Abstract
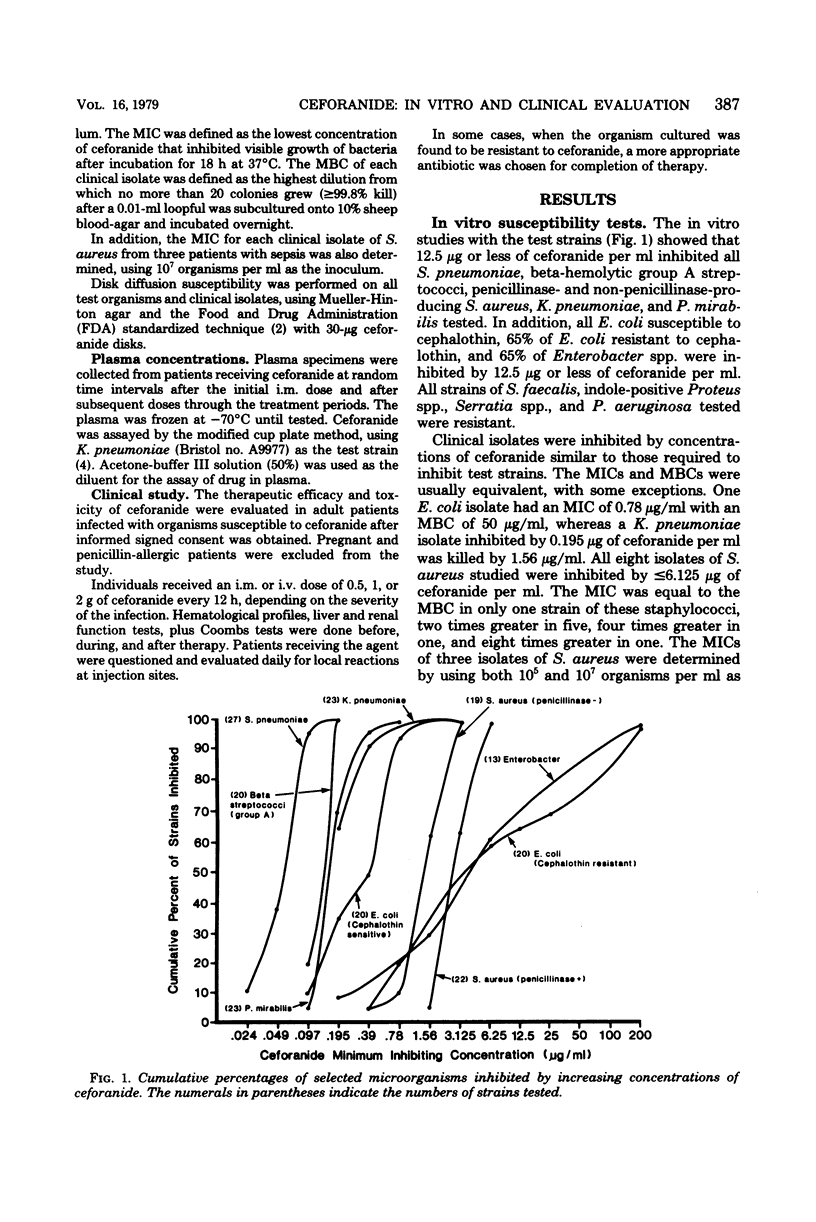
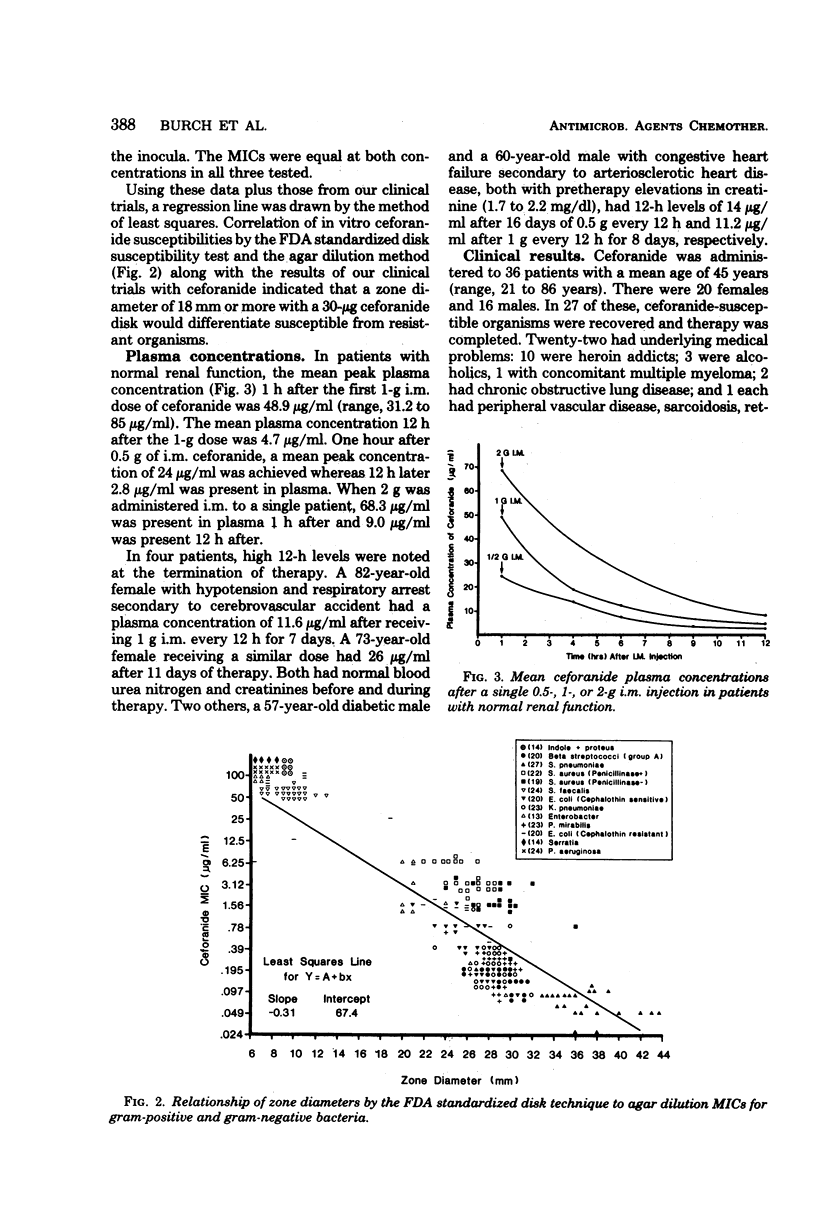
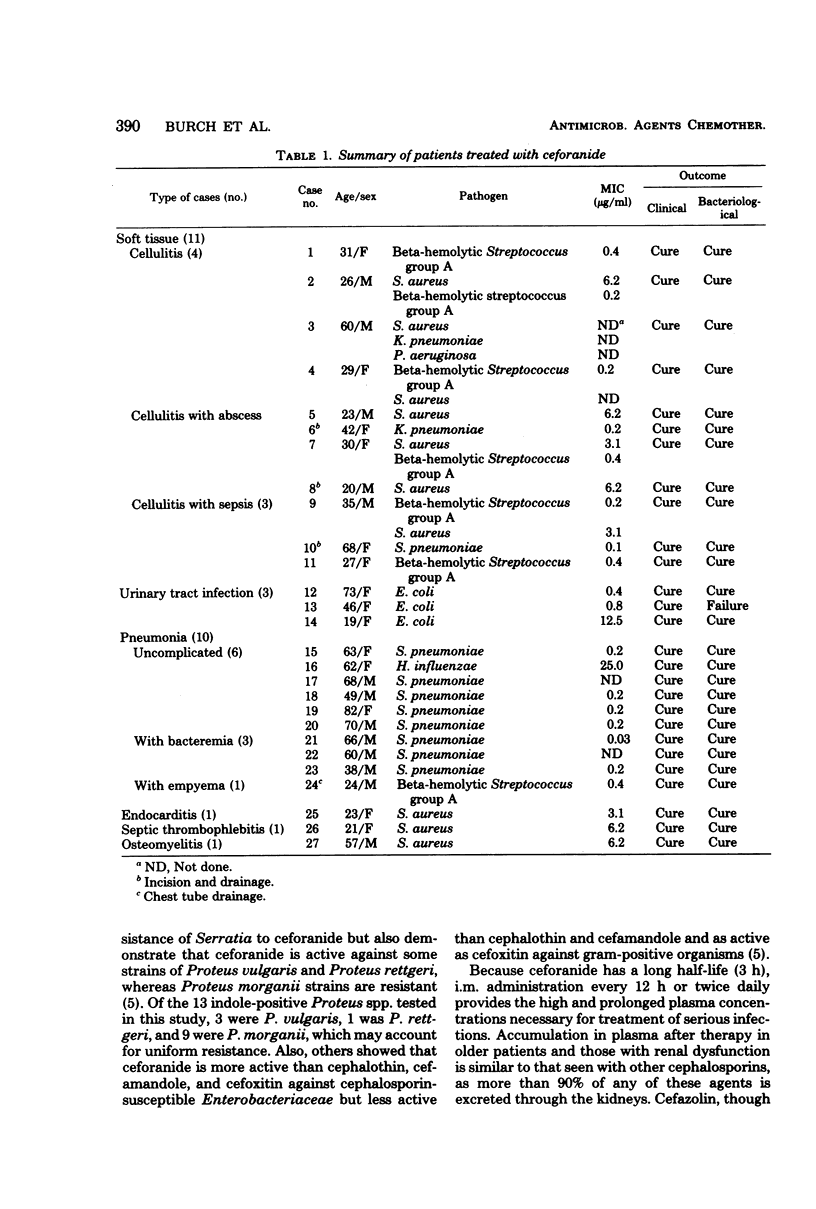
Ceforanide, a new cephalosporin antibiotic with a long half-life (3 h), can be administered twice daily. We evaluated its antimicrobial activity, pharmacology, and clinical efficacy. Twenty-seven patients with infections due to susceptible organisms received ceforanide, 0.5, 1, or 2 g, intramuscularly or intravenously every 12 h for 6 to 28 days. In vitro studies with the clinical isolates from 27 patients treated plus 263 additional isolates showed that ceforanide was active against cephalothin-susceptible gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. In addition, ceforanide inhibited 65% of cephalothin-resistant Escherichia coli and 65% of Enterobacter spp. at ≤12.5 μg/ml. After a single 1-g intramuscular dose, the mean peak plasma concentration at 1 h was 48.9 μg/ml and that at 12 h was 4.7 μg/ml. Plasma accumulation occurred in some patients. The infections included 10 pneumonias, 3 with bacteremia and 1 with empyema; 11 soft tissue infections, 4 with abscesses and 3 with sepsis; and 3 urinary tract infections. One case each of endocarditis, osteomyelitis, and septic thrombophlebitis, all due to Staphylococcus aureus, were treated. Clinical response was satisfactory in all patients; bacteriological response was satisfactory in 26 of 27 patients. Ceforanide was well tolerated. Three patients developed mild increases in liver enzymes, and one developed slight eosinophilia. In another case, the antibiotic was discontinued because of a fivefold rise in serum glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase (aspartate aminotransferase) and serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (alanine aminotransferase) and a twofold rise in lactic acid dehydrogenase and alkaline phosphatase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aswapokee N., Aswapokee P., Fu K. P., Neu H. C. In vitro activity and beta-lactamase stability of BL-S786 compared with those of other cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jul;14(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goering R. V., Sanders C. C., Sanders W., Jr Comparison of BL-S786 with cephalothin, cefamandole and cefoxitin in vitro and in treatment of experimental infections in mice. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Apr;31(4):363–372. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitner F., Misiek M., Pursiano T. A., Buck R. E., Chisholm D. R., DeRegis R. G., Tsai Y. H., Price K. E. Laboratory evaluation of BL-S786, a cephalosporin with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Sep;10(3):426–435. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.3.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadomy S., Wagner G., Carver M. In vitro and in vivo studies with BL-S786, cefoxitin, and cefamandole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):412–415. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver S. S., LeBlanc B. M., Bodey G. P. BL-S786 (ceforanide), a new parenteral cephalosporin: in vitro studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Feb;15(2):318–322. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



