Abstract
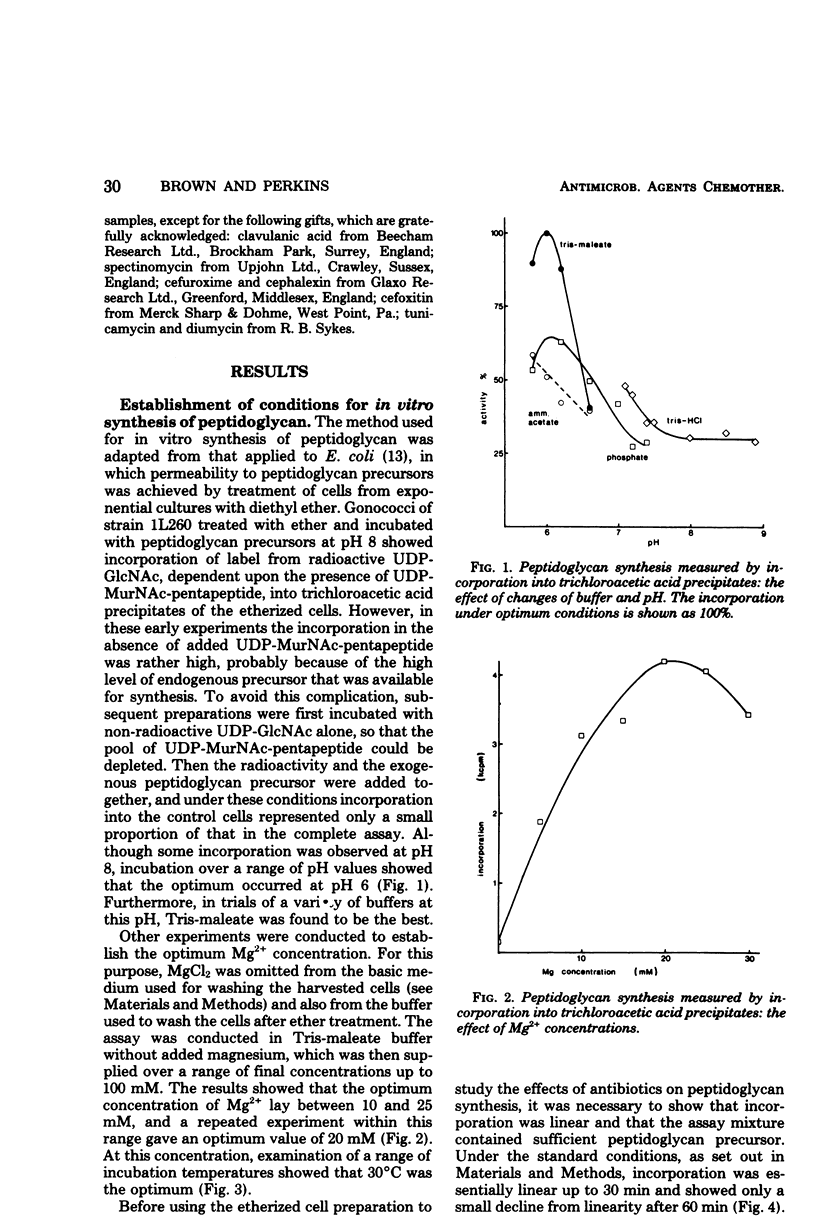
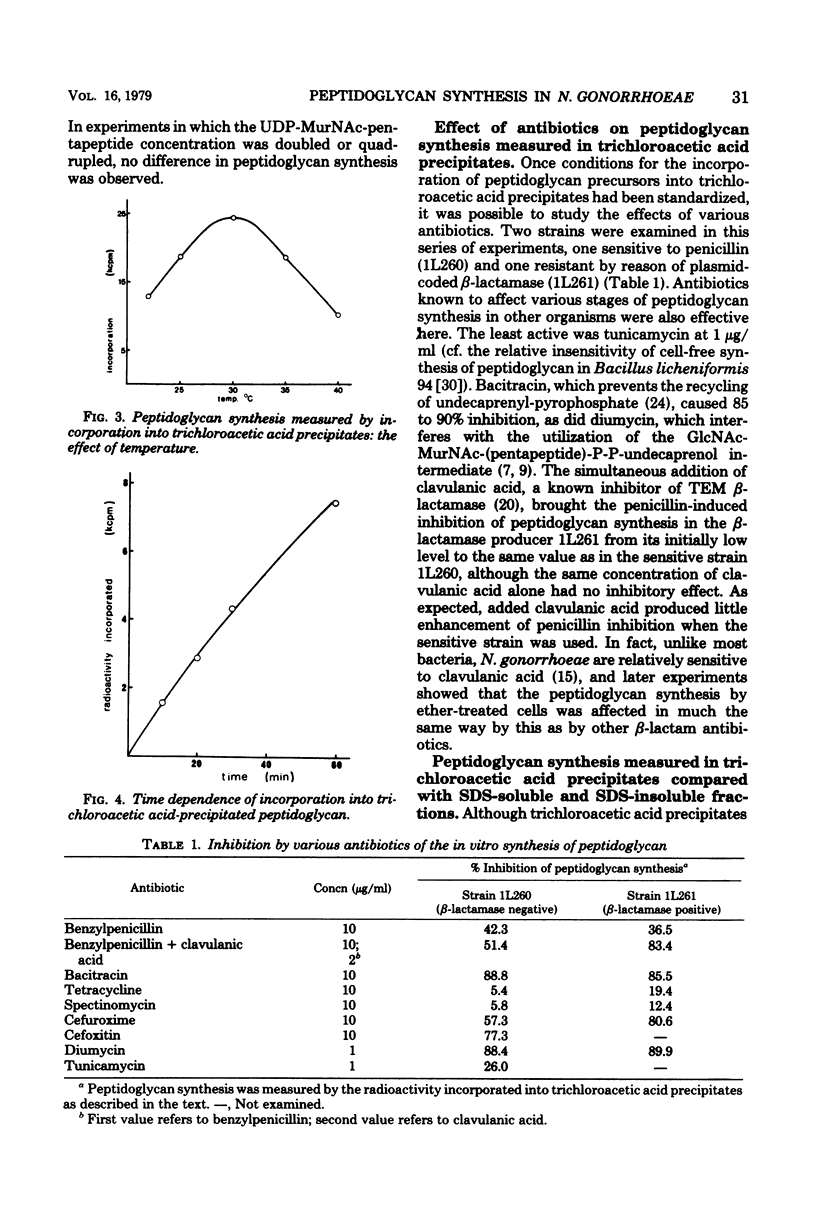
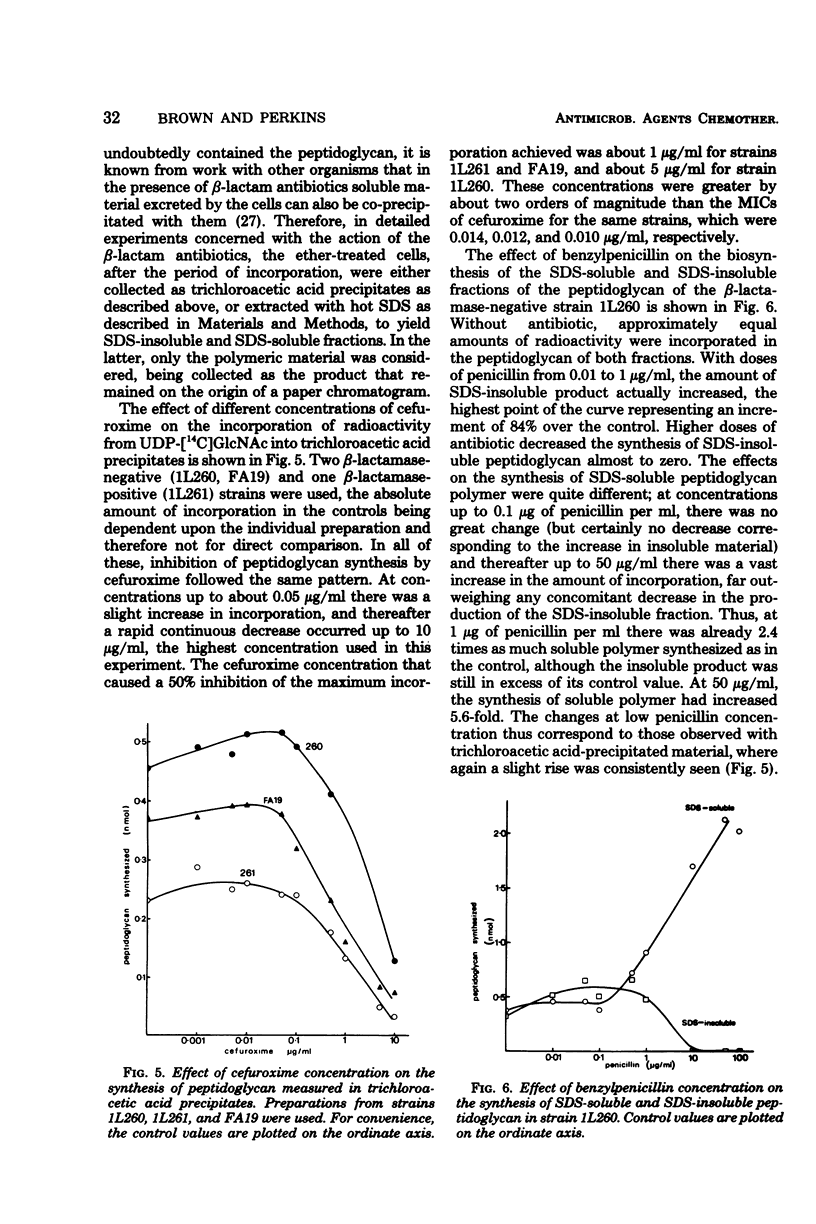
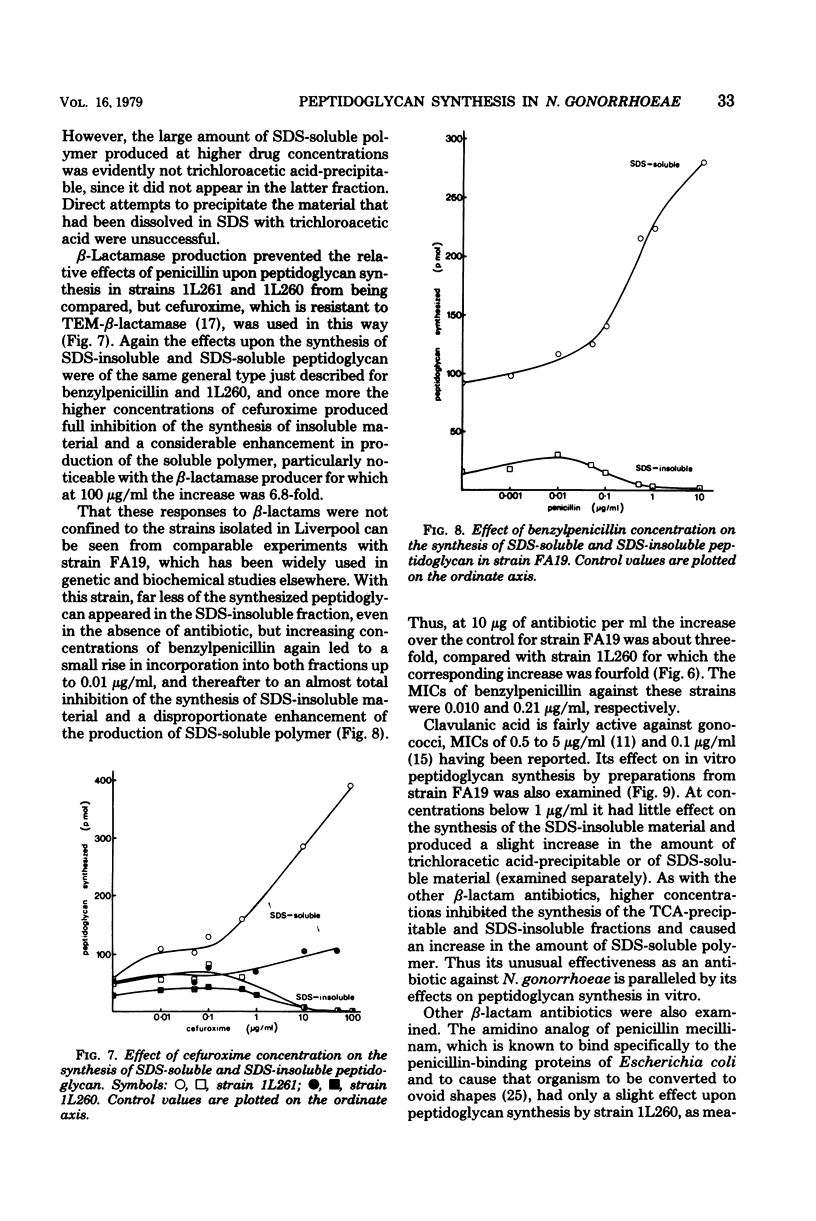
The synthesis in vitro of peptidoglycan by Neisseria gonorrhoeae was studied in organisms made permeable to nucleotide precursors by treatment with ether. Optimum synthesis occurred at 30°C in tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane-maleate buffer (0.05 M; pH 6) in the presence of 20 mM Mg2+. The incorporation from uridine 5′-diphosphate-N-acetyl-[14C]glucosamine into peptidoglycan, measured after precipitation of the cells with trichloroacetic acid, was sensitive to the β-lactam antibiotics, bacitracin, diumycin, and tunicamycin and relatively resistant to spectinomycin and tetracycline. Differences in sensitivity between preparations from a β-lactamase producer and a laboratory segregant derived from it were not great. Synthesized peptidoglycan was also fractionated into sodium dodecyl sulfate-soluble and -insoluble portions. β-Lactam antibiotics at concentrations equivalent to the minimal inhibitory concentrations for growth of the organisms did not inhibit peptidoglycan synthesis, but rather caused a small enhancement. At higher concentrations, above about 0.5 μg/ml, incorporation into sodium dodecyl sulfate-insoluble material was progressively inhibited, whereas the amount of sodium dodecyl sulfate-soluble product increased greatly, more than compensating for the loss of the precipitable fraction. Similar observations were made with three strains, and also with the β-lactam clavulanic acid, normally considered as a β-lactamase inhibitor rather than as itself an effective antibiotic.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashford W. A., Golash R. G., Hemming V. G. Penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Lancet. 1976 Sep 25;2(7987):657–658. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92467-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. H., Salton M. R. Some properties of a D-alanine carboxypeptidase in envelope fractions of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1065–1069. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1065-1069.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Roberts M., Mayer L. W., Falkow S. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase production in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):528–533. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. The concept of the penicillin target from 1965 until today. The thirteenth marjory stephenson memorial lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jul;101(1):13–33. doi: 10.1099/00221287-101-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Fazio M., Tomasz A. Effect of benzylpenicillin on the synthesis and structure of the cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):514–526. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Young F. E. Chemical composition and turnover of peptidoglycan in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1180–1185. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1180-1185.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnett P. E., Strominger J. L. Additional antibiotic inhibitors of peptidoglycan synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):231–236. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg E. J., Hellings J. A., van de Berg G. J. Inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis by the antibiotic diumycin A. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):485–491. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. W., Holmes K. K., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):712–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.712-717.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. M., Baker C. N., Thornsberry C. Inhibition of beta-lactamase in Neisseria gonorrhoeae by sodium clavulanate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Nov;14(5):794–796. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.5.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Yashouv-Gan Y., Schwarz U. Peptidoglycan biosynthesis in a thermosensitive division mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):1781–1790. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Yashouv-Gan Y., Schwarz U. Regulation of murein biosynthesis and septum formation in filamentous cells of Escherichia coli PAT 84. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1593–1600. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1593-1600.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Sykes R. B., Griffiths A., Thornton J. E. Cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic: activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):511–519. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival A., Rowlands J., Corkill J. E., Alergant C. D., Arya O. P., Rees E., Annels E. H. Penicillinase-producing Gonococci in Liverpool. Lancet. 1976 Dec 25;2(8000):1379–1382. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91919-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I. Beta-lactamase-producing, penicillin-resistant gonococcus. Lancet. 1976 Sep 25;2(7987):656–657. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92466-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C., Cole M. Clavulanic acid: a beta-lactamase-inhiting beta-lactam from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):852–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Molecular characterization of two beta-lactamase-specifying plasmids isolated from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):557–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.557-563.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon R., Hedges A. J., Edwards R. J. Distribution of levels of penicillin resistance among freshly isolated strains of N. gonorrhoeae. Application of a novel sensitivity assay. Br J Vener Dis. 1975 Aug;51(4):246–250. doi: 10.1136/sti.51.4.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siewert G., Strominger J. L. Bacitracin: an inhibitor of the dephosphorylation of lipid pyrophosphate, an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):767–773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosberg H. P., Hoffmann-Berling H. DNA synthesis in nucleotide-permeable Escherichia coli cells. I. Preparation and properties of ether-treated cells. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 28;58(3):739–753. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. B. The synthesis of peptidoglycan in an autolysin-deficient mutant of Bacillus licheniformis N.C.T.C. 6346 and the effect of beta-lactam antibiotics, bacitracin and vancomycin. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;141(1):227–241. doi: 10.1042/bj1410227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. B. Tunicamycin inhibition of bacterial wall polymer synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1977;78(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. S., Hebeler B. H., Morse S. A. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: penicillin enhancement of peptidoglycan hydrolysis. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):717–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.717-725.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. S., Hebeler B. H., Morse S. A. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: relationship between autolysis in buffer and the hydrolysis of peptidoglycan. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):210–219. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.210-219.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



