Abstract
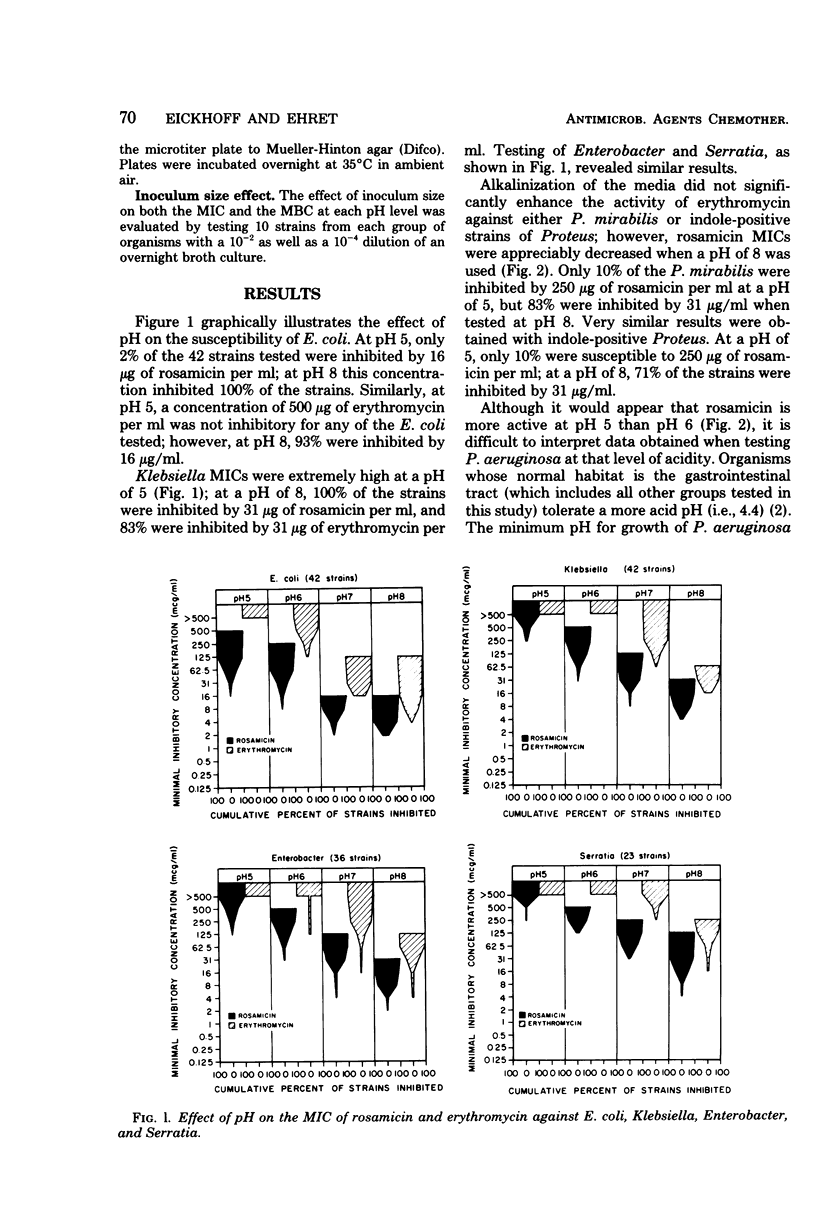
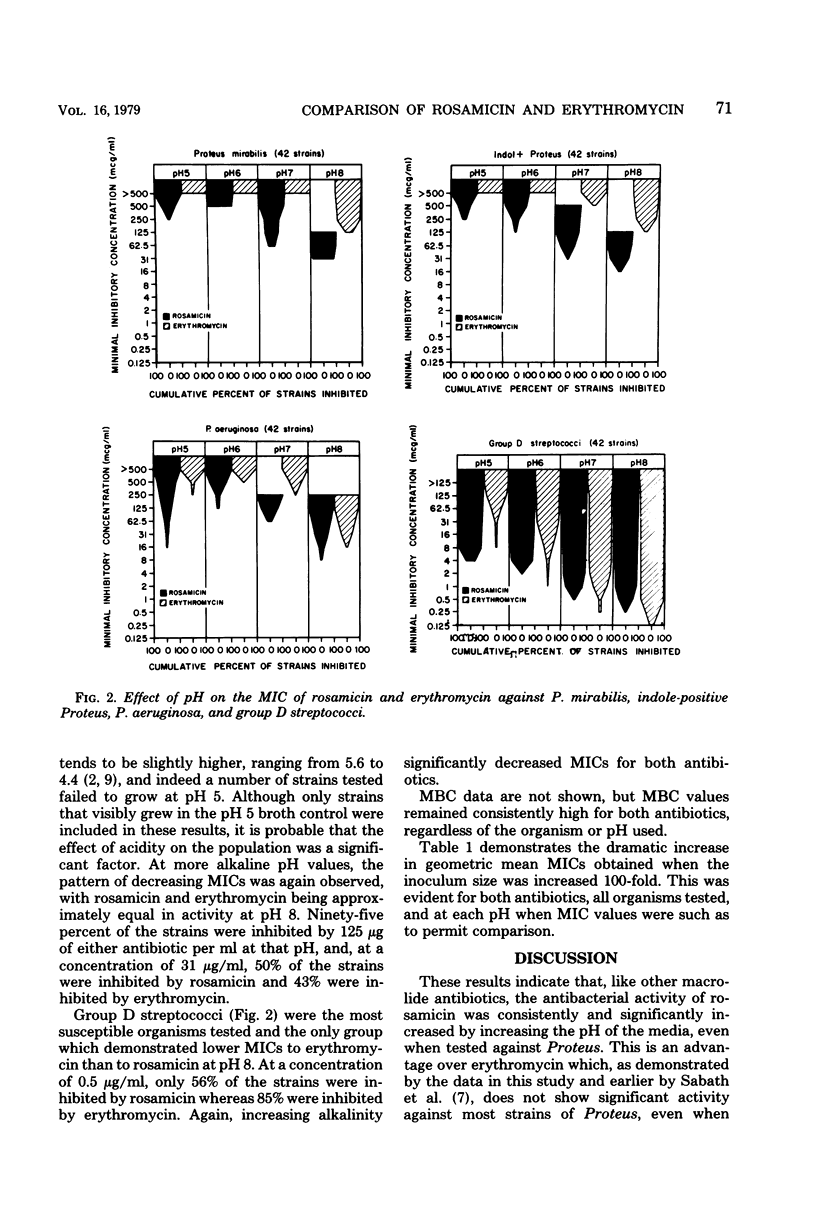
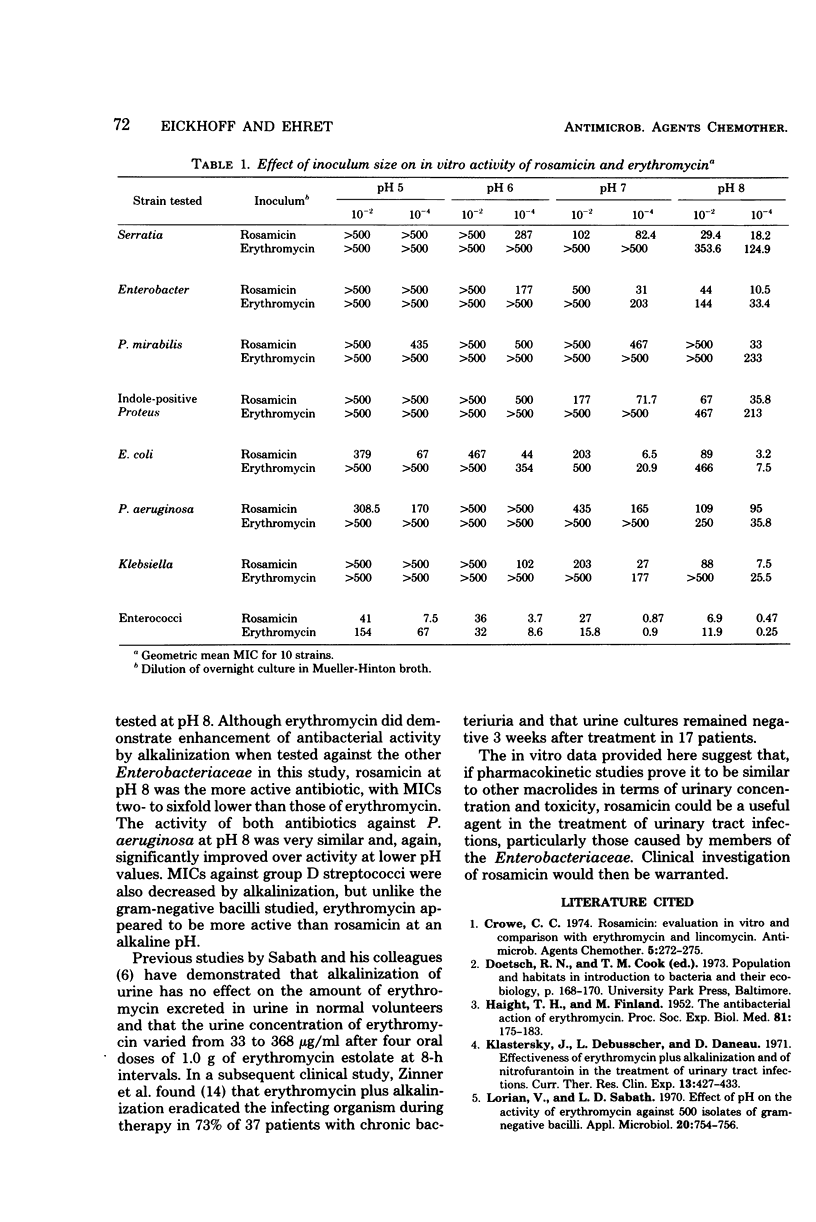
The in vitro activity of rosamicin and erythromycin was compared at various pH values against 311 strains of bacteria representing common urinary tract pathogens. Alkalinization of the media consistently and significantly increased the antibacterial activity of rosamicin against all of the organisms tested. This was also true for erythromycin except when tested against strains of Proteus. At pH 8, rosamicin was two- to sixfold more active than erythromycin against Enterobacteriaceae. The activity of both antibiotics against Pseudomonas aeruginosa was very similar when tested at pH 8. Erythromycin was twice as active as rosamicin at pH 8 against group D streptococci. The activity of both antibiotics was bacteriostatic and inoculum size dependent, regardless of the organism tested or the pH of the test media. The greater activity of rosamicin against Enterobacteriaceae warrants clinical investigation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crowe C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Rosamicin: evaluation in vitro and comparison with erythromycin and lincomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):272–275. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAIGHT T. H., FINLAND M. The antibacterial action of erythromycin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Oct;81(1):175–183. doi: 10.3181/00379727-81-19815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Debusscher L., Daneau D. Effectiveness of erythromycin plus alkalinization and of nitrofurantoin in the treatment of urinary tract infections. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1971 Jul;13(7):427–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorian V., Sabath L. D. Effect of pH on the activity of erythromycin against 500 isolates of gram-negative bacilli. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Nov;20(5):754–756. doi: 10.1128/am.20.5.754-756.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Gerstein D. A., Loder P. B., Finland M. Excretion of erythromycin and its enhanced activity in urine against gram-negative bacilli with alkalinization. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Dec;72(6):916–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Lorian V., Gerstein D., Loder P. B., Finland M. Enhancing effect on alkalinization of the medium on the activity of erythromycin against gram-negative bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1288–1292. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1288-1292.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagman G. H., Waitz J. A., Marquez J., Murawaski A., Oden E. M., Testa R. T., Weinstein M. J. A new Micromonospora-produced macrolide antibiotic, rosamicin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Nov;25(11):641–646. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz J. A., Drube C. G., Moss E. L., Jr, Weinstein M. J. Biological studies with rosamicin, a new Micromonospora-produced macrolide antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Nov;25(11):647–652. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAGAR Z. Sensitivity of E. coli, Ps. aeruginosa and B. proteus to erythromycin in various pH culture media. Chemotherapia (Basel) 1963;6:82–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinner S. H., Sabath L. D., Casey J. I., Finland M. Erythromycin and alkalinisation of urine in the treatment of urinary-tract infections due to gram-negative bacilli. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1267–1268. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91780-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


