Abstract
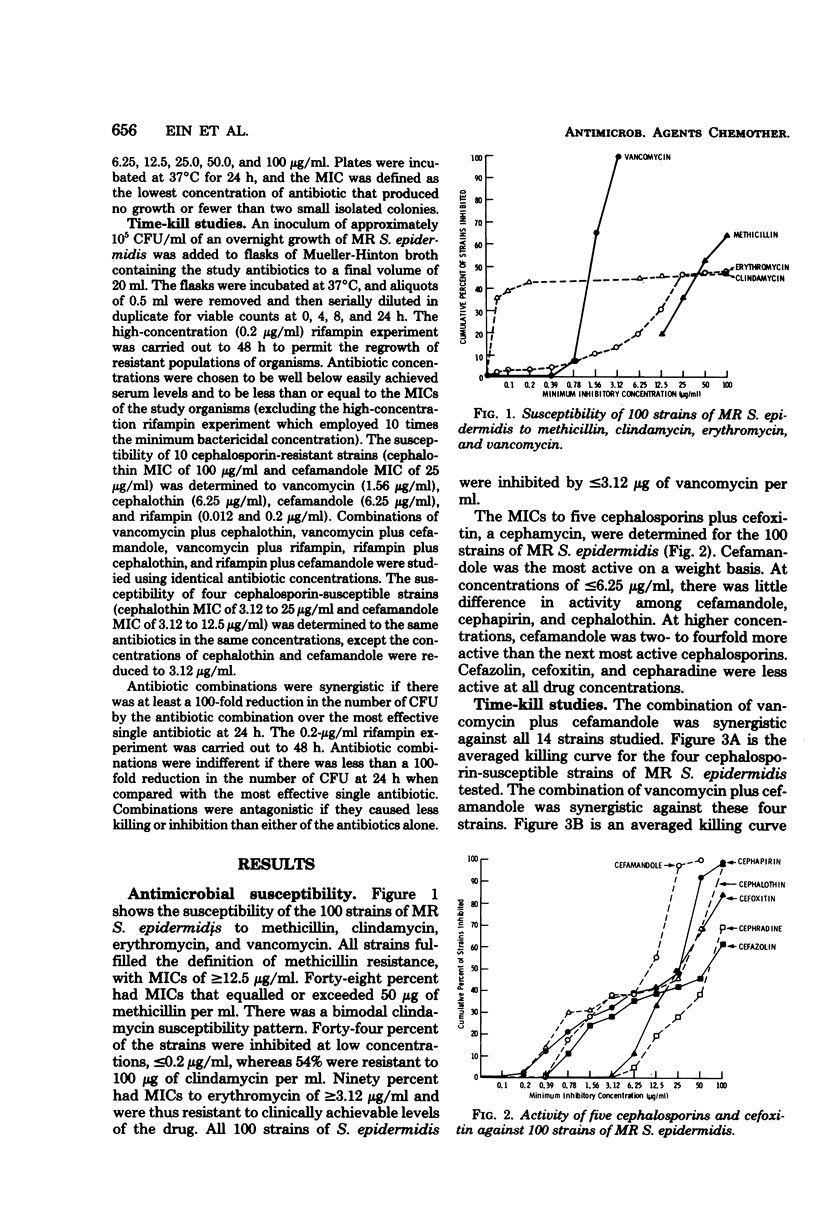
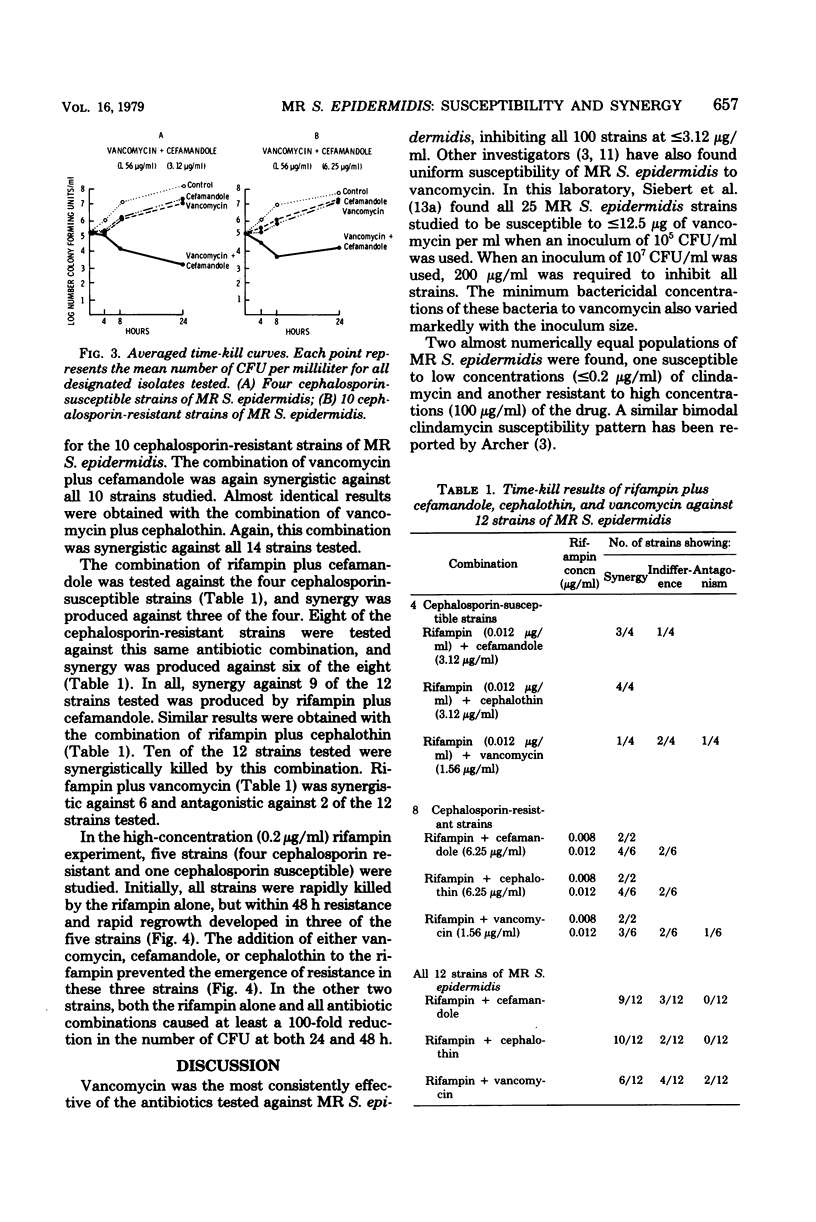
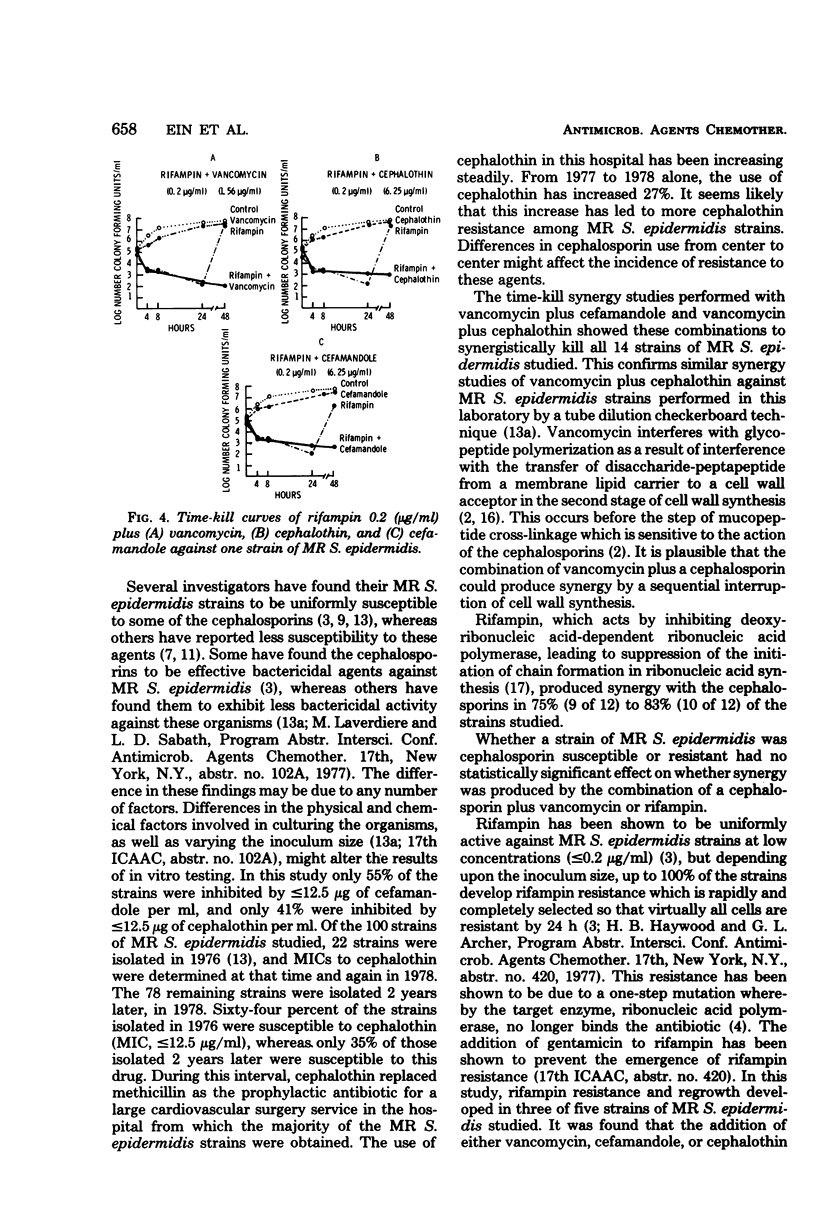
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis is an important cause of cerebrospinal fluid shunt infections and prosthetic valve endocarditis. Agar dilution minimum inhibitory concentrations were determined for 100 strains of methicillin-resistant S. epidermidis which were isolated from clinical specimens. Vancomycin inhibited all 100 strains at ≤3.12 μg/ml, whereas clindamycin inhibited only 46 strains at ≤12.5 μg/ml. Methicillin-resistant S. epidermidis strains were resistant to achievable levels of erythromycin, with 90 strains having a minimum inhibitory concentration of ≥3.12 μg/ml. Of the five cephalosporins and one cephamycin tested, cefamandole was the most active in vitro, inhibiting 97 strains at ≤25 μg/ml. Antibiotic synergism was examined by a quantitative bacterial time-kill method. Synergism (≥102 kill by the combination over the most effective single antibiotic at 24 h) was demonstrated with vancomycin (1.56 μg/ml) plus cefamandole (6.25 μg/ml) in 14 of 14 strains, vancomycin plus cephalothin (6.25 μg/ml) in 14 of 14 strains, vancomycin plus rifampin (0.008 to 0.012 μg/ml) in 6 of 12 strains, rifampin plus cefamandole in 9 of 12 strains, and rifampin plus cephalothin in 10 of 12 strains. The emergence of populations of bacteria resistant to 0.2 μg of rifampin per ml developed in three of five methicillin-resistant S. epidermidis strains tested. The addition of either vancomycin, cephalothin, or cefamandole to the rifampin prevented the emergence of resistance in these three strains. Clinical trials of synergistic antibiotic combination therapy for serious methicillin-resistant S. epidermidis infections are indicated.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON J. S., MATSUHASHI M., HASKIN M. A., STROMINGER J. L. LIPID-PHOSPHOACETYLMURAMYL-PENTAPEPTIDE AND LIPID-PHOSPHODISACCHARIDE-PENTAPEPTIDE: PRESUMED MEMBRANE TRANSPORT INTERMEDIATES IN CELL WALL SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:881–889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson F. M. Ventriculocardiac shunts. Identification and control of practical problems in 143 cases. J Pediatr. 1973 Feb;82(2):222–227. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80158-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L. Antimicrobial susceptibility and selection of resistance among Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates recovered from patients with infections of indwelling foreign devices. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):353–359. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faville R. J., Jr, Zaske D. E., Kaplan E. L., Crossley K., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Combined therapy with vancomycin and rifampin. JAMA. 1978 Oct 27;240(18):1963–1965. doi: 10.1001/jama.240.18.1963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverdiere M., Peterson P., Verhoef J., Williams D. N., Sabath L. D. In vitro activity of cephalosporins against methicillin-resistant, coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1978 Mar;137(3):245–250. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskell R. Importance of coagulase-negative staphylococci as pathogens in the urinary tract. Lancet. 1974 Jun 8;1(7867):1155–1158. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90634-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz P. D., Caswell K., Lindsay W. G., Nicoloff D. M. Antibiotic prophylaxis for open-heart surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1977 Apr;73(4):625–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson F. P., Brown C. S. The McKee-Farrar total hip replacement. Preliminary results and complications of 368 operations performed in five general hospitals. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972 Mar;54(2):257–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbaum S. C., Gardner P., Shillito J. Infections of cerebrospinal fluid shunts: epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and therapy. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):543–552. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert W. T., Moreland N., Williams T. W., Jr Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. South Med J. 1978 Nov;71(11):1353–1355. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197811000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert W. T., Moreland N., Williams T. W., Jr Synergy of vancomycin plus cefazolin or cephalothin against methicillin-resistance Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Apr;139(4):452–457. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.4.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert W. T., Williams T. W., Jr Prosthetic valve endocarditis. Compr Ther. 1978 Jan;4(1):53–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter L., Morris J. E., Starr A. Prosthetic valvular endocarditis. A 12-year review. Circulation. 1973 Jun;47(6):1319–1326. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.47.6.1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON T. S., STUART R. D. STAPHYLOCOCCUS ALBUS IN WOUND INFECTION AND IN SEPTICEMIA. Can Med Assoc J. 1965 Jul 3;93:8–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Mauro E., Synder L., Marino P., Lamberti A., Coppo A., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Rifampicin sensitivity of the components of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 May 10;222(5193):533–537. doi: 10.1038/222533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


