Abstract
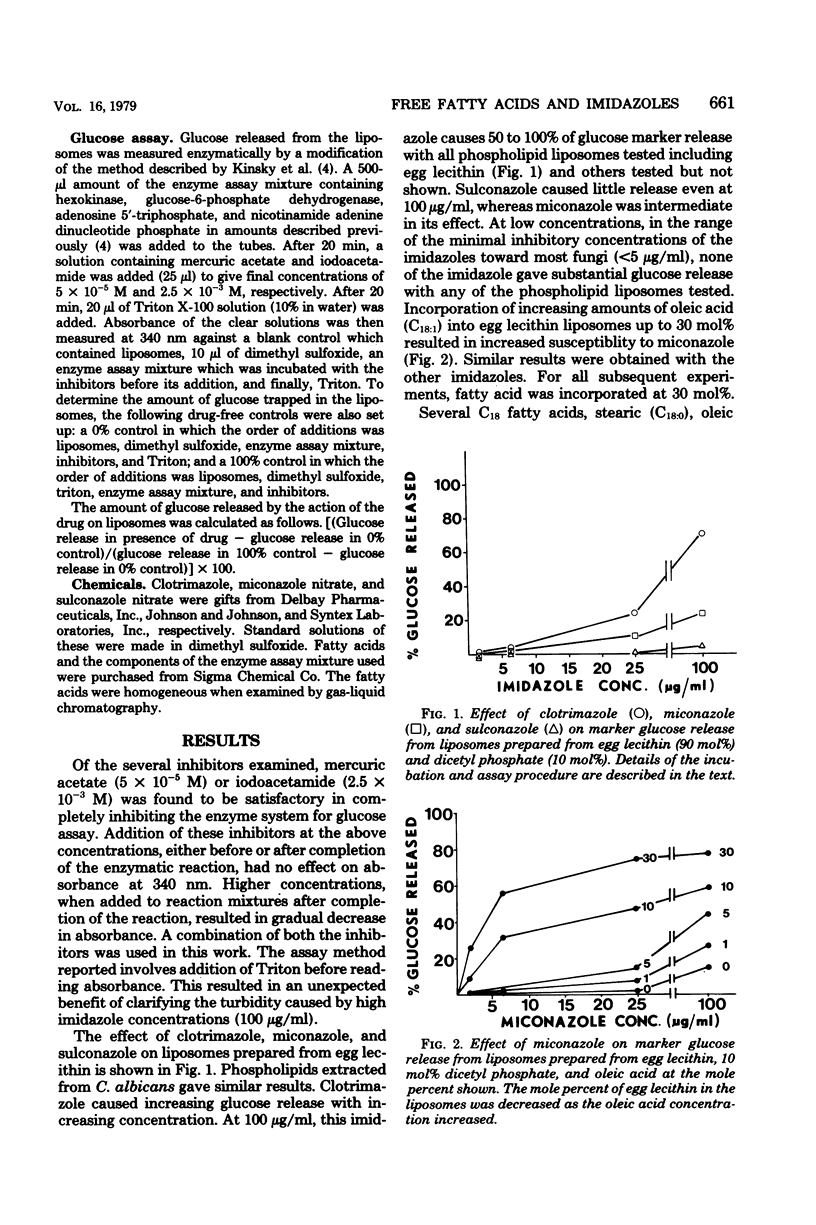
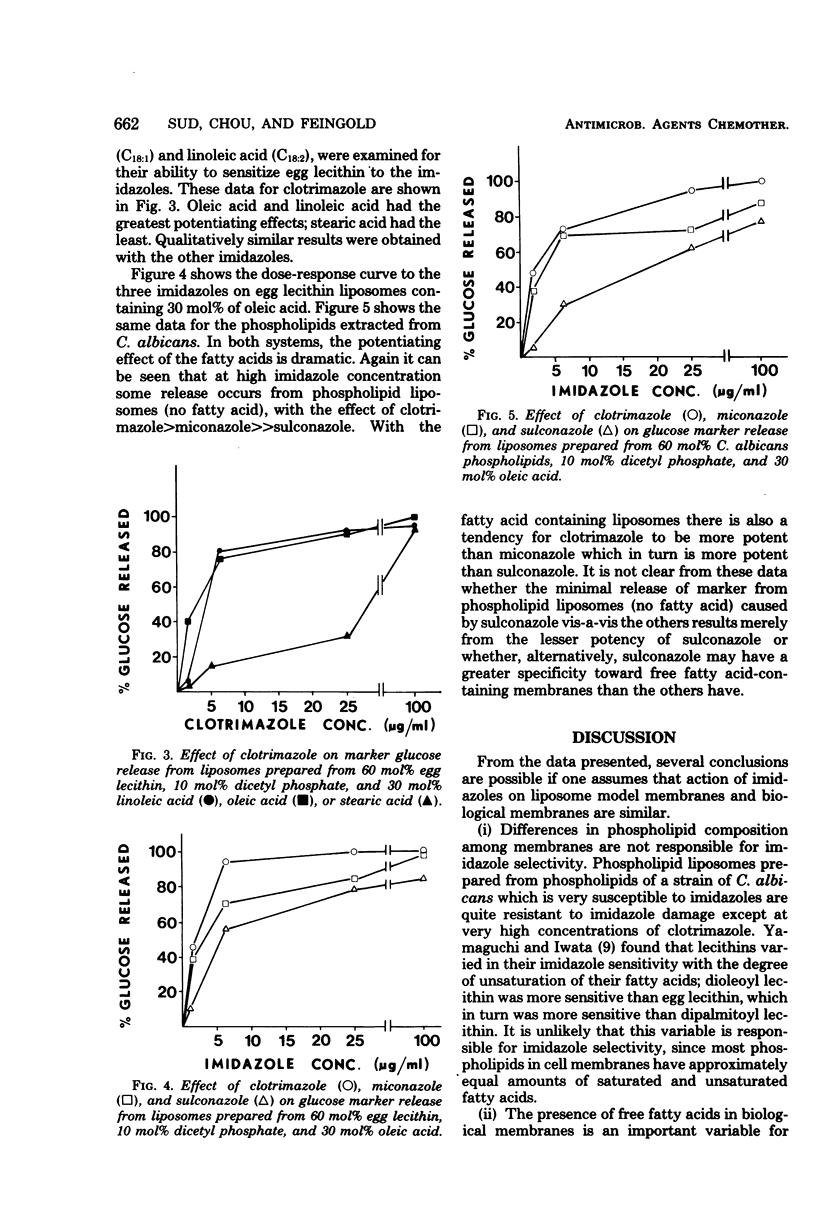
The presence of free fatty acids in liposome model membranes sensitizes these membranes to the action of the imidazole antifungals, clotrimazole, micronazole, and sulconazole. Unsaturation of the fatty acids is an important variable; the effect of linoleic and oleic acids is much greater than that of stearic acid. The imidazoles differ somewhat in action, with clotrimazole potency greatest both on membranes with and without fatty acids. Sulconazole has very little activity on membranes without fatty acids even at the highest concentrations tested. The data are discussed with reference to the susceptibility of various cells to the imidazoles and the specificity of imidazole action. A modification of the enzymatic method generally used for assay of marker glucose with liposome systems is also presented.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HsuChen C. C., Feingold D. S. Polyene antibiotic action on lecithin liposomes: effect of cholesterol and fatty acyl chains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 16;51(4):972–978. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata K., Yamaguchi H., Hiratani T. Mode of action of clotrimazole. Sabouraudia. 1973 Jul;11(2):158–166. doi: 10.1080/00362177385190321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C., Haxby J., Kinsky C. B., Demel R. A., van Deenen L. L. Effect of cholesterol incorporation on the sensitivity liposomes to the polyene antibiotic, filipin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 10;152(1):174–185. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda S., Uno J., Arai T. Target substances of some antifungal agents in the cell membrane. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):454–459. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGLETON W. S., GRAY M. S., BROWN M. L., WHITE J. L. CHROMATOGRAPHICALLY HOMOGENEOUS LECITHIN FROM EGG PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jan;42:53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02558256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreedhara Swamy K. H., Sirsi M., Ramananda Rao G. R. Studies on the mechanism of action of miconazole: effect of miconazole on respiration and cell permeability of Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Apr;5(4):420–425. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.4.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Iwata K. Effect of fatty acyl group and sterol composition on sensitivity of lecithin liposomes to imidazole antimycotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):706–711. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H. Protection by unsaturated lecithin against the imidazole antimycotics, clotrimazole and miconazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):423–426. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


