Abstract
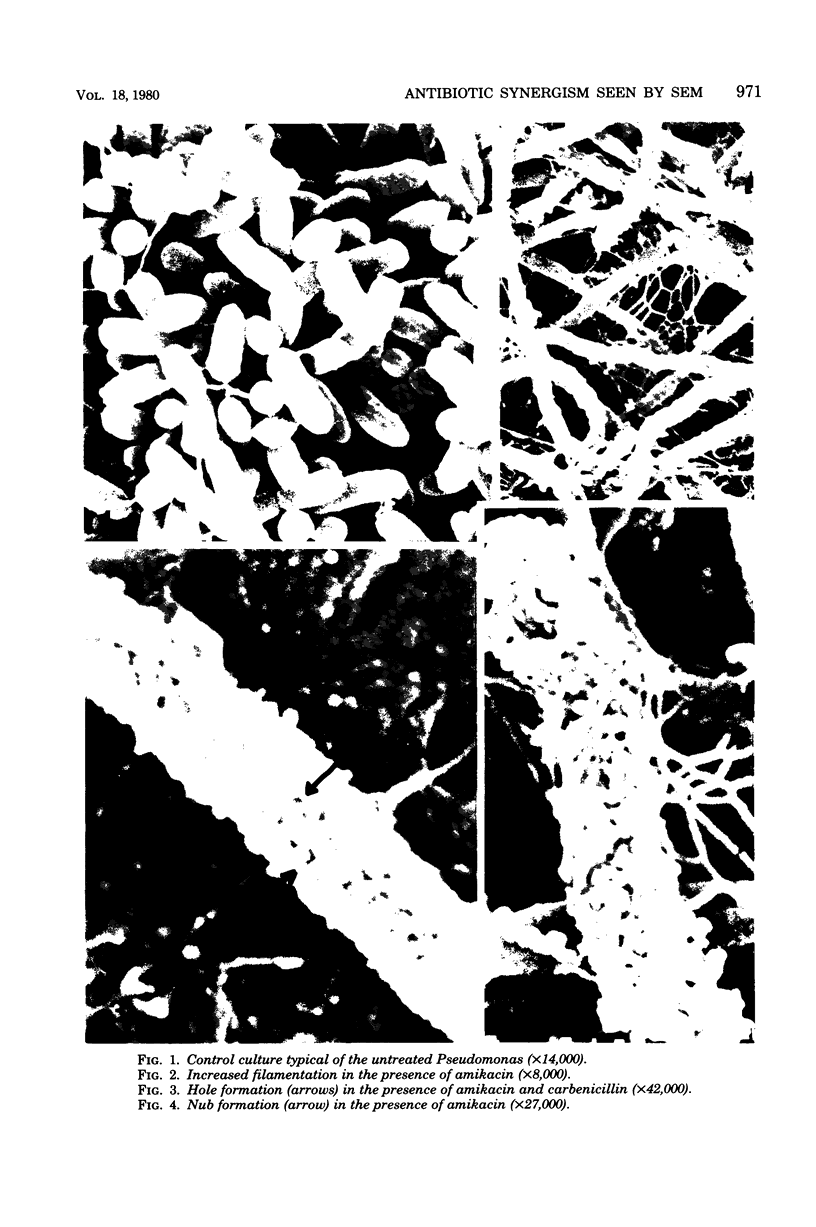
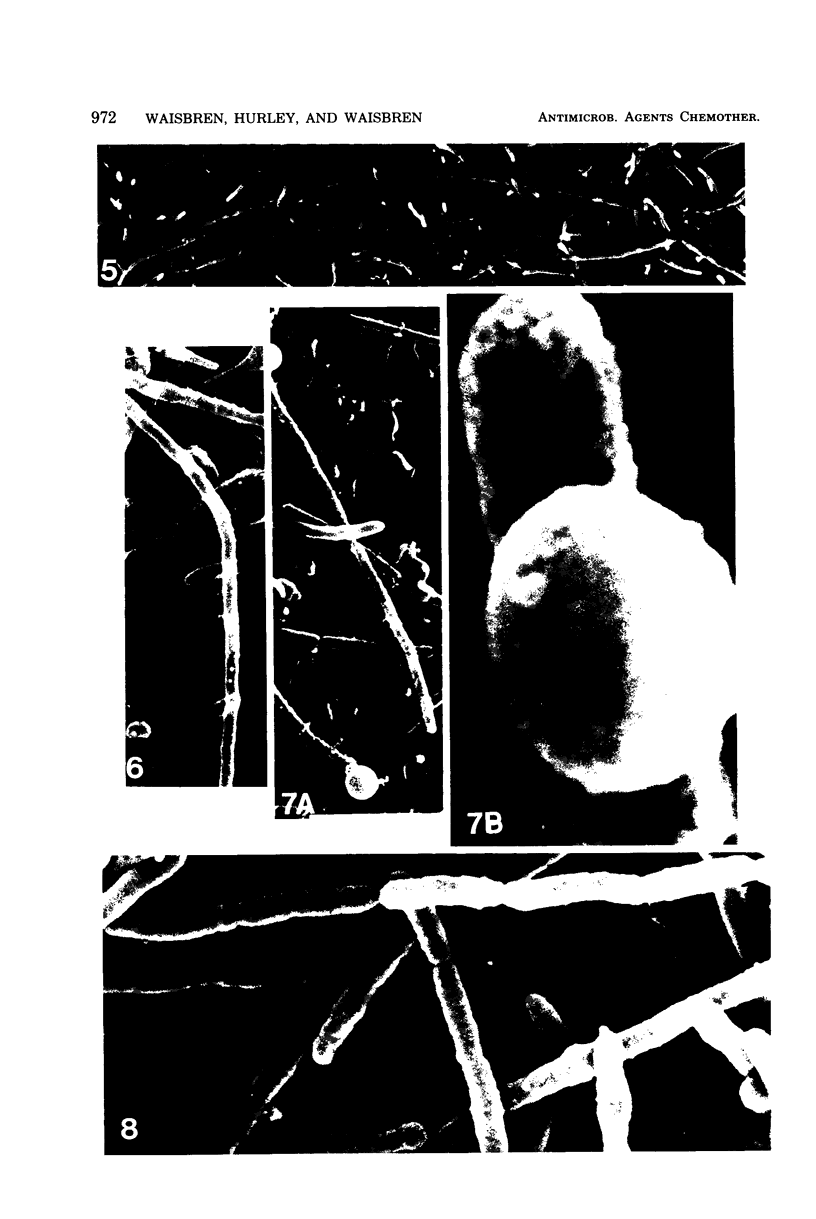
Antibiotic-induced changes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa were observed by means of a scanning electron microscope. Seven frequent and five less frequent morphological changes were noted. The frequent changes were: (i) elongation; (ii) chain formation; (iii) nub formation; (iv) spheroplasts; (v) surface holes or pits; (vi) super-elongation; and (vii) increased filamentation. The less frequent changes were: (i) rounded ends; (ii) streptococcal forms; (ii) stalked nubs; (iv) surface bulges; and (v) convoluted surfaces. A morphological equivalent of antibiotic synergism was found in which changes were noted due to synergistic combinations of antibiotics that were not observed when the antibiotics were used alone or when a nonsynergistic combination of antibiotics was used.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berenbaum M. C. A method for testing for synergy with any number of agents. J Infect Dis. 1978 Feb;137(2):122–130. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.2.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdett I. D., Murray R. G. Septum formation in Escherichia coli: characterization of septal structure and the effects of antibiotics on cell division. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):303–324. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.303-324.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERWIN C. P., WAISBREN B. A., KRUSE R. Clinical and laboratory studies of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas species. Am J Med Sci. 1953 Nov;226(5):525–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., O'Grady F. Antibiotic-induced surface changes in microorganisms demonstrated by scanning electron microscopy. Science. 1969 Mar 7;163(3871):1076–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3871.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike M., Iida K. Effect of polymyxin on the bacteriophage receptors of the cell walls of gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1402–1411. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1402-1411.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike M., Iida K., Matsuo T. Electron microscopic studies on mode of action of polymyxin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):448–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.448-452.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J., Inniss W. E. Electron microscopy of effect of polymyxin on Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1128–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1128-1130.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorian V., Atkinson B. Abnormal forms of bacteria produced by antibiotics. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 Nov;64(5):678–688. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/64.5.678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Acker G., Kleber I. Ultrastructural surface alterations of serratia marcescens after exposure to polymyxin B and/or fresh human serum. Chemotherapy. 1976;22(2):104–113. doi: 10.1159/000221919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAISBREN B. A., CARR C., DUNNETTE J. The tube dilution method of determining bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics. Am J Clin Pathol. 1951 Sep;21(9):884–891. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/21.9_ts.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]