Abstract
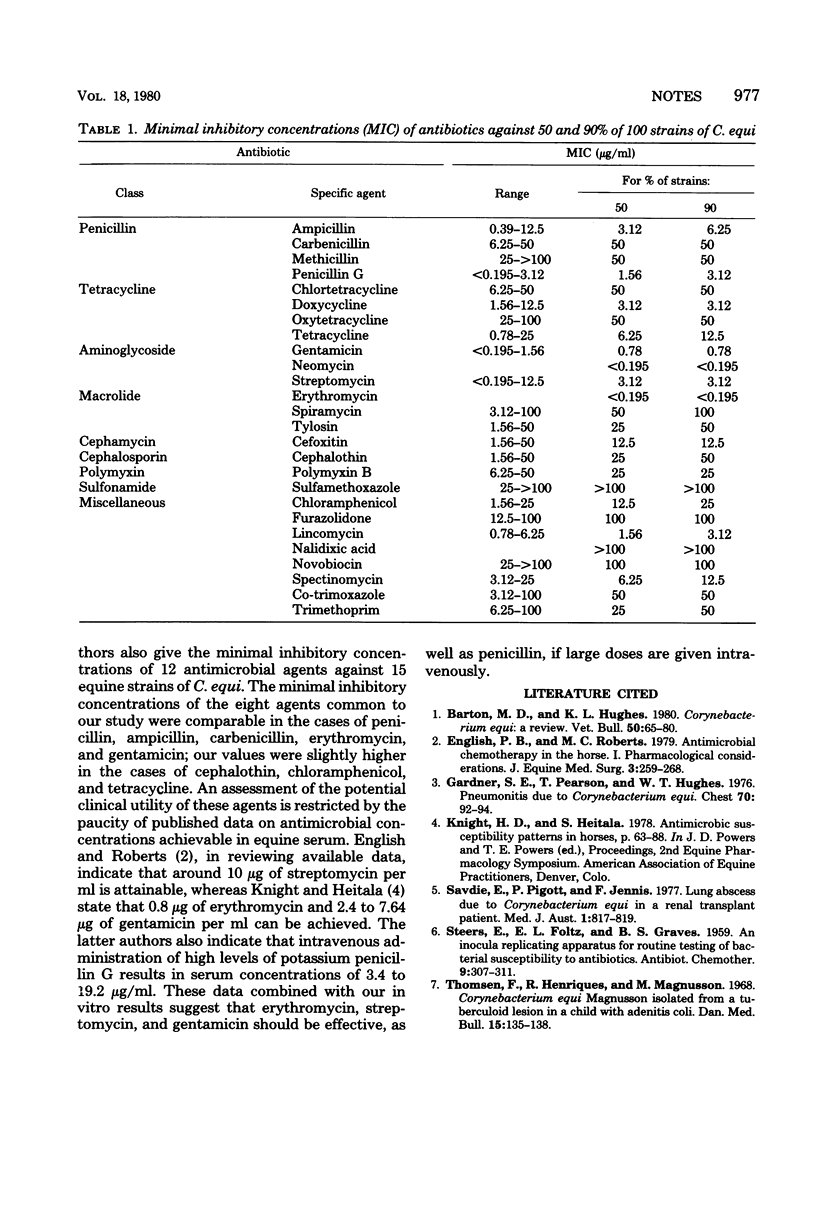
The minimal concentrations of 26 antimicrobial agents required to inhibit growth of 100 isolates of Corynebacterium equi in vitro have been determined. The most active agents were penicillin G, doxycycline, erythromycin, lincomycin, and the aminoglycosides.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gardner S. E., Pearson T., Hughes W. T. Pneumonitis due to Corynebacterium equi. Chest. 1976 Jul;70(1):92–94. doi: 10.1378/chest.70.1.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savdie E., Pigott P., Jennis F. Lung abscess due to Corynebacterium equi in a renal transplant recipient. Med J Aust. 1977 May 28;1(22):817–819. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1977.tb131143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen F., Henriques R., Magnusson M. Corynebacterium equi Magnusson isolated from a tuberculoid lesion in a child with adenitis colli. Dan Med Bull. 1968 May;15(5):135–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



