Abstract
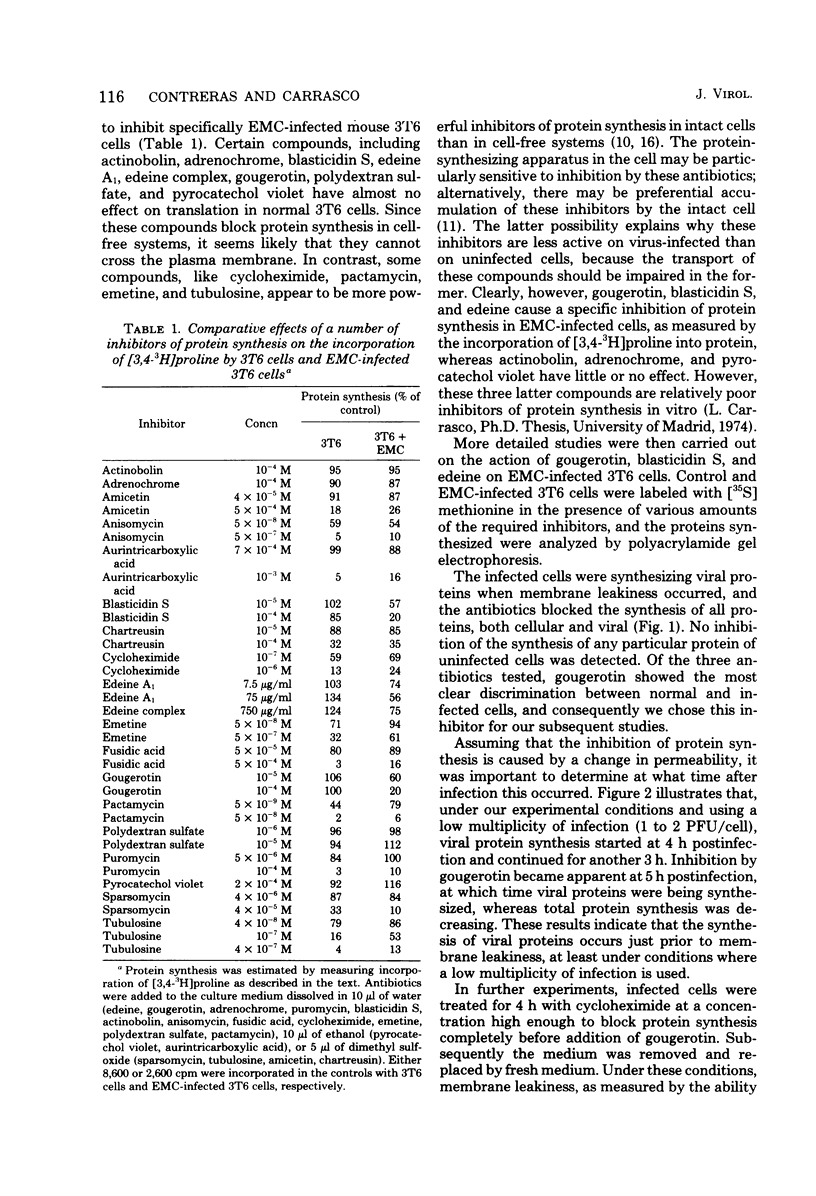
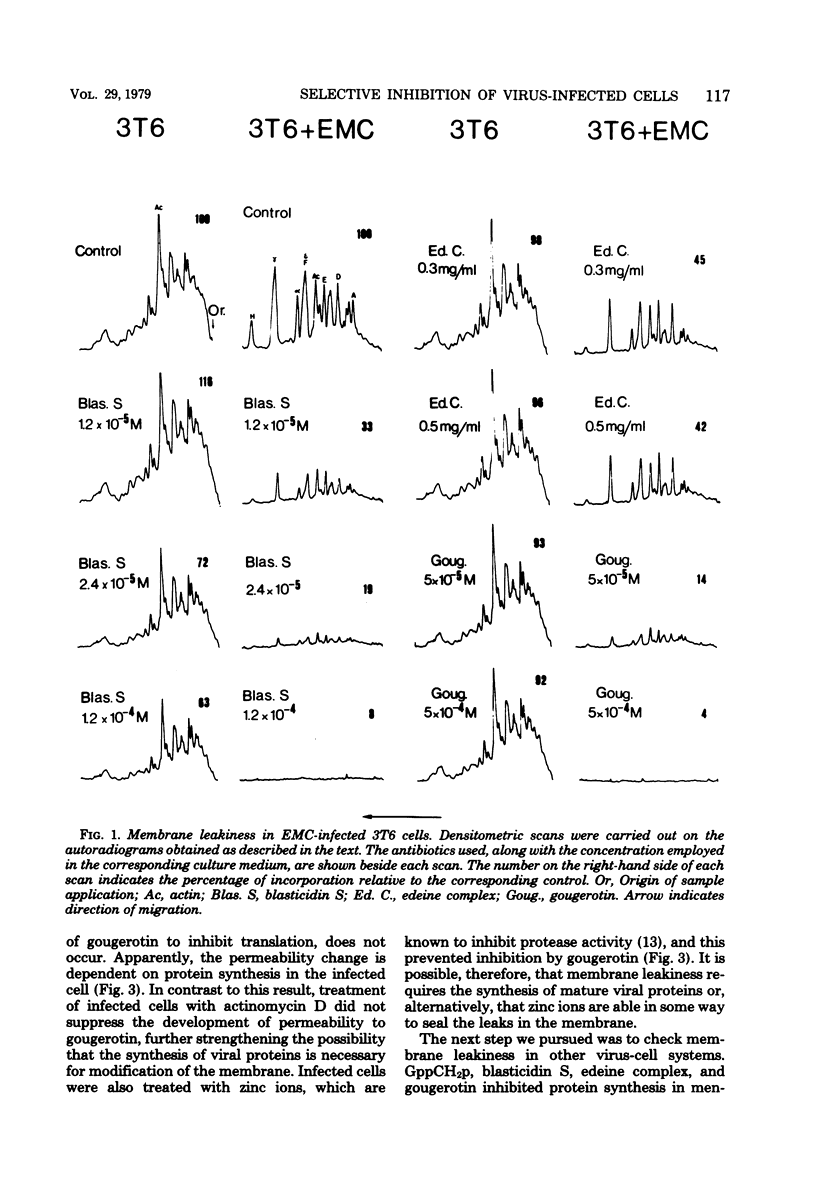
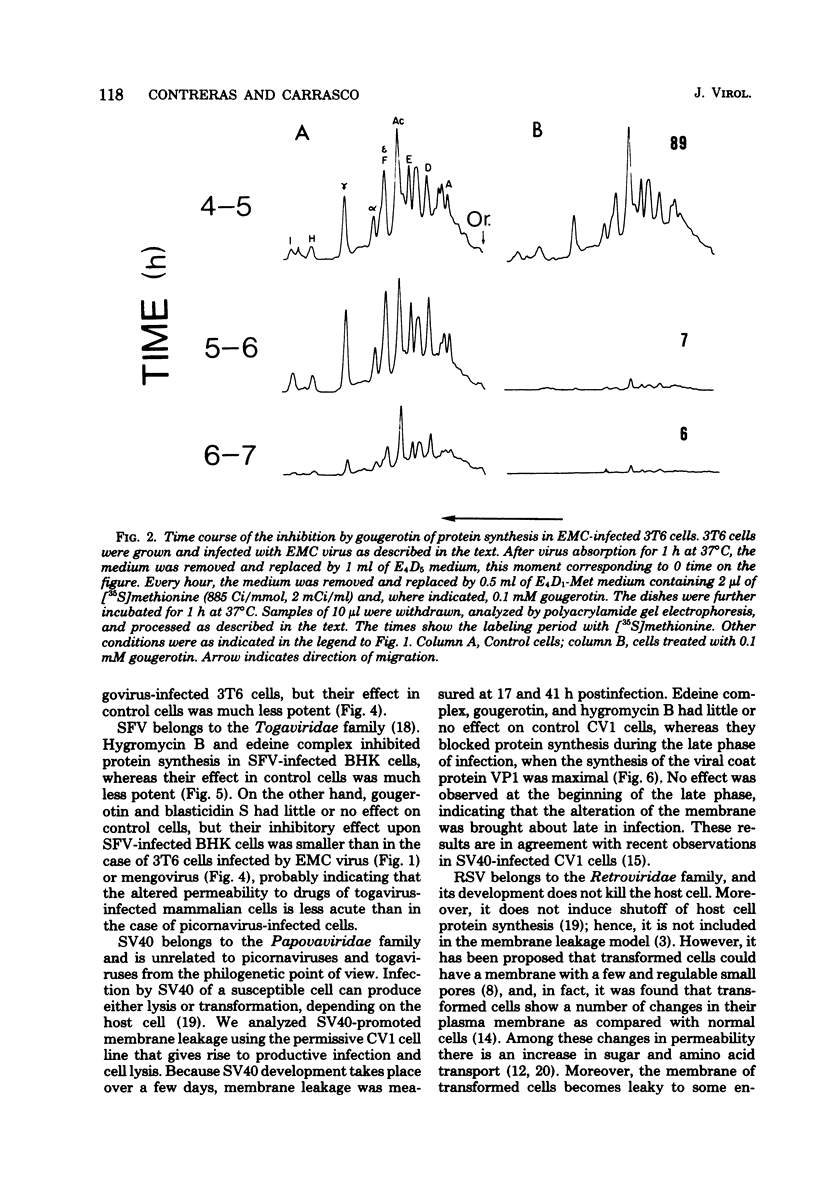
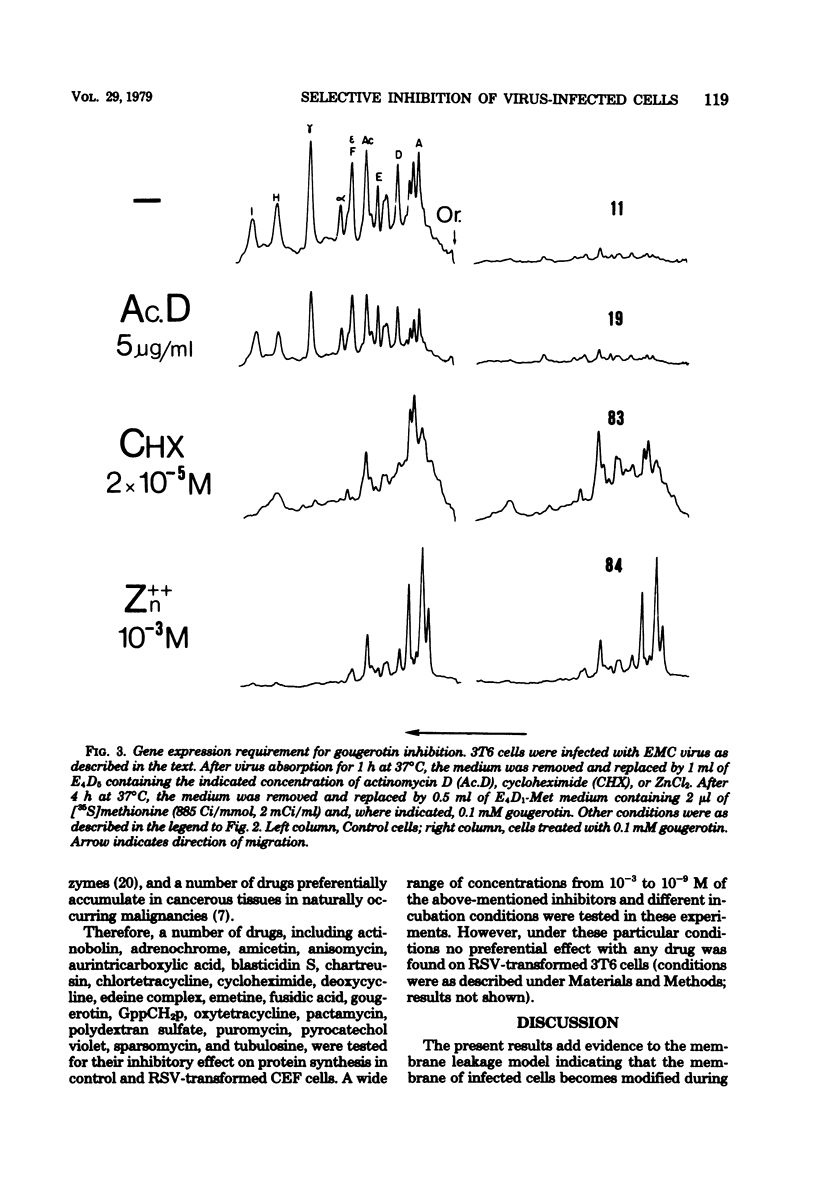
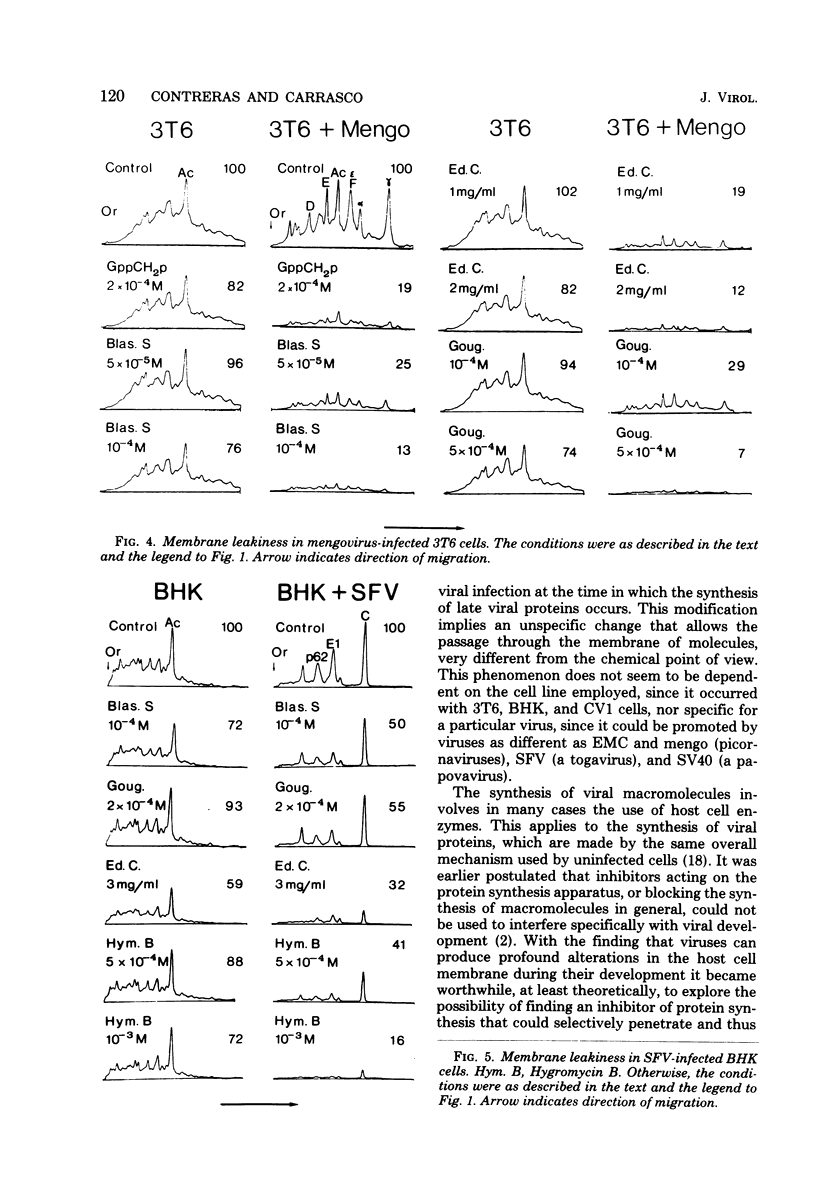
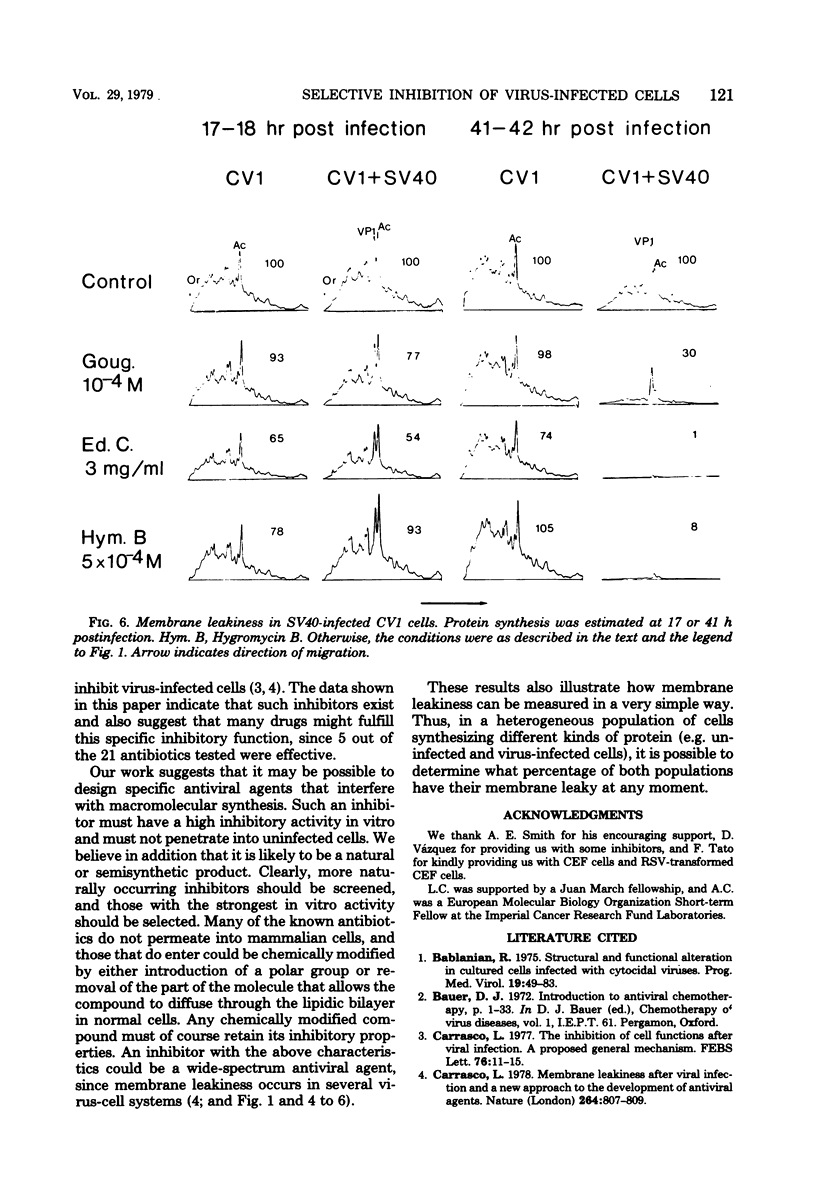
A number of translation inhibitors were tested for their effects on both control and encephalomyocarditis virus-infected mouse 3T6 cells. The virus-infected cells were specifically inhibited by gougerotin, edeine, and blasticidin S, whereas these drugs failed to penetrate into uninfected cells. Inhibition of infected cells by gougerotin became apparent when the synthesis of viral proteins commenced, suggesting that the latter process is accompanied by a permeability change in the cells that allows uptake of the drug. This permeability change was not observed in cells treated with cycloheximide soon after viral infection, although treatment with actinomycin D did not prevent inhibition of gougerotin. It is possible, therefore, that a specific viral protein is involved in the permeability change of the plasma membrane. Moreover, gougerotin was unable to inhibit protein synthesis in the presence of zinc ions, thus preventing gougerotin from entering into the infected cell. Membrane leakiness was not restricted to the encephalomyocarditis virus-3T6 system; it was also observed in mengovirus-infected 3T6 cells, Semliki Forest virus-infected BHK cells, and simian virus 40-infected CVI1 cells at the time in which the synthesis of late proteins is maximal.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carrasco L., Smith A. E. Sodium ions and the shut-off of host cell protein synthesis by picornaviruses. Nature. 1976 Dec 23;264(5588):807–809. doi: 10.1038/264807a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Smith A. E. Sodium ions and the shut-off of host cell protein synthesis by picornaviruses. Nature. 1976 Dec 23;264(5588):807–809. doi: 10.1038/264807a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L. The inhibition of cell functions after viral infection. A proposed general mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 1;76(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condit R. C. F factor-mediated inhibition of bacteriophage T7 growth: increased membrane permeability and decreased ATP levels following T7 infection of male Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):45–59. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J. Activated dyes as antitumor agents. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Apr;52(4):1333–1336. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.4.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARNHAM A. E., EPSTEIN W. THE INFLUENCE OF ENCEPHALOMYOCARDITIS (EMC) VIRUS INFECTION ON POTASSIUM TRANSPORT IN L CELLS. Virology. 1963 Nov;21:436–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grollman A. P. Inhibitors of protein biosynthesis. V. Effects of emetine on protein and nucleic acid biosynthesis in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 10;243(15):4089–4094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka M. Transport of sugars in tumor cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 29;355(1):77–104. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(74)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Trans-membrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. II. Surface changes associated with transformation and malignancy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 30;458(1):1–72. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(76)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norkin L. C. Cell killing by simian virus 40: impairment of membrane formation and function. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):872–879. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.872-879.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Inhibitors of ribosome functions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:487–562. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponta H., Altendorf K. H., Schweiger M., Hirsch-Kaufmann M., Pfennig-Yeh M. L., Herrlich P. E. coli membranes become permeable to ions following T7-virus-infection. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Dec 8;149(2):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00332882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



