Abstract
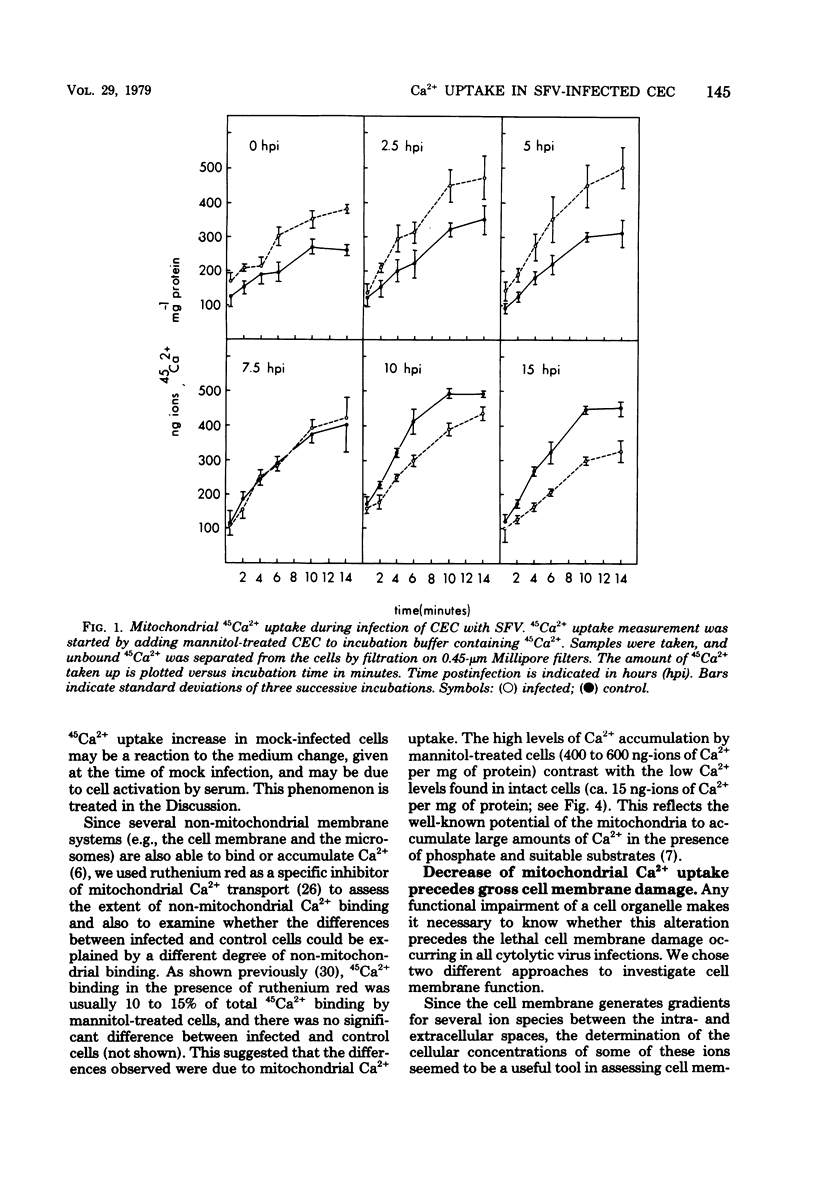
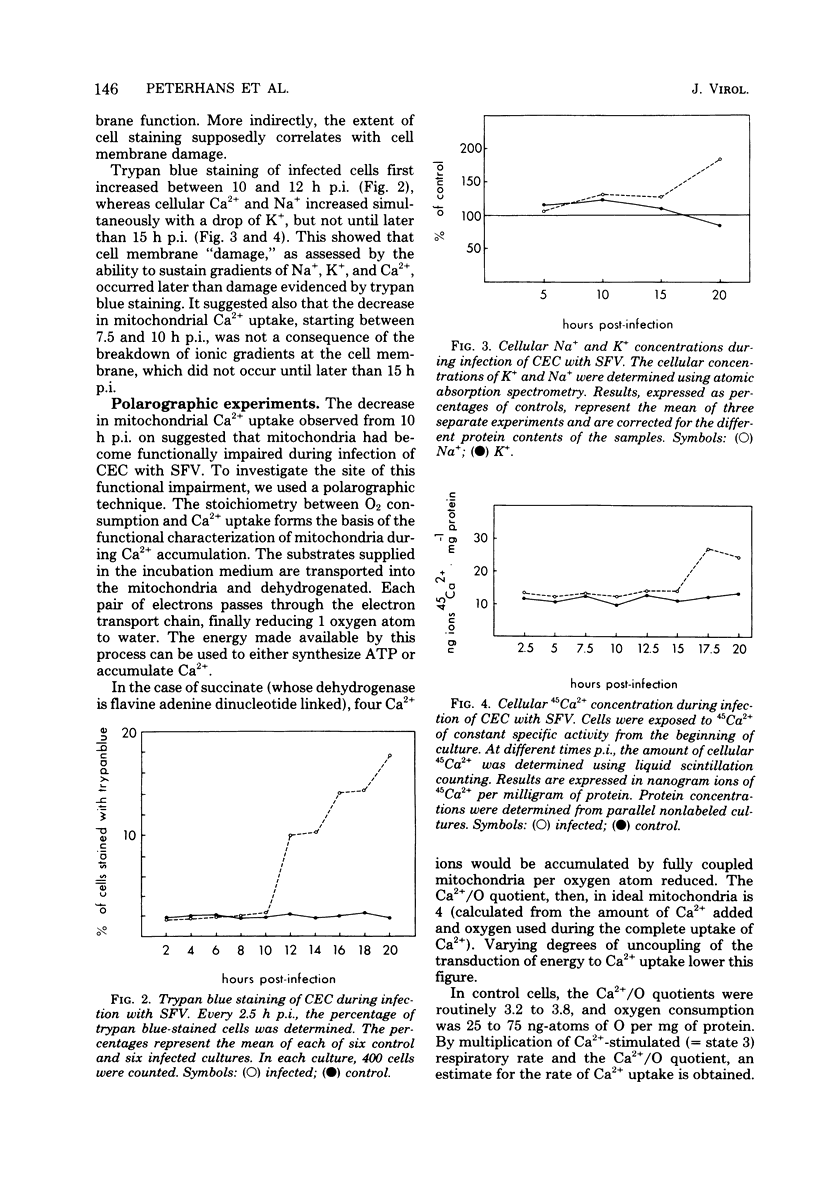
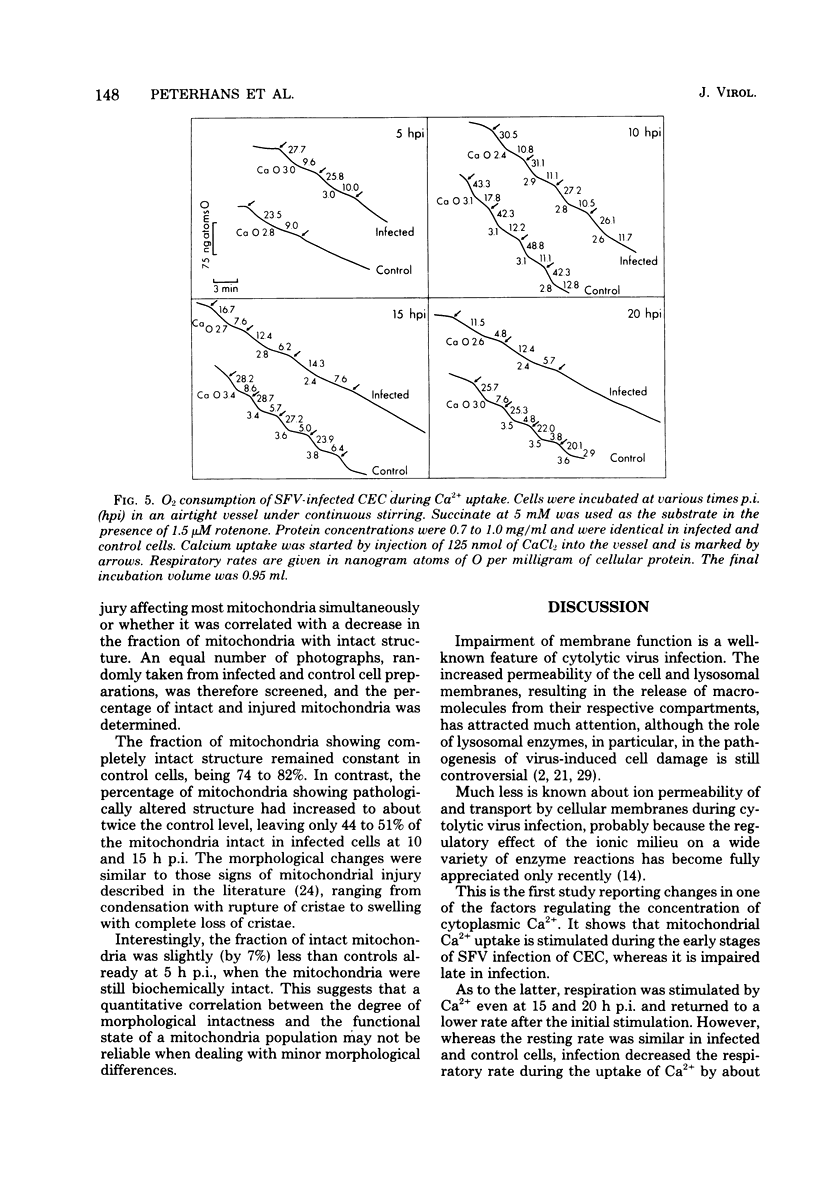
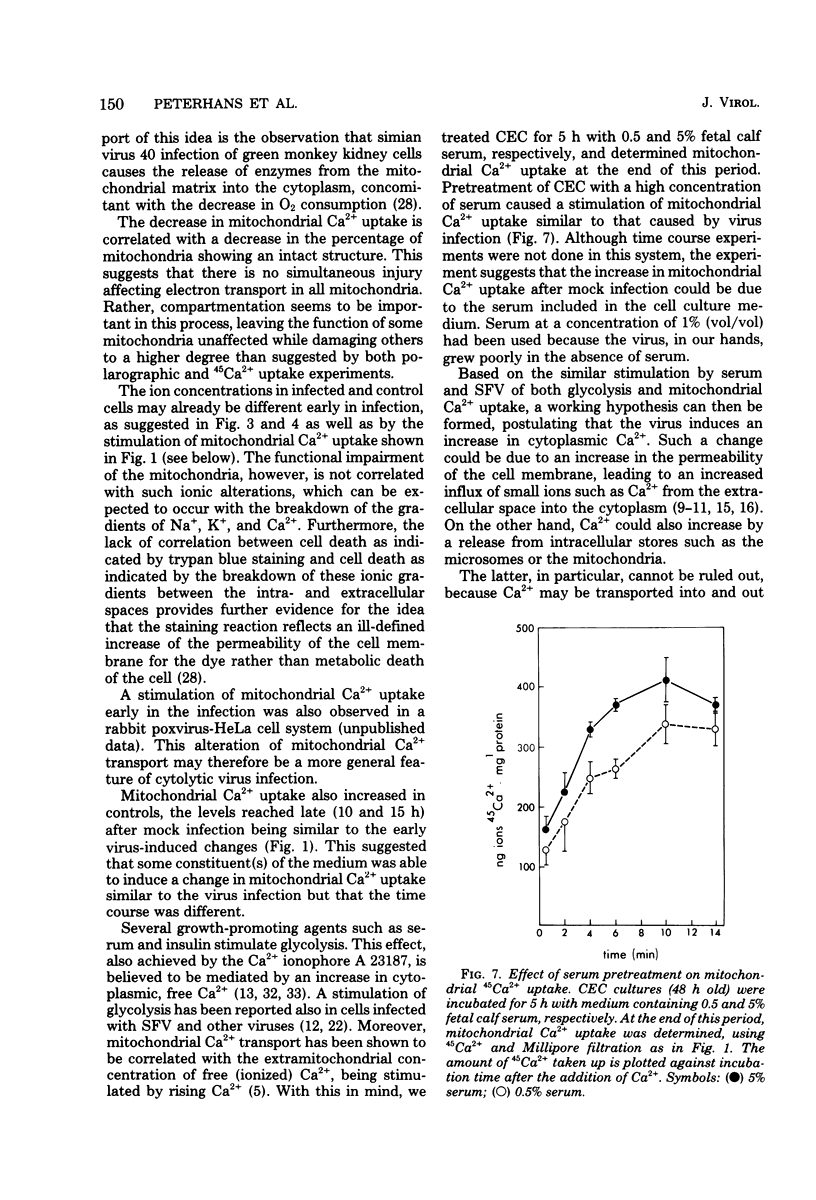
The key role of the mitochondria in the regulation of cellular Ca2+ led to a study of mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake during the infection of chicken embryo cells with Semliki Forest virus. Mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake was stimulated during the first 5 h of infection but declined later in infection. The early stimulation suggests an increase of cytoplasmic ionized Ca2+, whereas the later decrease indicates mitochondrial injury. This functional deterioration was correlated with an increase of the permeability of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Polarographic experiments showed that electron transport is impaired, whereas transduction of energy to Ca2+ uptake is intact.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON A. C., SANDELIN K. Activation of lysosomal enzymes in virus-infected cells and its possible relationship to cytopathic effects. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:879–887. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acosta D., Wenzel D. G. A permeability test for the study of mitochondrial injury in in vitro cultured heart muscle and endothelioid cells. Histochem J. 1975 Jan;7(1):45–56. doi: 10.1007/BF01004831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borle A. B. Calcium metabolism in HeLa cells and the effects of parathyroid hormone. J Cell Biol. 1968 Mar;36(3):567–582. doi: 10.1083/jcb.36.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butchko G. M., Armstrong R. B., Martin W. J., Ennis F. A. Influenza A viruses of the H2N2 subtype are lymphocyte mitogens. Nature. 1978 Jan 5;271(5640):66–67. doi: 10.1038/271066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Rossi C. S., Lehninger A. L. Energy-coupling in mitochondria during resting or state 4 respiration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 18;19(5):609–614. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90383-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L. Membrane leakiness after viral infection and a new approach to the development of antiviral agents. Nature. 1978 Apr 20;272(5655):694–699. doi: 10.1038/272694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Smith A. E. Sodium ions and the shut-off of host cell protein synthesis by picornaviruses. Nature. 1976 Dec 23;264(5588):807–809. doi: 10.1038/264807a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L. The inhibition of cell functions after viral infection. A proposed general mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 1;76(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassells A. C., Burke D. C. Changes in the constitutive enzymes of chick cells following infection with Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1973 Feb;18(2):135–141. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-2-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond I., Legg A., Schneider J. A., Rozengurt E. Glycolysis in quiescent cultures of 3T3 cells. Stimulation by serum, epidermal growth factor, and insulin in intact cells and persistence of the stimulation after cell homogenization. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):866–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham A. C. Do viruses use calcium ions to shut off host cell functions? Nature. 1977 May 26;267(5609):375–376. doi: 10.1038/267375c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egberts E., Hackett P. B., Traub P. Alteration of the intracellular energetic and ionic conditions by mengovirus infection of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells and its influence on protein synthesis in the midphase of infection. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):591–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.591-597.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P., Giberman E. Enhancement of potassium influx, in baby hamster kidney cells and chicken erythrocytes, during adsorption of parainfluenza 1 (Sendai) virus. FEBS Lett. 1973 Apr 1;31(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80089-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberger J. S., Phillips S. M., Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. Induction of mouse type-C RNA virus by lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):317–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman J., Wilson D. E. Newcastle disease virus-induced plasma membrane damage. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):101–113. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDENMANN J., GIFFORD G. E. Studies on vaccinia virus plaque formation and its inhibition by interferon. III. A simplified plaque inhibition assay of interferon. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:302–309. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho K. U., Trump B. F. Studies on the pathogenesis of cell injury: effects of inhibitors of metabolism and membrane function on the mitochondria of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Lab Invest. 1975 Feb;32(2):163–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L. Specific inhibition of mitochondrial Ca++ transport by ruthenium red. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 22;42(2):298–305. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroni C., Schumann G. Mitogen induction of murine C-type viruses. II. Effect of B-lymphocyte mitogens. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norkin L. C. Cell killing by simian virus 40: impairment of membrane formation and function. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):872–879. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.872-879.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterhans E., Browse E., Wyler R. Functional state of cultured chick embryo cell mitochondria investigated in situ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 25;75(4):1078–1085. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91492-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Bygrave F. L. A kinetic study of mitochondrial calcium transport. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 15;55(3):497–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. A., Diamond I., Rozengurt E. Glycolysis of quiescent cultures of 3T3 cells. Addition of serum, epidermal growth factor, and insulin increases the activity of phosphofructokinase in a protein synthesis-independent manner. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):872–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schudt C., Gaertner U., Pette D. Insulin action on glucose transport and calcium fluxes in developing muscle cells in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep;68(1):103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelock E. F., Toy S. T. Participation of lymphocytes in viral infections. Adv Immunol. 1973;16:123–184. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. F., Woodruff J. J. T lymphocyte interaction with viruses and virus-infected tissues. Prog Med Virol. 1975;19:120–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




