Abstract
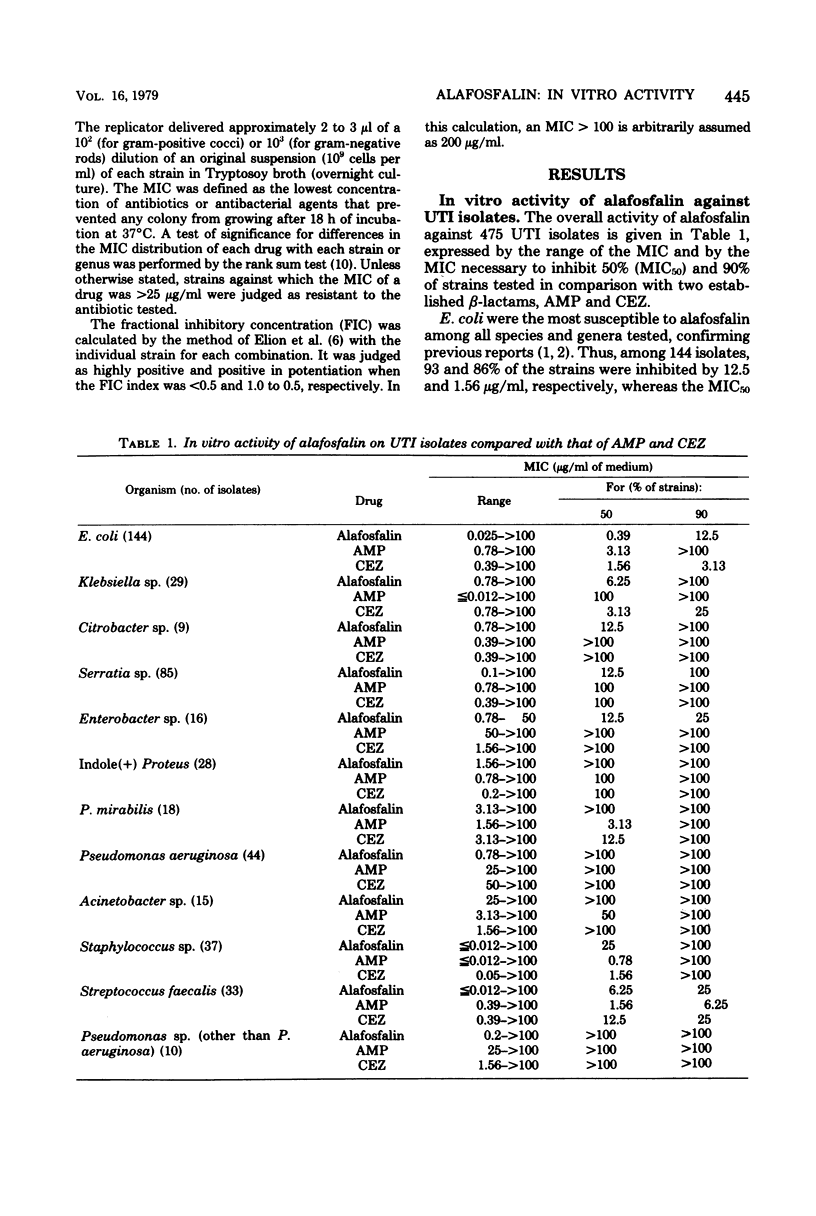
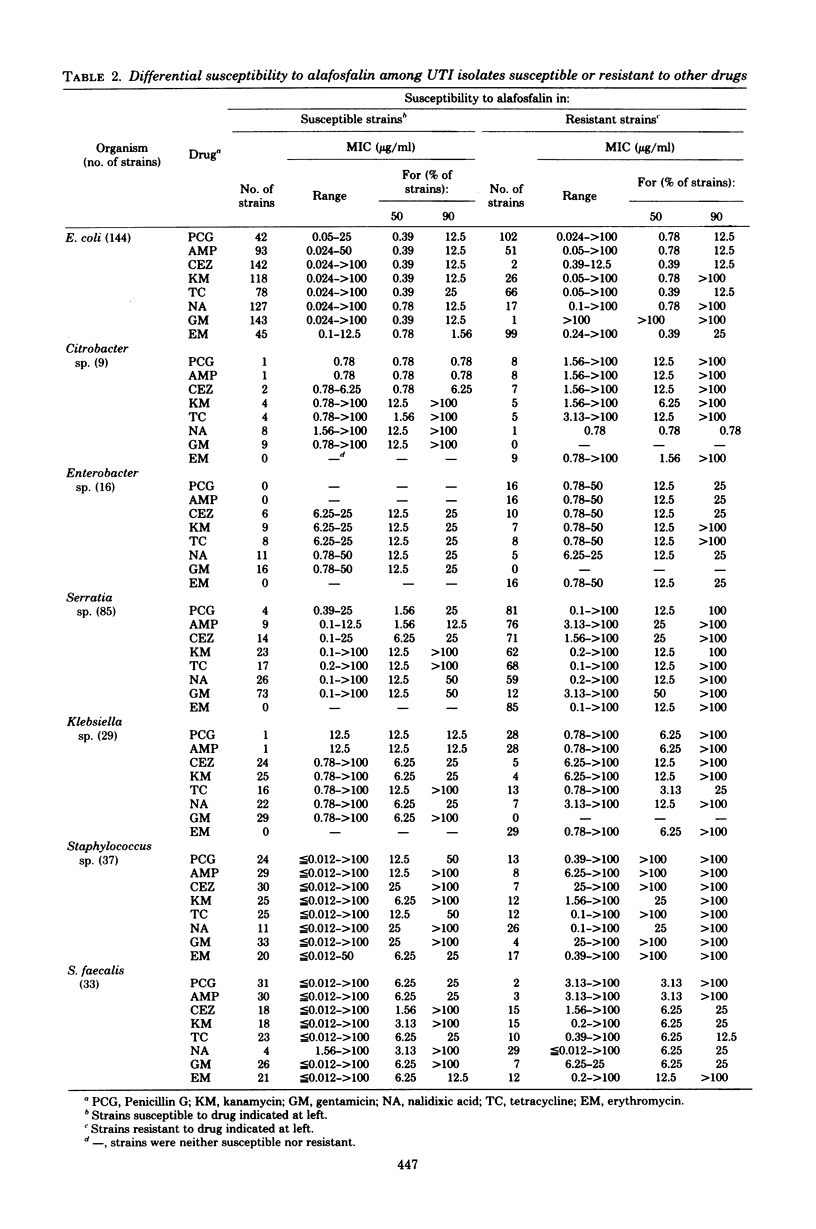
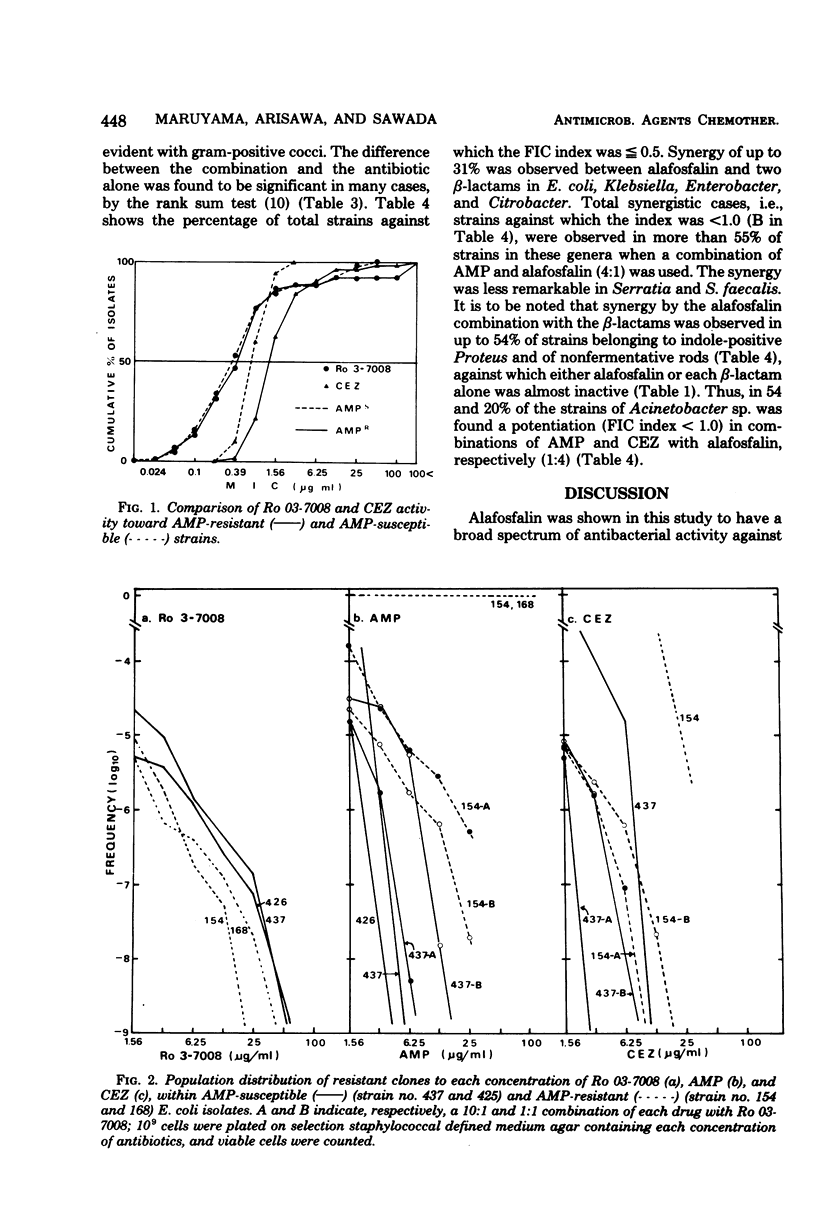
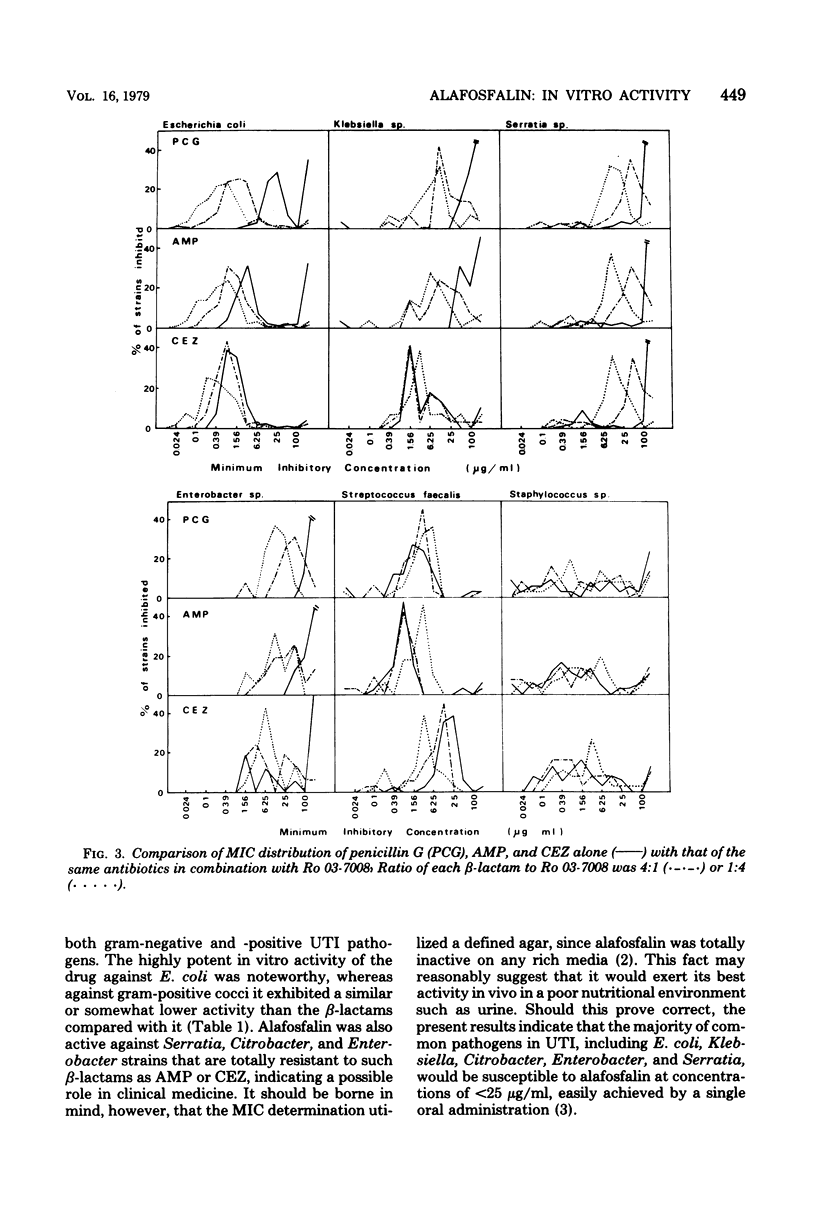
A new phosphonopeptide, alafosfalin, was evaluated for in vitro antibacterial activity and for synergism with beta-lactams, using 475 Japanese clinical isolates from urinary tract infections. Alafosfalin was found to be highly active against Escherichia coli and moderately active against Serratia, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, and Citrobacter, but less active against gram-positive organisms than were beta-lactams such as cephazolin or ampicillin and inactive against indole-positive Proteus, Pseudomonas, and Acinetobacter. Potentiation with the two beta-lactams (fractional inhibitory concentration less than or equal to 0.5) was found in 10 to 40% of susceptible strains in 4:1 and 1:4 combinations, and to a lesser extent in those species or genera that were insensitive to alafosfalin alone. No cross resistance was seen between alafosfalin and the beta-lactams or any other commonly used antibacterial agents tested. Effect on selected ampicillin-resistant strains, differential sensitivity to alafosfalin among resistant strains of various types, and sensitivity of alafosfalin-insensitive E. coli and Klebsiella to other antibiotics are also discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. G., Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Holmes S. W., Lambert R. W., Nisbet L. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides as antibacterial agents: alaphosphin and related phosphonopeptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):684–695. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. G., Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Holmes S. W., Lambert R. W., Nisbet L. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides, a new class of synthetic antibacterial agents. Nature. 1978 Mar 2;272(5648):56–58. doi: 10.1038/272056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Lambert R. W., Lloyd W. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides as antibacterial agents: mechanism of action of alaphosphin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):696–705. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Lambert R. W., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides as antibacterial agents: rationale, chemistry, and structure-activity relationships. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):677–683. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELION G. B., SINGER S., HITCHINGS G. H. Antagonists of nucleic acid derivatives. VIII. Synergism in combinations of biochemically related antimetabolites. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



