Abstract
BACKGROUND
The hemolytic–uremic syndrome consists of the triad of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and renal failure. The common form of the syndrome is triggered by infection with Shiga toxin–producing bacteria and has a favorable outcome. The less common form of the syndrome, called atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome, accounts for about 10% of cases, and patients with this form of the syndrome have a poor prognosis. Approximately half of the patients with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome have mutations in genes that regulate the complement system. Genetic factors in the remaining cases are unknown. We studied the role of thrombomodulin, an endothelial glycoprotein with anticoagulant, antiinflammatory, and cytoprotective properties, in atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome.
METHODS
We sequenced the entire thrombomodulin gene (THBD) in 152 patients with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome and in 380 controls. Using purified proteins and cell-expression systems, we investigated whether thrombomodulin regulates the complement system, and we characterized the mechanisms. We evaluated the effects of thrombomodulin missense mutations associated with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome on complement activation by expressing thrombomodulin variants in cultured cells.
RESULTS
Of 152 patients with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome, 7 unrelated patients had six different heterozygous missense THBD mutations. In vitro, thrombomodulin binds to C3b and factor H (CFH) and negatively regulates complement by accelerating factor I–mediated inactivation of C3b in the presence of cofactors, CFH or C4b binding protein. By promoting activation of the plasma procarboxypeptidase B, thrombomodulin also accelerates the inactivation of anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a. Cultured cells expressing thrombomodulin variants associated with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome had diminished capacity to inactivate C3b and to activate procarboxypeptidase B and were thus less protected from activated complement.
CONCLUSIONS
Mutations that impair the function of thrombomodulin occur in about 5% of patients with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome.
The hemolytic–uremic syndrome consists of the triad of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and acute renal failure. It is one of the thrombotic microangiopathies, along with thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura and preeclampsia.1 The hemolytic–uremic syndrome is the most common cause of acute renal failure among children, a condition for which 50 to 75% of patients require dialysis.2 More than 85% of cases of the hemolytic–uremic syndrome are referred to as “typical”; these are preceded by diarrhea caused by strains of Escherichia coli3–5 that produce Shiga-like toxins, which have proinflammatory and prothrombotic effects on the vascular endothelium.6 Most cases of typical hemolytic–uremic syndrome have a favorable outcome, although in approximately 25% of the patients, there is residual renal dysfunction. In contrast, the less common, “atypical,” form of the hemolytic–uremic syndrome is not linked to Shiga toxin–producing bacteria; it may be familial or sporadic, it often recurs, and it almost always follows an aggressive course. End-stage renal failure develops in 50% of patients with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome, and 25% of patients die as a result of the syndrome.7
An association between atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome and uncontrolled complement activation has been established.8 Approximately 50% of patients have heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in genes encoding inhibitors of the alternative pathway of the complement system: factor H (CFH),9,10 factor I (CFI),11 membrane cofactor protein (MCP),12,13 CFH-related proteins (CFHR),14 and C4b binding protein (C4bBP).15 Gain-of-function mutations in genes encoding factor B (CFB)16 and C3,17 which promote alternative-pathway activation, have been reported in a few cases, and antibodies against CFH have been observed in 2 to 10% of patients14,18 (Fig. 1). The cause of atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome in the remaining 50% of cases is unknown.
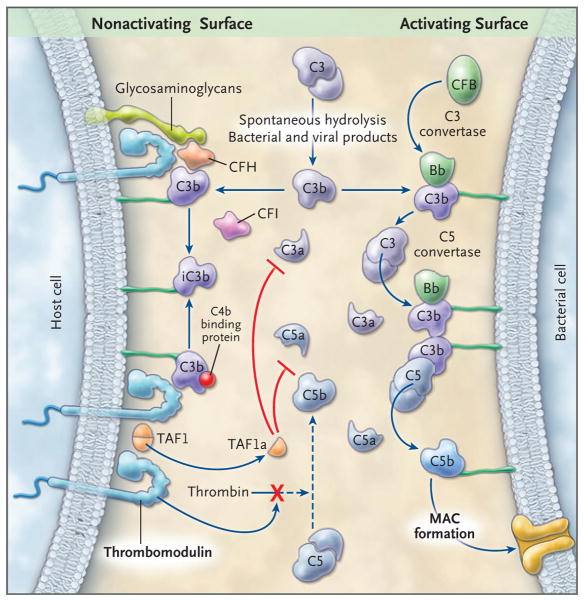
Figure 1. Alternative Pathway of Complement Activation and Regulation.
In this schematic representation, the alternative pathway cascade on a complement-activating surface is shown on the right side, and the proposed mechanisms of complement regulation by thrombomodulin on host cells are shown on the left side. C3 spontaneously undergoes cleavage at a slow rate, amplified by bacterial and viral products. C3 releases the anaphylatoxin C3a and the fragment C3b, which is deposited on almost all cell surfaces that are in contact with plasma. C3b deposited on bacterial surfaces that lack complement regulators binds to CFB to form the C3 convertase of the alternative pathway, an enzyme complex (C3bBb) that cleaves additional C3 molecules. C3b also participates in the formation of the C5 convertase (C3b2Bb), which by cleaving C5, releases C5a, an anaphylatoxin, and C5b, which initiates assembly of the membrane attack complex (MAC), a pore-like structure that inserts into the cell membranes, causing cell activation or lysis. In host cells, several membrane-anchored and fluid-phase regulators control this cascade. CFH and C4bBP in the fluid phase bind to cell-surface glycosaminoglycans and to C3b and act as cofactors for CFI-mediated cleavage of C3b to iC3b. This reduces downstream activation of C3 and C5, thereby protecting the cell membrane. Thrombomodulin, an integral membrane protein on all endothelial cells, provides additional protection of the membrane by enhancing CFI-mediated inactivation of C3b in the presence of either CFH or C4bBP; by binding to thrombin, thereby preventing it from activating C5; and by promoting the generation of carboxypeptidase B (TAFIa), which inactivates C3a and C5a. See Glossary for explanation of complement components.
Several lines of evidence point to a role of thrombomodulin in the pathogenesis of atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome. Thrombomodulin is a ubiquitous transmembrane endothelial-cell glycoprotein. It accelerates thrombin-mediated activation of protein C,19 which down-regulates further thrombin generation, thereby suppressing clot formation. Activated protein C also has antiinflammatory and cytoprotective properties.20 Thrombomodulin enhances thrombin-mediated activation of plasma procarboxypeptidase B (thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor [TAFI]), an inhibitor of fibrinolysis21 that also inactivates complement-derived anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a.22–24 Thrombomodulin, through its lectin-like domain, interferes with inflammation by suppressing leukocyte trafficking and dampening complement activation.25,26
The strategic location of thrombomodulin throughout the vasculature and its role in regulating coagulation, innate immunity, and complement activation led us to hypothesize that variants of the gene encoding thrombomodulin (THBD) confer a predisposition to endothelial injury and microvascular thrombosis, which is manifested clinically as the atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome. We identified six THBD variants in seven patients with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome. We also showed that thrombomodulin is a negative regulator of the complement system and that thrombomodulin mutations associated with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome cause defective complement regulation.
METHODS
PATIENTS
We recruited for this study 152 consecutive patients with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome from the International Registry of Recurrent and Familial HUS/TTP.27 A diagnosis of atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome was made in patients who had one or more episodes of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia associated with acute renal failure.28 Patients in whom the hemolytic–uremic syndrome was associated with Shiga toxin–producing bacteria were excluded. Healthy controls, unrelated to each other or to the patients, were matched according to sex and geographic origin. Details of the diagnostic criteria and participant selection are provided in the Methods section in the Supplementary Appendix, available with the full text of this article at NEJM.org.
We screened these 152 patients for mutations in CFH, MCP, CFI, and THBD. Patients with THBD mutations were also screened for CFB and C3 mutations. Since functional abnormalities in the von Willebrand factor–cleaving metalloproteinase, ADAMTS13, have been associated with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome, we also measured its activity with the use of a collagen-binding assay when possible.29 The study was approved by the bioethics committee of the Province of Bergamo, Italy. Participants or their legal guardians provided written informed consent.
Glossary
| Complement component | Effect on Complement Activation | Major Functions* |
|---|---|---|
| Alternative pathway | Promotes | One of three complement pathways that opsonize and kill pathogens, it is antibody-independent, is activated by spontaneous hydrolysis of C3 in plasma, and is amplified by C3b deposition on the surface of pathogens |
| C3 convertase | Promotes | Enzyme complex (C3bBb) that cleaves C3 to C3a and C3b |
| C4b binding protein (C4bBP) | Suppresses | Circulating cofactor for CFI-mediated inactivation of C3b and C4b |
| C5 convertase | Promotes | Enzyme complex (C3b2Bb) that cleaves C5 to C5a and C5b |
| CFH-related proteins (CFHR) | Suppress | Circulating proteins derived from ancestral duplications of CFH gene; a regulatory function has been suggested by their ability to bind C3b |
| Complement factor B (CFB) | Promotes | A circulating zymogen that, after binding to C3b, is cleaved by CFD, generating an active subunit Bb; it allows formation of the C3 and C5 convertases, thereby promoting complement activation |
| Complement factor C3 (C3) | Promotes | A circulating zymogen and a major component necessary for activation of the complement cascade |
| Complement factor C3a (C3a) | Promotes | A complement activation fragment of C3, that is a potent anaphylatoxin |
| Complement factor C3b (C3b) | Promotes | A key component of complement activation, it is a cleavage product of C3 that binds to the surfaces of cells and pathogens and promotes complement activation and opsonization |
| Complement factor C5 (C5) | Promotes | A circulating zymogen and major component necessary for activation of the complement cascade |
| Complement factor C5a (C5a) | Promotes | A complement activation fragment of C5, that is a potent anaphylatoxin |
| Complement factor D (CFD) | Promotes | A circulating serine protease that activates CFB |
| Complement factor H (CFH) | Suppresses | Circulating cofactor for CFI-mediated inactivation of C3b |
| Complement factor I (CFI) | Suppresses | Circulating serine protease that inactivates C3b and C4b |
| iC3b | Suppresses | CFI-inactivated form of C3b that cannot promote complement activation |
| Membrane attack complex (MAC) | Promotes | Pore-like structures made by one molecule of C5b and one molecule each of C6, C7, C8 and C9 (C5b-9) that insert into the cell membranes, causing lysis |
| Membrane cofactor protein (MCP) | Suppresses | Membrane-bound complement inhibitor with cofactor activity for CFI-mediated inactivation of C3b and C4b |
These functions were selected for relevance to the current report.
STUDY ASSESSMENTS
The sequencing methods and in vitro assays that were used to measure the effects of purified thrombomodulin or cell-surface thrombomodulin on the generation and deposition of C3b proteolytic fragments and on thrombin-mediated activation of TAFI are described in the Methods section in the Supplementary Appendix. A description of the statistical analyses is also included in the Supplementary Appendix.
RESULTS
THBD SINGLE-NUCLEOTIDE POLYMORPHISMS
We sequenced bidirectionally the entire coding region of the THBD gene (which lacks introns) in 380 controls and 152 patients with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome: 31 patients with CFH mutations (20.4%), 1 with anti-CFH antibodies (0.7%), 10 with MCP mutations (6.6%), and 5 with CFI mutations (3.3%). Six amino acid–changing, heterozygous mutations of THBD were identified in seven unrelated patients (4.6%); none of these mutations were found in the controls. None of the 380 controls had any synonymous or nonsynonymous single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the coding region, with the exception of a known common THBD coding SNP (rs1042579), a C→T change at base 1418, leading to replacement of alanine 473 by valine (A473V).30 Genotyping was confirmed with the use of the Sequenom MassARRAY system31; this system was also used to determine the frequency of A473V and the other known THBD variants (including those within the 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions) in 268 additional healthy subjects (see details of genotyping and SNP analyses in the Methods section in the Supplementary Appendix). The allele frequencies of the A473V SNP did not differ significantly between patients with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome and controls (P = 0.93). This was also the case for six common SNPs in the 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions of THBD (rs1040585, rs2424505, rs6076016, rs1042580, rs3176123, and rs1962) (Table 1 in the Supplementary Appendix). Clinical data and pedigrees of mutation carriers are provided in Table 1 and Figure 2 and in the case reports in the Supplementary Appendix.
Table 1.
Characteristics of Patients with Atypical Hemolytic–Uremic Syndrome and Thrombomodulin Gene Mutations.*
| Patient No. | Amino Acid Change in Thrombomodulin Protein | Pedigree No. | Age yr |
Sex | Clinical Findings | Prodrome | Serum Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F635 | A43T | 185 | 24 | Male | Recurrent atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome (first episode at 1 year of age); end-stage renal disease; eight siblings, four with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome (three died) | None | Slight decrease in C3, normal C4 and CFH |
| F163 | D53G | 8 | 8 | Male | Recurrent atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome (first episode at 6 months of age); two siblings, one of whom had atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome and died | Viruslike illness | Transient decrease in C3, normal C4 and CFH, normal ADAMTS13 activity |
| S884 | V81I | 4 | Male | Single episode of atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome, which occurred at 15 months of age | Viruslike illness | Low C3, normal C4 and CFH, normal ADAMTS13 activity | |
| S511 | P495S | 10 | Female | Recurrent atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome (first episode at 3 years of age); residual renal dysfunction | None | Low C3 | |
| S015 | P501L | 15 | Male | Recurrent atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome (first episode at 6 months of age); end-stage renal disease; mother died of pulmonary fibrosis | None | Normal C3, slight increase in C4, normal CFH and ADAMTS13 activity | |
| S665 | D486Y | 23 | Male | Single episode of atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome, which occurred at 6 years of age; residual renal dysfunction | None | Normal C3, C4, and CFH; normal ADAMTS13 activity | |
| S924 | D486Y | 19 | Female | One episode of atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome after renal transplantation, which occurred at 15 years of age; end-stage renal disease | None | Normal C3 and C4, slight increase in CFH |
All patients with thrombomodulin-protein mutations were unrelated. The two patients with the D486 mutation had different geographic origins: Patient S665 was from Italy, and Patient S924 was from the United States and did not have Italian ancestry. Therefore, a common founder origin for the mutation in these two patients is unlikely, although it could not be ruled out.
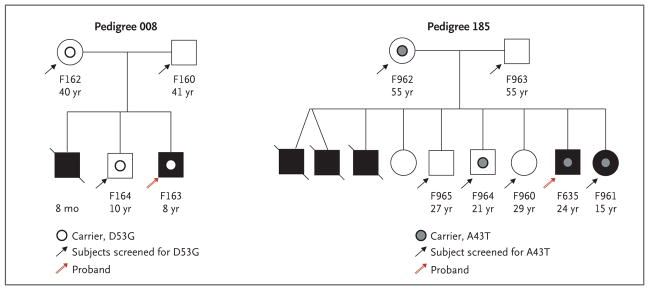
Figure 2. Pedigrees of Patients with Familial Atypical Hemolytic–Uremic Syndrome.
Solid symbols (squares for male family members and circles for female family members) indicate affected persons, and slashes deceased persons. The patient number and age are shown below each symbol.
Three patients (two with a family history of atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome [Patients F635 and F163] and one with sporadic atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome [Patient S884]) were heterozygous for mutations that cause amino acid changes in the lectin-like domain of thrombomodulin (A43T in Patient F635, D53G in Patient F163, and V81L in Patient S884).
Patient F635 had had several episodes of the hemolytic–uremic syndrome in infancy, leading to chronic renal failure. He had eight siblings, three of whom had died during acute episodes of the hemolytic–uremic syndrome. A sister (Patient F961), who also carried the A43T mutation, had had one episode of the hemolytic–uremic syndrome during infancy. The mother (Patient F962) and another sibling (Patient F964) were also heterozygous carriers, but neither they nor the other siblings had symptoms or signs of the hemolytic–uremic syndrome (Pedigree 185 in Fig. 2).
In Pedigree 008 (Fig. 2), the unaffected brother and mother of Patient F163 carried the D53G mutation, whereas the father did not. The deceased sibling was not tested.
Four additional patients with sporadic atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome (Patients S511, S015, S665, and S924) had missense mutations in the serine–threonine-rich region of thrombomodulin (P495S in Patient S511, P501L in Patient S015, and D486Y in Patients S665 and S924, who were not related to each other).
In the case of all carriers of the thrombomodulin mutation, the disease was evident during childhood, and in two patients (F163 and S884), it was preceded by a viruslike illness. No patient carried a concurrent mutation in CFH, MCP, CFI, CFB, or C3, nor did any of them have anti-CFH auto-antibodies. ADAMTS13 activity was normal in Patients S015, S884, F163, and S703. Four of the patients with thrombomodulin mutations (F635, F163, S884, and S511) had low serum C3 levels. C4 levels were normal in all the patients. These findings suggest that thrombomodulin mutations are associated with excess activation of the alternative complement pathway.9
THROMBOMODULIN AND COMPLEMENT ACTIVATION
To test whether genetic variations of THBD contribute to the activation of complement, we examined the ability of wild-type and mutant thrombomodulin to provide protection against complement activation on the cell surface.32–34 CHO-K1 cells were stably transfected with empty vector (control) or with vector expressing thrombomodulin. Complement activation was induced by incubating cells with complement-fixing anti-CHO antibodies, followed by C6-depleted serum. Staining of total C3b plus inactivated C3b (iC3b) (with an anti-C3c antibody that recognizes both C3b and iC3b) and of iC3b alone (with a specific anti-iC3b antibody) was quantified by flow cytometry. The expression of wild-type thrombomodulin, as compared with the control vector, resulted in an increase by a median factor of 2.6 (range 2.4 to 2.7) in the percentage of C3b that was cleaved to iC3b on the cell surface, as calculated by the ratio of iC3b to (C3b+iC3b) on staining (Fig. 3A). This indicates that thrombomodulin provides protection against complement activation.
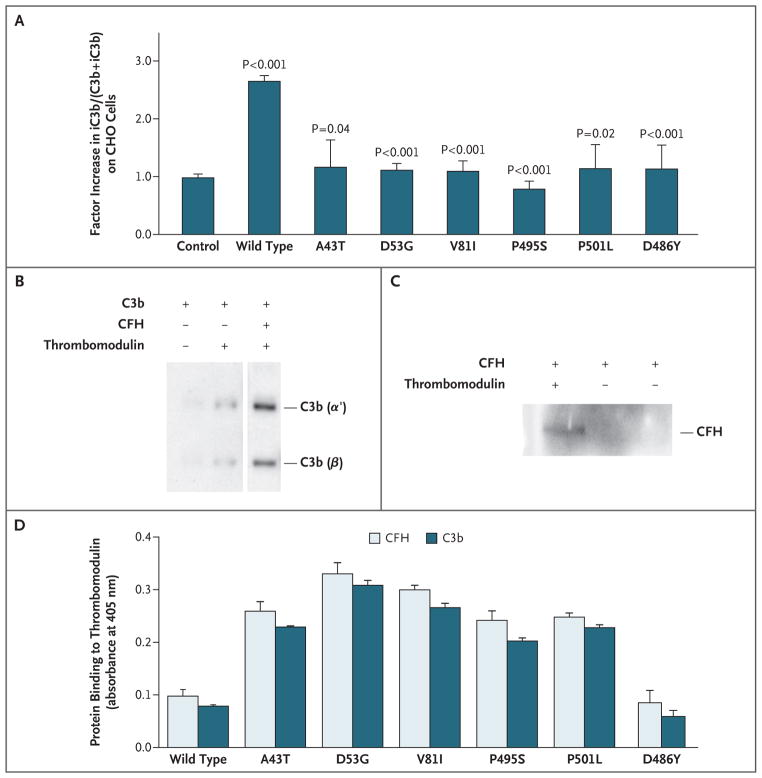
Figure 3. Effect of Mutations Associated with Atypical Hemolytic–Uremic Syndrome on the Ability of Thrombomodulin to Enhance Complement Inactivation.
CHO-K1 cells were stably transfected for equal cell-surface expression of wild-type and mutated forms of thrombomodulin (Panel A). The control column represents cells stably transfected with empty vector. The amount of iC3b relative to (C3b+iC3b) deposited on the CHO cells after complement activation in serum was measured with the use of flow cytometry (see the Methods section of the Supplementary Appendix). Cells expressing wild-type thrombomodulin provided significant protection, as compared with control cells. Variants had a significantly lower percentage of iC3b on the cell surface than wild-type cells. The P value for wild type is for the comparison of wild-type thrombomodulin with control cells. Other P values are for the comparison of variants with wild-type thrombomodulin. The results shown are the mean values from three independent experiments. In Panels B and C, the direct interaction of CFH and C3b with thrombomodulin is shown by coprecipitations followed by immunoblotting, with the use of immobilized thrombin (IIa)–sepharose to pull down thrombomodulin in the presence of purified proteins (1 μg each). C3b interacts with thrombomodulin, and this interaction is increased in the presence of CFH (Panel B). CFH directly interacts with thrombomodulin (Panel C). HEK293 cells were stably transfected for equal expression of wild-type and thrombomodulin variants, and membrane preparations were immobilized in 96-well plates (Panel D). Binding of biotinylated C3b or CFH was quantified with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, as described in the Methods section in the Supplementary Appendix. As compared with binding to wild-type thrombomodulin, there was a significant increase in specific binding of C3b or CFH to all thrombomodulin variants (P<0.001) except for D486Y (P = 0.73 and P = 0.80, for binding of C3b and CFH to D486Y, respectively). Nonspecific signals, determined with non–thrombomodulin-expressing cells, were subtracted from the results. Assays were performed in triplicate. See the Glossary for an explanation of complement components.
As compared with CHO-K1 cells that were transfected with wild-type thrombomodulin, all cells that were transfected with the other thrombomodulin variants were less effective in converting C3b to iC3b on the cell surface after immune-complex–initiated complement activation (Fig. 3A).
THROMBOMODULIN AND C3b AND CFH
Inactivation of surface-bound C3b depends on the binding of CFH to heparan sulfate molecules and C3b. CFH mutations associated with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome disrupt such binding to endothelial cells, diminishing the capacity of CFH to suppress complement activation.35 Since thrombomodulin is present on the surface of all endothelial cells, we tested whether it interacts with CFH and facilitates CFI-mediated C3b cleavage to yield iC3b. Coprecipitation studies showed specific CFH and C3b binding to thrombomodulin (Fig. 3B and 3C).
After immobilizing cell-membrane preparations of HEK293 cells expressing wild-type thrombomodulin or the thrombomodulin variants associated with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome, we measured the binding of biotinylated CFH or C3b with the use of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Surprisingly, the binding of CFH and C3b to all the thrombomodulin variants, except D486Y, was significantly increased, as compared with the binding to wild-type thrombomodulin (Fig. 3D).
THROMBOMODULIN AND C3b INACTIVATION
We next tested whether the enhanced binding to the thrombomodulin variants was associated with alterations in the functional relationship of these proteins. The activity of thrombomodulin in complement regulation in solution was tested by incubating recombinant thrombomodulin with combinations of C3b, CFI, and either CFH or C4bBP (CFI cofactors) (Fig. 4). Thrombomodulin enhanced CFI-mediated inactivation of C3b in a dose-dependent manner in the presence of either CFH or C4bBP (Fig. 4B and 4C). As expected, there was no C3b cleavage by CFI in the absence of a cofactor (data not shown).
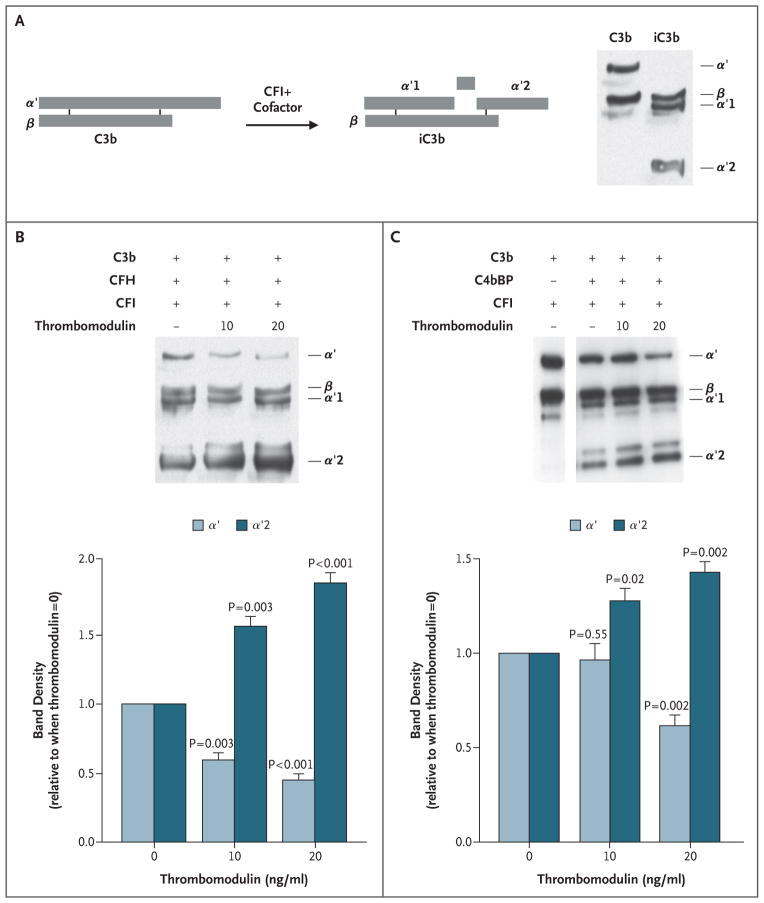
Figure 4. Inactivation of Complement Factor C3b by Complement Factor I, as Facilitated by Thrombomodulin.
Panel A is a diagrammatic representation of cleavage and conversion of C3b to its inactivated form (iC3b) by CFI in the presence of cofactors (CFH, C4bBP). On the right is a Western blot of reduced purified C3b and iC3b, revealing component fragments. Reactions were performed with purified proteins (Panels B and C). After 90 minutes of reaction in solution with the purified proteins, reactions were separated by means of sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacryl-amide-gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) followed by Western blotting with anti-C3 antibodies. Increasing the concentrations of thrombomodulin yielded more inactivation of C3b (less α′ and more α′2), as quantified by densitometry of three blots (Panel B). With the use of the same approach, thrombomodulin also significantly enhanced the cofactor activity of C4bBP in CFI-mediated inactivation of C3b (Panel C). T bars indicate standard errors. See the Glossary for an explanation of complement components.
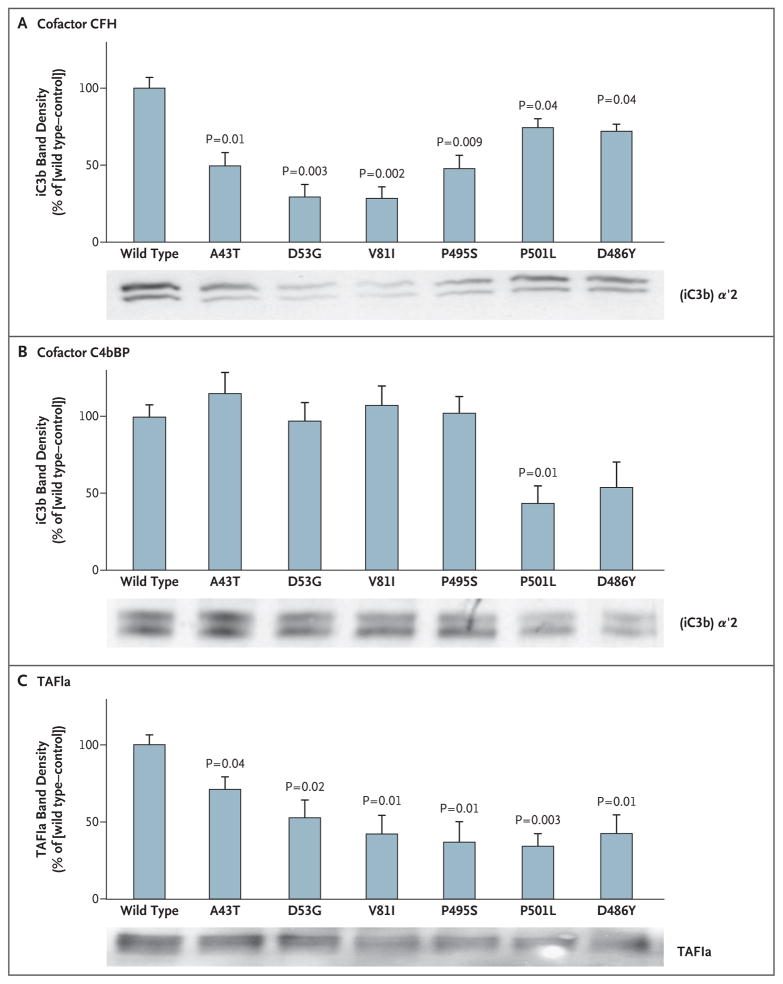
The effect of thrombomodulin mutations associated with the atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome on the capacity of thrombomodulin to enhance CFI-mediated inactivation of C3b was evaluated on the surface of a series of HEK293 cells that expressed each of the variants in equal amounts. In the presence of CFH, thrombomodulin variants were less effective than wild-type thrombomodulin in enhancing CFI-mediated conversion of C3b to iC3b (Fig. 5A). Diminished CFI-mediated inactivation of C3b in the presence of C4bBP was apparent only with the P501L mutation (Fig. 5B), a finding that is consistent with the predominance of CFH as a CFI cofactor.
Figure 5. Effect of Thrombomodulin Mutations Associated with Atypical Hemolytic–Uremic Syndrome on Inactivation of Complement Factor C3b and on Activation of Plasma Procarboxypeptidase B (TAFI).
HEK293 cells were stably transfected for equal expression of wild-type and thrombomodulin variants. CFI-mediated inactivation of C3b in the presence of CFH (Panel A) or C4bBP (Panel B) was assessed by Western blotting, and densitometry was performed to measure the generation of inactive cleavage fragment (iC3b) α′2, relative to control cells transfected with empty vector. Mutant forms of thrombomodulin were significantly less effective than wild-type thrombomodulin in facilitating CFI-mediated inactivation of C3b in the presence of CFH. Only the P501L variant exhibited defects in C4bBP cofactor activity. Thrombin–thrombomodulin–dependent generation of TAFIa was determined by incubating TAFI and thrombin on HEK293 cells expressing thrombomodulin (Panel C). Significantly less TAFIa was generated with thrombomodulin variants. The results shown are the mean values for three independent experiments. T bars indicate standard errors. See the Glossary for an explanation of complement components.
THROMBOMODULIN MUTATIONS AND TAFI
Thrombomodulin also supports thrombin-mediated conversion of TAFI to activated TAFI (TAFIa), low levels of which have been associated with the hemolytic–uremic syndrome.36 We tested the effect of the thrombomodulin variants on thrombin-mediated generation of TAFIa, as assessed by the appearance of a 36-kD fragment37 (Fig. 5C). We found that generation of TAFIa was significantly reduced with all the variants associated with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome, as compared with wild-type thrombomodulin.
DISCUSSION
We identified six missense mutations in the gene encoding thrombomodulin in seven unrelated patients with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome, accounting for 4.6% of the 152 cases. We also found that the resultant thrombomodulin variants did not protect cultured cells against complement activation. SNPs in the coding region of the THBD gene are rare,38–40 and only eight missense changes are reported in the dbSNP database (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/SNP). One insertion frameshift mutation has been described in a kindred with myocardial infarction,41 whereas no homozygous mutations have been reported. All the THBD gene mutations that we identified were heterozygous.
In one carrier of a mutation, the disease was first manifested when the person was 15 years of age, and in four carriers, the hemolytic–uremic syndrome has not developed. These data suggest that mutation of a single THBD allele is not sufficient by itself to cause atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome. Rather, additional factors — environmental, genetic, or epigenetic — are probably required. Indeed, in two patients, episodes of the hemolytic–uremic syndrome were triggered by viruslike illnesses. This finding is relevant to thrombomodulin, since the expression of thrombomodulin is down-regulated during inflammation and infection.42–45 Overall, the findings are similar to those observed with mutations in CFH, CFI, C3, C4bBP, and CFB in the hemolytic–uremic syndrome, which are often missense mutations (in the case of CFH, CFI and C3)17,27 and are usually heterozygous4,9–13,15–17 and associated with disease after an infection.27
Thrombomodulin is a 557-amino-acid endothelial glycoprotein that is anchored to the cell by a short cytoplasmic tail and a single transmembrane domain.46 A series of six epidermal growth-factor–like repeats are required for thrombin-mediated generation of activated protein C, which has anticoagulant and cytoprotective properties, and the generation of activated TAFI, which has C3a-degrading and C5a-degrading properties.23,47,48 Farthest from the transmembrane domain is the lectinlike domain, which confers resistance to proinflammatory stimuli, including endotoxin and ischemia–reperfusion.25,49 It is notable that three of the missense mutations that we found to be associated with atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome are in the lectinlike domain of thrombomodulin.
The A43T mutation is a rare variant that has been associated with venous thrombosis,50 atherosclerosis, and myocardial infarction.51 A computer-generated model of the lectinlike domain of thrombomodulin predicts that A43 is positioned on the surface of the molecule, where it could potentially bind to proteins in the circulation.52 This observation is in line with our findings that thrombomodulin variants associated with the atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome that involve the lectinlike domain alter CFH and C3b binding and, in turn, the regulation of complement activation.
The other three mutations in sporadic cases of atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome — D486Y, P495S, and P501L — reside in the serine–threonine-rich region of thrombomodulin. D486Y and P501L have been reported rarely in patients with venous thrombosis.53 These mutations are near the consensus sequence for attachment of chondroitin sulfate at serine 49254; in vitro, P495S and P501L moderately reduce expression of thrombomodulin on the cell surface, and P495S decreases the affinity of thrombomodulin for thrombin.55 All three of these variants exhibited defects in suppressing activation of the alternative complement pathway through CFI-mediated C3b inactivation in vitro, implicating them in the pathogenesis of atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome. The additional impairment in TAFIa generation probably aggravates the disease.36 Thrombomodulin has a binding site for C3b and CFH, thereby accelerating CFI-mediated inactivation of C3b. Beyond these activities, which negatively regulate the alternative pathway, thrombomodulin plays a wider role in suppressing complement-mediated cell injury. Thrombomodulin interferes with thrombin-mediated activation of C556 and is necessary for thrombin-mediated generation of TAFIa. Thus, in addition to its role in coagulation, thrombomodulin interacts with several complement pathways (Fig. 1).
Despite advances in delineating the pathogenesis of atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome, effective therapies are lacking, and in most patients, end-stage renal failure requiring dialysis develops. Since thrombomodulin simultaneously suppresses the complement and coagulation systems, its administration may have therapeutic value for some patients with the atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome. The efficacy and safety of recombinant thrombomodulin for disseminated intravascular coagulation have been shown in a phase 3 clinical trial.57
In conclusion, we have shown that thrombomodulin is a negative regulator of the complement system and that mutant variants of thrombomodulin may contribute to the development of atypical hemolytic–uremic syndrome.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (DK71221), Istituto Superiore della Sanità (Project no. 526D/9), Fondazione ART Per La Ricerca Sui Trapianti (Milan) (all to Drs. Noris and Remuzzi), Fonds voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (FWO #G.0675.08, to Dr. Conway), and Fondation Leducq in Paris (to Drs. C.T. Esmon and N.L. Esmon).
We thank the clinicians and patients for their membership in and support of the International Registry of Recurrent and Familial HUS/TTP (for a full list of the coordinators and investigators of the registry, see the Supplementary Appendix), with particular thanks to Dr. Kenneth Lieberman, Mrs. Rachel Dominguez, Dr. Avi Katz, Prof. Clifford E. Kashtan, Prof. Francesco Emma, and Dr. Rosa Bellantuono; Drs. Elena Bresin, Chiara Mossali, and Gaia Pianetti (Mario Negri Institute for Pharmacological Research, Clinical Research Center for Rare Diseases, Ranica, Bergamo, Italy) for collecting clinical data and biologic samples for sequencing of complement genes; and the personnel of the VIB Genetic Service Facility for generating THBD sequences.
Footnotes
Drs. C.T. Esmon and N.L. Esmon report holding licenses and patents related to protein C and activated protein C that are unrelated to this article; and Dr. Conway, holding a patent for the use of the lectinlike domain of thrombomodulin as an antiinflammatory agent. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
- 1.Zheng XL, Sadler JE. Pathogenesis of thrombotic microangiopathies. Annu Rev Pathol. 2008;3:249–77. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pathmechdis.3.121806.154311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Constantinescu AR, Bitzan M, Weiss LS, et al. Non-enteropathic hemolytic uremic syndrome: causes and short-term course. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43:976–82. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2004.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Moake JL. Thrombotic microangiopathies. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:589–600. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra020528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Noris M, Remuzzi G. Hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:1035–50. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004100861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Razzaq S. Hemolytic uremic syndrome: an emerging health risk. Am Fam Physician. 2006;74:991–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Morigi M, Galbusera M, Binda E, et al. Verotoxin-1-induced up-regulation of adhesive molecules renders microvascular endothelial cells thrombogenic at high shear stress. Blood. 2001;98:1828–35. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.6.1828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kavanagh D, Goodship TH, Richards A. Atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Br Med Bull. 2006;77–78:5–22. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldl004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jokiranta TS, Zipfel PF, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Taylor CM, Goodship TJ, Noris M. Where next with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome? Mol Immunol. 2007;44:3889–900. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Caprioli J, Bettinaglio P, Zipfel PF, et al. The molecular basis of familial hemolytic uremic syndrome: mutation analysis of factor H gene reveals a hot spot in short consensus repeat 20. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:297–307. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V122297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pérez-Caballero D, González-Rubio C, Gallardo ME, et al. Clustering of missense mutations in the C-terminal region of factor H in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2001;68:478–84. doi: 10.1086/318201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kavanagh D, Richards A, Noris M, et al. Characterization of mutations in complement factor I (CFI) associated with hemolytic uremic syndrome. Mol Immunol. 2008;45:95–105. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Kemp EJ, Good-ship JA, et al. The development of atypical haemolytic-uraemic syndrome is influenced by susceptibility factors in factor H and membrane cofactor protein: evidence from two independent cohorts. J Med Genet. 2005;42:852–6. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2005.030783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Monteferrante G, Brioschi S, Caprioli J, et al. Genetic analysis of the complement factor H related 5 gene in haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Mol Immunol. 2007;44:1704–8. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2006.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zipfel PF, Edey M, Heinen S, et al. Deletion of complement factor H-related genes CFHR1 and CFHR3 is associated with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. PLoS Genet. 2007;3(3):e41. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Blom AM, Bergstrom F, Edey M, et al. A novel non-synonymous polymorphism (p. Arg240His) in C4b-binding protein is associated with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome and leads to impaired alternative pathway cofactor activity. J Immunol. 2008;180:6385–91. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.9.6385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Goicoechea de Jorge E, Harris CL, Esparza-Gordillo J, et al. Gain-of-function mutations in complement factor B are associated with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:240–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603420103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Frémeaux-Bacchi V, Miller E, Liszewski MK, et al. Mutations in complement C3 predispose to development of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood. 2008;112:4948–52. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-01-133702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Józsi M, Licht C, Strobel S, et al. Factor H autoantibodies in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome correlate with CFHR1/CFHR3 deficiency. Blood. 2008;111:1512–4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-109876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Esmon C. Do-all receptor takes on coagulation, inflammation. Nat Med. 2005;11:475–7. doi: 10.1038/nm0505-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bernard GR, Vincent JL, Laterre PF, et al. Efficacy and safety of recombinant human activated protein C for severe sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:699–709. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200103083441001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bajzar L, Manuel R, Nesheim M. Purification and characterization of TAFI, a thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:14477–84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.24.14477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Campbell WD, Lazoura E, Okada N, Okada H. Inactivation of C3a and C5a octapeptides by carboxypeptidase R and carboxypeptidase N. Microbiol Immunol. 2002;46:131–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2002.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Myles T, Nishimura T, Yun TH, et al. Thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor: a potential regulator of vascular inflammation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:51059–67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306977200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nishimura T, Myles T, Piliponsky AM, Kao PN, Berry GJ, Leung LL. Thrombin-activatable procarboxypeptidase B regulates activated complement C5a in vivo. Blood. 2007;109:1992–7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-03-012567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Conway EM, Van de Wouwer M, Pollefeyt S, et al. The lectin-like domain of thrombomodulin confers protection from neutrophil-mediated tissue damage by suppressing adhesion molecule expression via nuclear factor kappaB and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Exp Med. 2002;196:565–77. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Van de Wouwer M, Plaisance S, De Vriese A, et al. The lectin-like domain of thrombomodulin interferes with complement activation and protects against arthritis. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:1813–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.02033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Caprioli J, Noris M, Brioschi S, et al. Genetics of HUS: the impact of MCP, CFH, and IF mutations on clinical presentation, response to treatment, and outcome. Blood. 2006;108:1267–79. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-10-007252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P. Acute renal failure — definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care. 2004;8:R204–R212. doi: 10.1186/cc2872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Remuzzi G, Galbusera M, Noris M, et al. von Willebrand factor cleaving protease (ADAMTS13) is deficient in recurrent and familial thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood. 2002;100:778–85. doi: 10.1182/blood-2001-12-0166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wu KK, Aleksic N, Ahn C, Boerwinkle E, Folsom AR, Juneja H. Thrombomodulin Ala455Val polymorphism and risk of coronary heart disease. Circulation. 2001;103:1386–9. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.103.10.1386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.van den Boom D, Ehrich M. Discovery and identification of sequence polymorphisms and mutations with MALDI-TOF MS. Methods Mol Biol. 2007;366:287–306. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-030-0_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Barilla-LaBarca ML, Liszewski MK, Lambris JD, Hourcade D, Atkinson JP. Role of membrane cofactor protein (CD46) in regulation of C4b and C3b deposited on cells. J Immunol. 2002;168:6298–304. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.12.6298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Liszewski MK, Atkinson JP. Membrane cofactor protein (MCP; CD46): isoforms differ in protection against the classical pathway of complement. J Immunol. 1996;156:4415–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liszewski MK, Leung MK, Schraml B, Goodship TH, Atkinson JP. Modeling how CD46 deficiency predisposes to atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Mol Immunol. 2007;44:1559–68. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2006.08.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Manuelian T, Hellwage J, Meri S, et al. Mutations in factor H reduce binding affinity to C3b and heparin and surface attachment to endothelial cells in hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2003;111:1181–90. doi: 10.1172/JCI16651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sucker C, Hetzel GR, Farokhzad F, et al. Association of genotypes of thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitors with thrombotic microangiopathies — a pilot study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22:1347–50. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfl753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Buelens K, Hillmayer K, Compernolle G, Declerck PJ, Gils A. Biochemical importance of glycosylation in thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. Circ Res. 2008;102:295–301. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.157099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Faioni EM, Franchi F, Castaman G, Biguzzi E, Rodeghiero F. Mutations in the thrombomodulin gene are rare in patients with severe thrombophilia. Br J Haematol. 2002;118:595–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2002.03644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Heit JA, Petterson TM, Owen WG, Burke JP, de Andrade M, Melton LJ., III Thrombomodulin gene polymorphisms or haplotypes as potential risk factors for venous thromboembolism: a population-based case-control study. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3:710–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kaare M, Ulander VM, Painter JN, Ahvenainen T, Kaaja R, Aittomäki K. Variations in the thrombomodulin and endothelial protein C receptor genes in couples with recurrent miscarriage. Hum Reprod. 2007;22:864–8. doi: 10.1093/humrep/del436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kunz G, Ireland HA, Stubbs PJ, Kahan M, Coulton GC, Lane DA. Identification and characterization of a thrombomodulin gene mutation coding for an elongated protein with reduced expression in a kindred with myocardial infarction. Blood. 2000;95:569–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Taylor FB., Jr Studies on the inflammatory-coagulant axis in the baboon response to E. coli: regulatory roles of proteins C, S, C4bBP and of inhibitors of tissue factor. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1994;388:175–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Van de Wouwer M, Collen D, Conway EM. Thrombomodulin-protein C-EPCR system: integrated to regulate coagulation and inf lammation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:1374–83. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000134298.25489.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Faust SN, Levin M, Harrison OB, et al. Dysfunction of endothelial protein C activation in severe meningococcal sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:408–16. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200108093450603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Vercellotti GM. Effects of viral activation of the vessel wall on inflammation and thrombosis. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1998;9(Suppl 2):S3–S6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Weiler H, Isermann BH. Thrombomodulin. J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1:1515–24. doi: 10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Weiler-Guettler H, Christie PD, Beeler DL, et al. A targeted point mutation in thrombomodulin generates viable mice with a prethrombotic state. J Clin Invest. 1998;101:1983–91. doi: 10.1172/JCI2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Weiler H, Lindner V, Kerlin B, et al. Characterization of a mouse model for thrombomodulin deficiency. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001;21:1531–7. doi: 10.1161/hq0901.094496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Geudens N, Van de Wouwer M, Vanaudenaerde B, et al. The lectin-like domain of thrombomodulin protects against ischemia-reperfusion lung injury. Eur Respir J. 2008;32:862–70. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00157107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Norlund L, Zöller B, Ohlin A-K. A novel thrombomodulin gene mutation in a patient suffering from sagittal sinus thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1997;78:1164–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Doggen CJ, Kunz G, Rosendaal FR, et al. A mutation in the thrombomodulin gene, 127G to A coding for Ala25Thr, and the risk of myocardial infarction in men. Thromb Haemost. 1998;80:743–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Villoutreix B, Dahlback B. Molecular model for the C-type lectin domain of human thrombomodulin. J Mol Model. 1998;4:310–22. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ohlin AK, Marlar RA. Thrombomodulin gene defects in families with thromboembolic disease — a report on four families. Thromb Haemost. 1999;81:338–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Gerlitz B, Hassell T, Vlahos CJ, Parkinson JF, Bang NU, Grinnell BW. Identification of the predominant glycosaminoglycan-attachment site in soluble recombinant human thrombomodulin: potential regulation of functionality by glycosyltransferase competition for serine474. Biochem J. 1993;295:131–40. doi: 10.1042/bj2950131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kunz G, Ohlin AK, Adami A, Zöller B, Svensson P, Lane DA. Naturally occurring mutations in the thrombomodulin gene leading to impaired expression and function. Blood. 2002;99:3646–53. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.10.3646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Huber-Lang M, Sarma JV, Zetoune FS, et al. Generation of C5a in the absence of C3: a new complement activation pathway. Nat Med. 2006;12:682–7. doi: 10.1038/nm1419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Saito H, Maruyama I, Shimazaki S, et al. Efficacy and safety of recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin (ART-123) in disseminated intravascular coagulation: results of a phase III, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:31–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.02267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.