Abstract
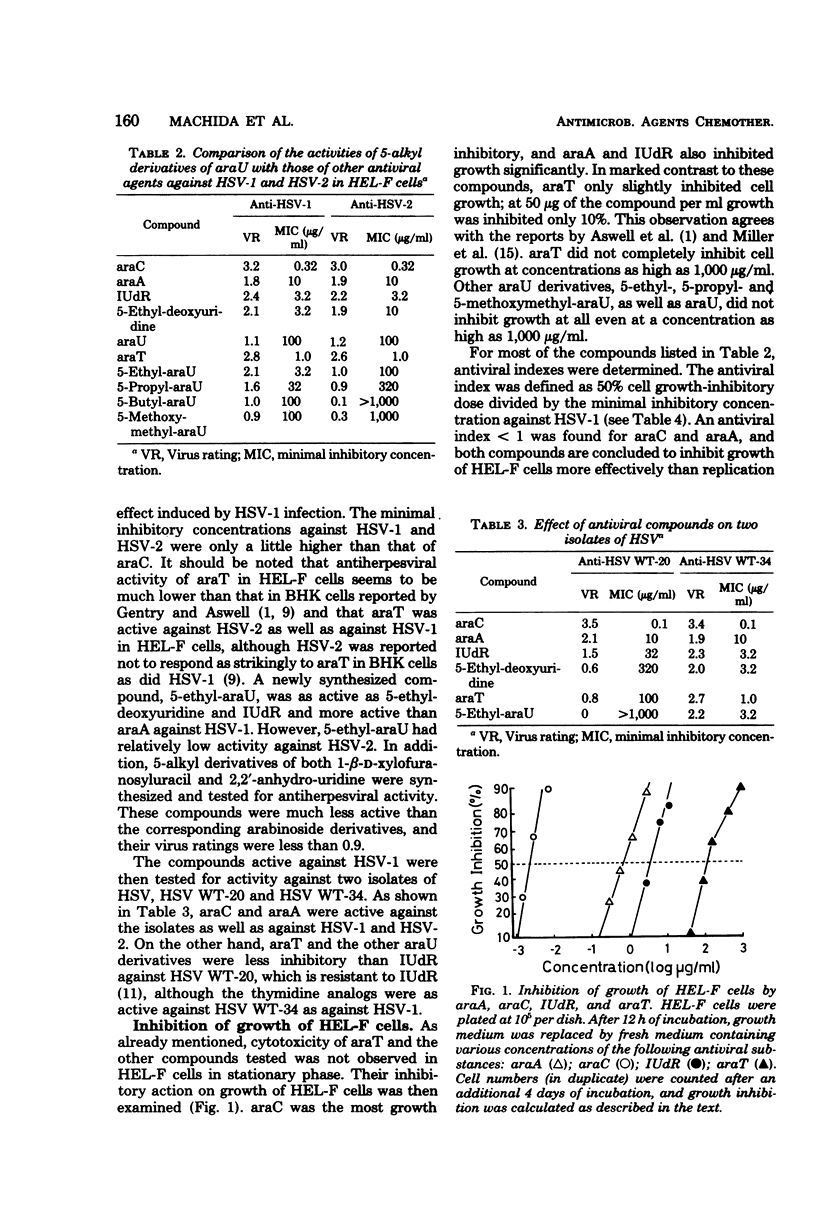
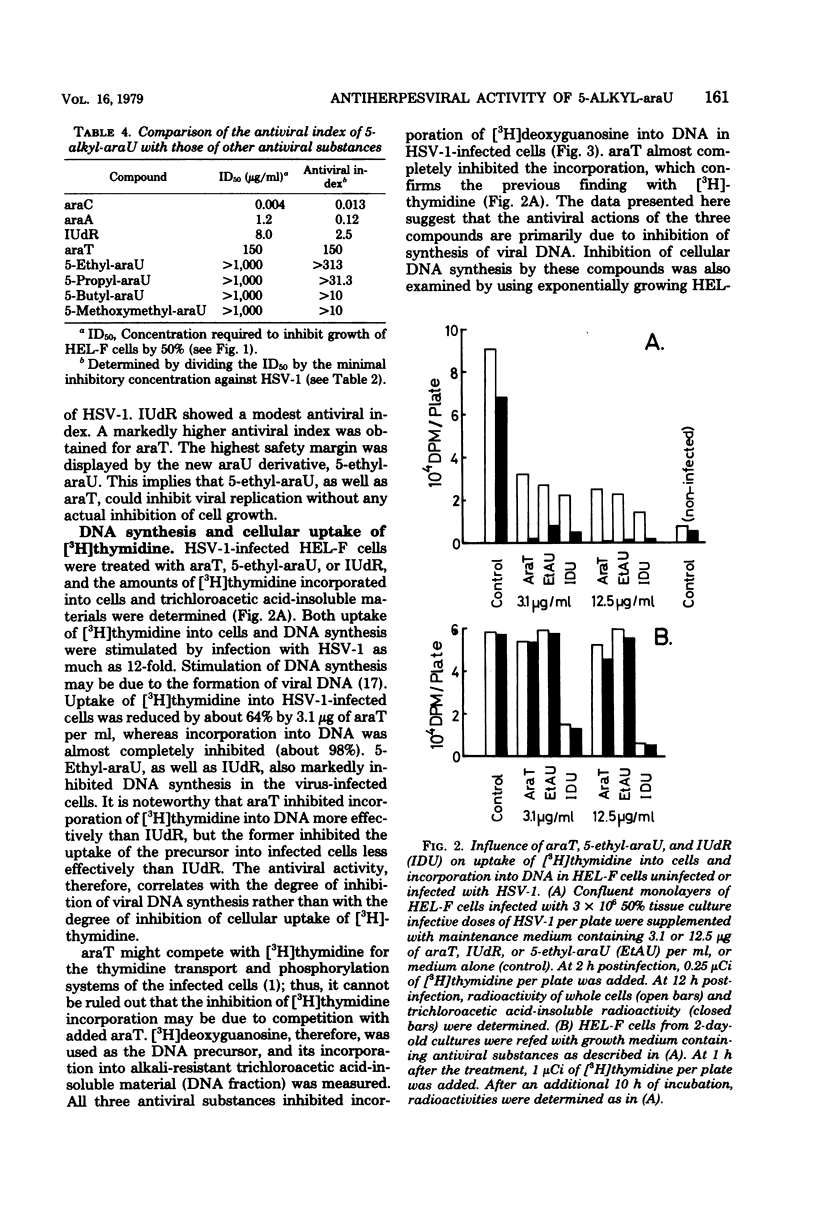
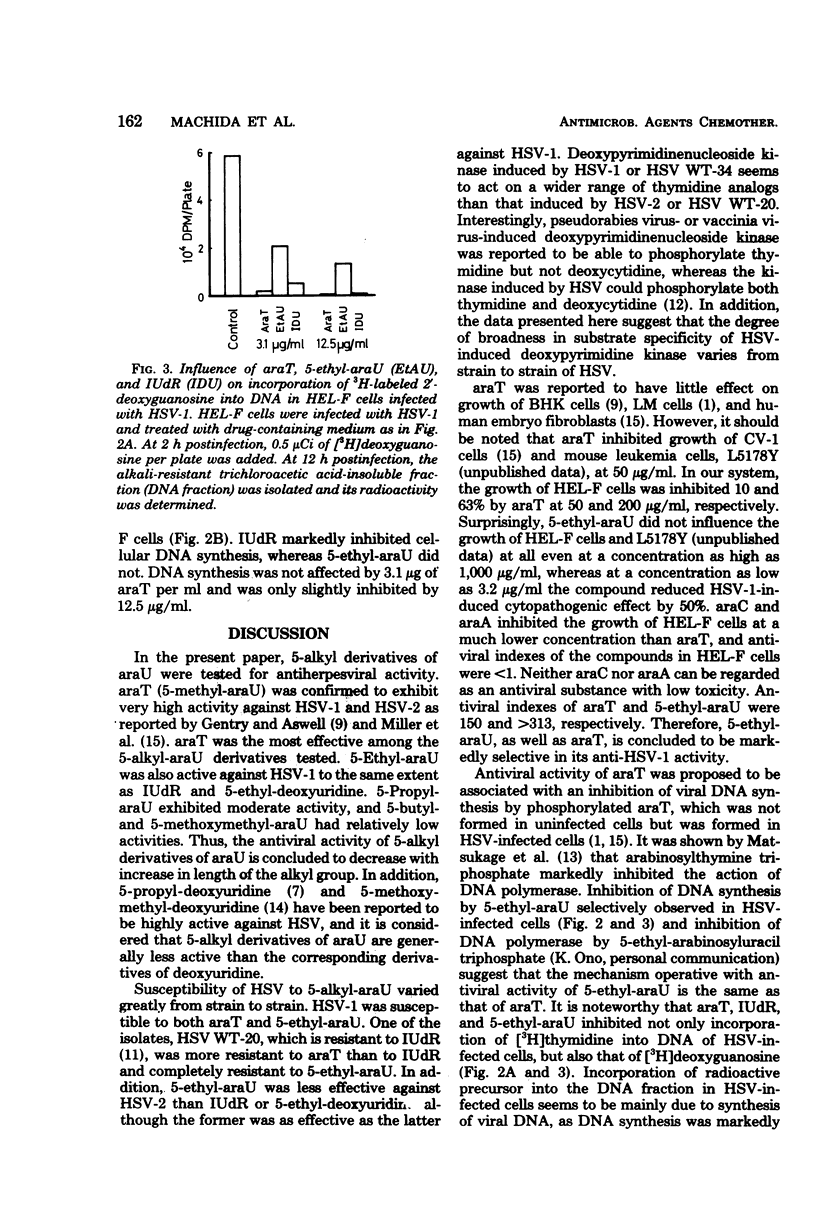
Several 5-alkyl derivatives of 1-β-d-arabinofuranosyluracil (araU) were tested for antiherpesviral activity and inhibitory action on cell growth in human embryonic lung fibroblasts. 1-β-d-Arabinofuranosylcytosine, 9-β-d-arabinofuranosyladenine, and 5-iododeoxyuridine (IUdR) were included as reference materials. Among the 5-alkyl derivatives of araU, arabinosylthymine was the most active, followed by 5-ethyl- and 5-propyl-araU. 5-Ethyl-araU was as active as IUdR and more active than 9-β-d-arabinofuranosyladenine against herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 and did not inhibit cell growth at a concentration as high as 1,000 μg/ml. 5-Butyl- and 5-methoxymethyl-araU, as well as araU, exhibited relatively low activity. The araU derivatives tested were as active against HSV WT-34, an isolate from a patient with keratitis, as against HSV type 1. Against an IUdR-resistant isolate, HSV WT-20, arabinosylthymine was less inhibitory than IUdR. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in HSV type 1-infected cells was markedly inhibited by arabinosylthymine, IUdR, and 5-ethyl-araU, whereas cellular deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in uninfected cells was significantly inhibited by IUdR but not by arabinosylthymine or 5-ethyl-araU.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aswell J. F., Allen G. P., Jamieson A. T., Campbell D. E., Gentry G. A. Antiviral activity of arabinosylthymine in herpesviral replication: mechanism of action in vivo and in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):243–254. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswell J. F., Gentry G. A. Cell-dependent antiherpesviral activity of 5-methylarabinosylcytosine, an intracellular ara-T donor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:342–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb21969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiuk L. A., Meldrum B., Gupta V. S., Rouse B. T. Comparison of the antiviral effects of 5-methoxymethyl-deoxyuridine with 5-iododeoxyuridine, cytosine arabinoside, and adenine arabinoside. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Dec;8(6):643–650. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.6.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C. A rational approach to the development of antiviral chemotherapy: alternative substrates of herpes simplex virus Type 1 (HSV-1) and Type 2 (HSV-2) thymidine kinase (TK). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:594–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb21992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Domin B. A., Sharma R. A., Bobek M. Antiviral action and cellular toxicity of four thymidine analogues: 5-ethyl-,5-vinyl-, 5-propyl-, and 5-allyl-2'- deoxyuridine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):119–122. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Goz B., Neenan J. P., Ward D. C., Prusoff W. H. Selective inhibition of herpes simplex virus by 5-amino-2,5-dideoxy-5-iodouridine. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1284–1285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1284-1285.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Shugar D. Antiviral activity of 5-ethyl pyrimidine deoxynucleosides. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 May 15;24(10):1073–1078. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry G. A., Aswell J. F. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus replication by araT. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):294–296. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton A., Nichol A. W. Nucleotides. V. Purine ribonucleoside 2',3'-cyclic carbonates. Preparation and use for the synthesis of 5'-monosubstituted nucleosides. Biochemistry. 1966 Jun;5(6):2076–2082. doi: 10.1021/bi00870a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. T., Gentry G. A., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Induction of both thymidine and deoxycytidine kinase activity by herpes viruses. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):465–480. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukage A., Ono K., Ohashi A., Takahashi T., Nakayama C., Saneyoshi M. Inhibitory effect of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylthymine 5'-triphosphate and 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine 5'-triphosphate on DNA polymerases from murine cells and oncornavirus. Cancer Res. 1978 Sep;38(9):3076–3079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum J. B., Gupta V. S., Saunders J. R. Cell culture studies on the antiviral activity of ether derivatives of 5-hydroxymethyldeoxyuridine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Oct;6(4):393–396. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.4.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Iltis J. P., Rapp F. Differential effect of arabinofuranosylthymine of the replication of human herpesviruses. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):679–684. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.679-684.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B., ROANE P. R., Jr THE MULTIPLICATION OF HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS. II. THE RELATION BETWEEN PROTEIN SYNTHESIS AND THE DUPLICATION OF VIRAL DNA IN INFECTED HEP-2 CELLS. Virology. 1964 Feb;22:262–269. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Huffman J. H., Allen L. B., Meyer R. B., Jr, Shuman D. A., Simon L. N., Robins R. K. In vitro antiviral activity of 6-substituted 9-beta-D-ribofuranosylpurine 3', 5'-cyclic phosphates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jun;5(6):652–657. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.6.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Huffman J. H. Use of disposable micro tissue culture plates for antiviral and interferon induction studies. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):797–801. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.797-801.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



