Abstract
Six antineoplastic antibiotics showed little antibacterial activity against 28 strains of four species of gram-negative enteric bacteria. By using the cellophane transfer technique, combinations of these agents with 16 antibacterial drugs usually showed indifference. However, combinations of mitomycin C, especially with the aminoglycosides, were synergistic on strains of Escherichia coli, Proteus, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Bleomycin, on the other hand, often showed antagonism on strains of E. coli and K. pneumoniae with the beta-lactams, aminoglycosides, and other antibacterial agents. Checkerboard titrations and kinetic killing curves confirmed these findings.
Full text
PDF
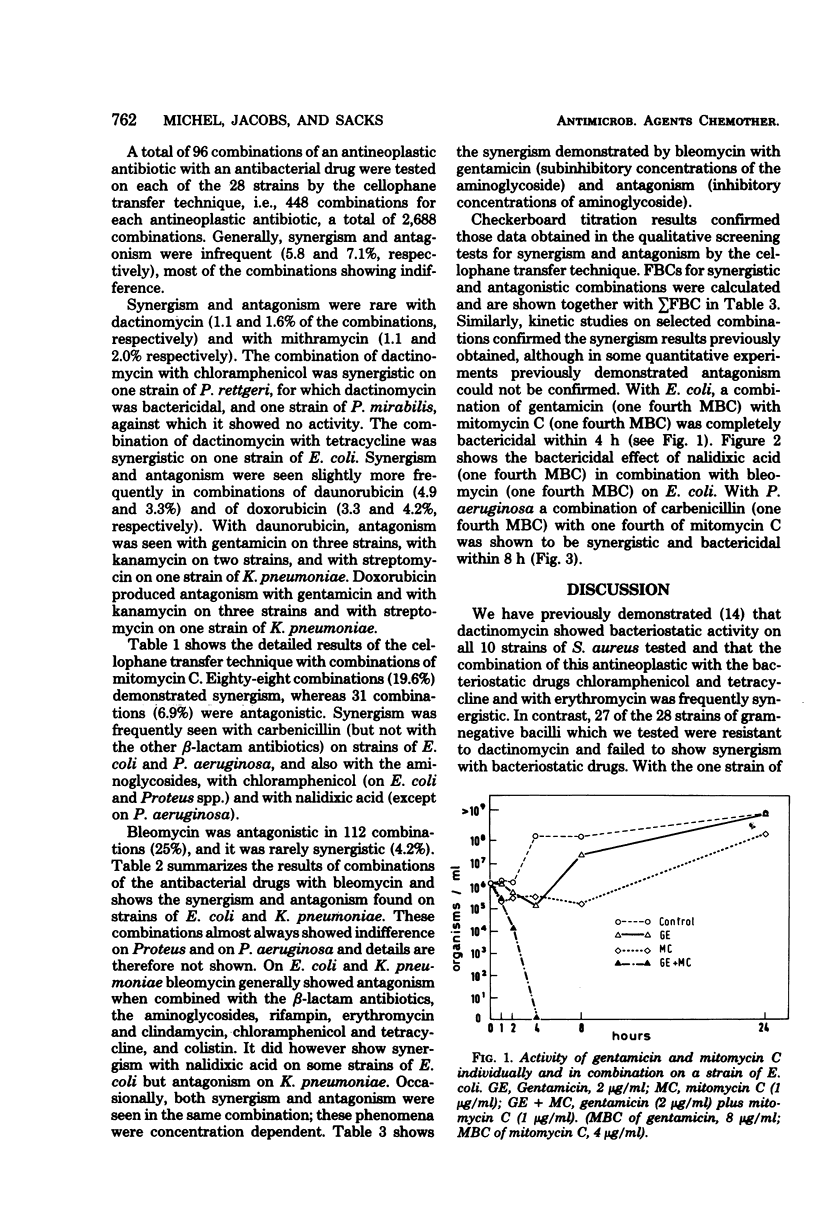
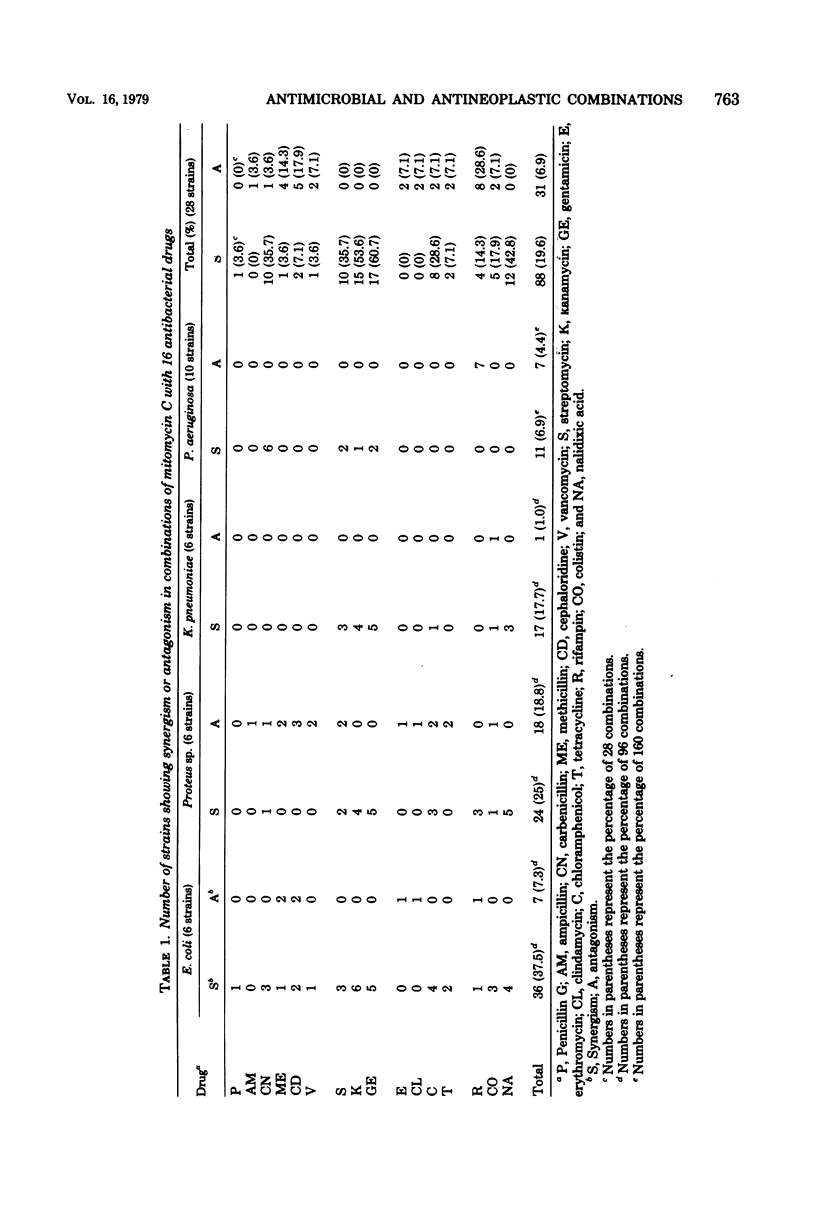
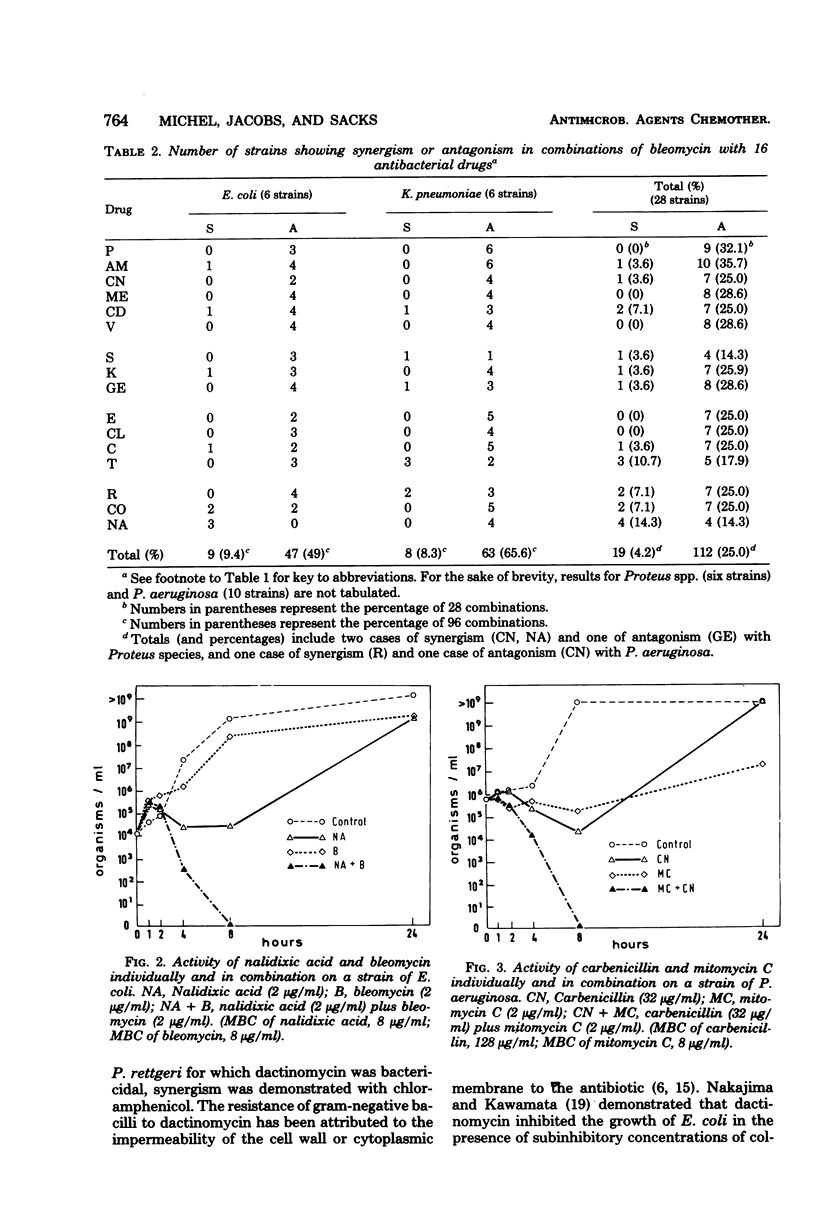
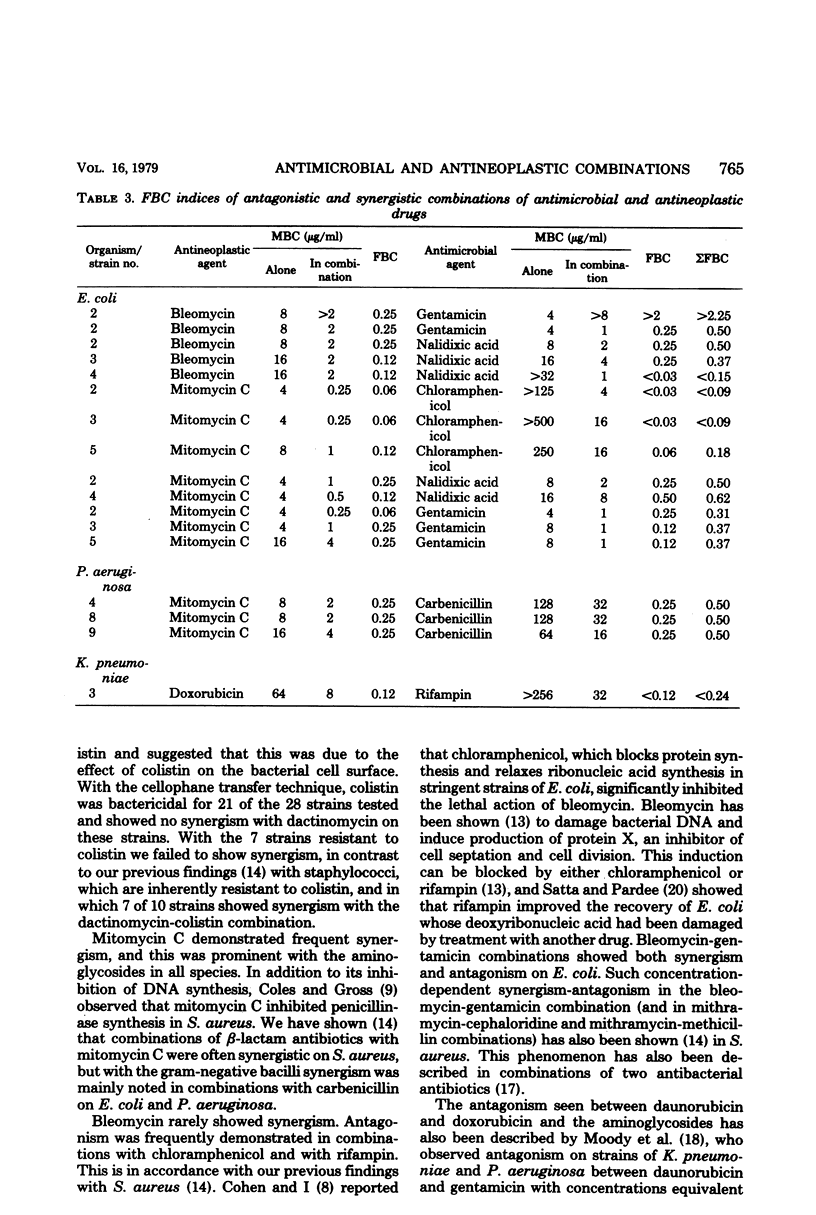

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P. Infections in cancer patients. Cancer Treat Rev. 1975 Jun;2(2):89–128. doi: 10.1016/s0305-7372(75)80005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHABBERT Y. A., PATTE J. C. Cellophane transfer: application to the study of activity of combinations of antibiotics. Appl Microbiol. 1960 Jul;8:193–199. doi: 10.1128/am.8.4.193-199.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHABBERT Y. A., WATERWORTH P. M. STUDIES ON THE "CARRY-OVER" OF ANTIBIOTICS USING THE CELLOPHANE TRANSFER TECHNIQUE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:314–316. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHABBERT Y. Une technique nouvelle d'étude de l'action bactéricide des associations d'antibiotiques: le transfert sur cellophane. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1957 Sep;93(3):289–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLUZEL R., VAURS R., CLUZEL-NIGAY M., VERNER M. [A new technic for the study of the bactericidal power of antibiotic combinations derived from "transfer on cellophane": the cross arrangement]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1960 Jun;98:928–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. K., Costerton J. W., Singh A. P., Ingram J. M. Susceptibility of whole cells and spheroplasts of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to actinomycin D. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Mar;3(3):399–406. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. S., I J. Synthesis and the lethality of bleomycin in bacteria. Cancer Res. 1976 Aug;36(8):2768–2774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles N. W., Gross R. The effect of mitomycin C on the induced synthesis of penicillinase in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jul 26;20(3):366–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD L. P., WATERWORTH P. M. Methods of testing combined antibiotic bactericidal action and the significance of the results. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Jul;15:328–338. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.4.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J., Pardee A. B. DNA synthesis inhibition and the induction of protein X in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 15;101(4):459–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs J. Y., Michel J., Sacks T. Bactericidal effect of combinations of antimicrobial drugs and antineoplastic antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):580–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacAlister T. J., Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J. Effect of the removal of outer cell wall layers on the actinomycin susceptibility of a gram-negative bacterium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 May;1(5):447–449. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.5.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J., Jacobs J., Sacks T. Bactericidal synergistic effect due to chloramphenicol-induced inhibition of staphyloccal penicillinase. Chemotherapy. 1977;23(1):32–36. doi: 10.1159/000221968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. R., Morris M. J., Young V. M., Moyé L. A., 3rd, Schimpff S. C., Wiernik P. H. Effect of two cancer chemotherapeutic agents on the antibacterial activity of three antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Nov;14(5):737–742. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.5.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männistö P. Absorption of rifampin from various preparations and pharmaceutic forms. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Mar;21(3):370–374. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977213370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Kawamata J. Effect of colistin on actinomycin sensitivity of Escherichia coli. Biken J. 1965 Jun;8(2):115–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satta G., Pardee A. B. Inhibition of Escherichia coli division by protein X. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1492–1500. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1492-1500.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff S. C. Diagnosis of infection in patients with cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1975 Aug;11SUPPL:29–38. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-08-019964-1.50008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



