition of Escherichia coli W by D-norvalyl-D-alanine: an analogue of D-alanine in position 4 of the peptide subunit of peptidoglycan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):638–644. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins H. R., Nieto M. The chemical basis for the action of the vancomycin group of antibiotics. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):348–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANKMAN S., GOLD V., HIGA S., SQUIRES R. On the mode of action of a peptide inhibitor of growth in P. cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Sep 25;9:25–31. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANKMAN S., HIGA S., FLORSHEIM H. A., SCHVO Y., GOLD V. Peptide studies. II. Growth-promoting activity of peptides of L-leucine and L- and D-valine for lactic acid bacteria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Feb;86:204–209. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90405-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMMONDS S., HARRIS J. I., FRUTON J. S. Inhibition of bacterial growth by leucine peptides. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jan;188(1):251–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J., Strominger J. L. Mechanism of action of penicillins: a proposal based on their structural similarity to acyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. The role of energy coupling in the transport of beta-galactosides by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2200–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



